Abstract
Panel count data are frequently encountered in follow-up studies such as clinical trials, reliability researches, and insurance studies. Models about this type data usually assume the linearity form of the covariate variables on the log conditional mean function. However, the linearity assumption cannot be always guaranteed in practical applications, especially when high-dimensional covariates exist under investigation. In this paper, we propose a more flexible conditional mean regression model of panel count data with an unknown link function to describe the possible nonlinearity of the covariate effects. The partial likelihood procedure is developed to estimate the unknown link function and the regression parameters simultaneously by first approximating the unknown link function by polynomial splines, and then a two-step iterative algorithm is developed for computing implementation. Finally, the Breslow-type estimator is constructed for the baseline mean function. Asymptotic results of the proposed estimators are discussed under some regularity conditions. In addition, penalized spline estimation procedure is also introduced as an extension. Extensive numerical studies are carried out and indicate that the proposed procedure works well. Finally, two applications of bladder cancer study and skin cancer study are also presented for illustration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dong C, Gao J, Tjstheim D (2015) Estimation for single-index and partially linear single-index integrated models. Ann Stat 44(1):425–453
Feng Y, Wang Y, Wang W, Chen Z (2021) Robust estimation of semiparametric transformation model for panel count data. J Syst Sci Complexity 34(6):2334–2356
Härdle W, Stoker TM (1989) Investigating smooth multiple regression by the method of average derivatives. J Am Stat Assoc 84(408):157–178
Härdle W, Hall P, Ichimura H (1993) Optimal smoothing in single-index models. Ann Stat 21(1):157–178
He X, Tong X, Sun J (2009) Semiparametric analysis of panel count data with correlated observation and follow-up times. Lifetime Data Anal 15(2):177–196
Hu X, Sun J, Wei LJ (2003) Regression parameter estimation from panel counts. Scand J Stat 30(1):25–43
Huang J, Liu L (2006) Polynomial spline estimation and inference of proportional hazards regression models with flexible relative risk form. Biometrics 62(3):793–802
Ichimura H (1993) Semiparametric least squares (SLS) and weighted SLS estimation of single-index models. J Econ 58(1):71–120
Kong E, Xia Y (2007) Variable selection for the single-index model. Biometrika 94(1):217–229
Li J, Zhang R (2011) Partially varying coefficient single-index proportional hazards regression models. Comput Stat Data Anal 55(1):389–400
Li N, Zhao H, Sun J (2013) Semiparametric transformation models for panel count data with correlated observation and follow-up times. Stat Med 32(17):3039–3054
Li J, Li Y, Zhang R (2017) B-spline variable selection for the single-index models. Stat Pap 58:691–706
Ling N, Cheng L, Vieu P, Ding H (2022) Missing responses at random in functional single index model for time series data. Stat Pap 63(2):665–692
Liu L (2004) Semiparametric and nonparametric models for survival data. Ph. D. thesis, University of Pennsylvania
Lu M, Li C (2017) Penalized estimation for proportional hazards models with current status data. Stat Med 36(30):4893–4907
Lu M, Zhang Y (2007) Estimation of the mean function with panel count data using monotone polynomial splines. Biometrika 94(3):705–718
Lu M, Zhang Y, Huang J (2009) Semiparametric estimation methods for panel count data using monotone B-splines. J Am Stat Assoc 104(487):1060–1070
Nielsen JD, Dean CB (2008) Clustered mixed nonhomogeneous Poisson process spline models for the analysis of recurrent event panel data. Biometrics 64(3):751–761
Qin F, Yu Z (2021) Penalized spline estimation for panel count data model with time-varying coefficients. Comput Stat 36(2):2413–2434
Sun Y (2010) Estimation of semiparametric regression model with longitudinal data. Lifetime Data Anal 16(2):271–298
Sun J, Kalbfleisch JD (1995) Estimation of the mean function of point processes based on panel data. Stat Sin 5(1):279–289
Sun J, Zhao X (2013) Statistical analysis of panel count data. Springer, New York
Sun J, Kopciuk KA, Lu X (2008) Polynomial spline estimation of partially linear single-index proportional hazards regression models. Comput Stat Data Anal 53(1):176–188
Wang W (2004) Proportional hazards regression models with unknown link function and time-dependent covariates. Stat Sin 14(3):885–905
Wang Y, Wang W, Zhao X (2022) Local logarithm partial likelihood estimation of panel count data model with an unknown link function. Comput Stat Data Anal 166(4):107346
Wellner J, Zhang Y (2000) Two estimators of the mean of a counting process with panel count data. Ann Stat 28(3):779–814
Wu T, Yu K, Yan Y (2010) Single-index quantile regression. J Multivar Anal 101(7):1607–1621
Xue L, Liang H (2010) Polynomial spline estimation for a generalized additive coefficient model. Scand J Stat 37(1):26–46
Xue L, Zhu L (2006) Empirical likelihood for single-index models. J Multivar Anal 97(6):1295–1312
Yu P, Du J, Zhang Z (2020) Single-index partially functional linear regression model. Stat Pap 61(3):1107–1123
Zhang H, Sun J, Wang D (2013) Variable selection and estimation for multivariate panel count data via the seamless-\({L}_{{m_0}}\) penalty. Can J Stat 41(2):368–385
Zhao X, Tong X, Sun J (2013) Robust estimation for panel count data with informative observation times. Comput Stat Data Anal 57(1):33–40
Acknowledgements
This paper was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grand No. 12101549 and 12001485, the Ministry of Education Humanities and Social Sciences Research Youth Project of China under Grand No. 21YJCZH153, the Characteristic & Preponderant Discipline of Key Construction Universities in Zhejiang Province (Zhejiang Gongshang University-Statistics) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Provincial Universities of Zhejiang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendices
Appendix I: Tables and figures
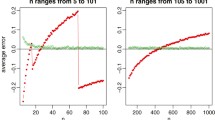
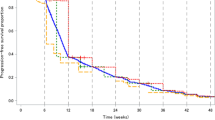
See Tables 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and Figs. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6.
Appendix II: Formulas for \(H(\alpha ,\gamma )\) and \(\mathrm{var}({\hat{\beta }},{\hat{\gamma }})\)
The Hessian matrix of \(\alpha \) and \(\gamma \) is defined as
Let \({\tilde{Z}}_i=(Z_{i2},\ldots ,Z_{ip})^\top \) and \(\xi _i=-Z_{i1}\alpha /(1-\Vert \alpha \Vert _2^2)^{1/2}+{\tilde{Z}}_i\), \(i=1,\ldots ,n\). Denote \(A=(a_{ij})\) as a \((p-1)\times (p-1)\) matrix with entries \(a_{ii}=1+\alpha _i^2/(1-\Vert \alpha \Vert _2^2)\) and \(a_{ij}=\alpha _i\alpha _j/(1-\Vert \alpha \Vert _2^2)\) if \(i\ne j\). Then we can have
where
and
The matrix \(H_{\alpha ,\gamma }\) is given as \(H_{\alpha ,\gamma }=H_{14}+H_{15}+H_{16}\), where
and
The matrix \(H_{\gamma ,\gamma }\) is the same as the one given in Subsection (3.1). From the transformation, \(\beta =((1-\Vert \alpha \Vert _2^2)^{1/2}, \alpha _1,\ldots ,\alpha _{p-1})^\top \), we can easily get
Therefore, by the delta method, we can get
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Wang, W. & Zhao, X. Polynomial spline estimation of panel count data model with an unknown link function. Stat Papers 64, 1805–1832 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00362-022-01364-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00362-022-01364-2