Abstract
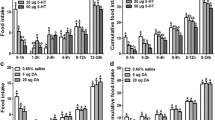
In rainbow trout, the food intake inhibition induced by serotonin occurs through 5-HT2C and 5-HT1A receptors, though the mechanisms involved are still unknown. Therefore, we assessed if a direct stimulation of 5-HT2C and 5-HT1A serotonin receptors (resulting in decreased food intake in rainbow trout), affects gene expression of neuropeptides involved in the control of food intake, such as pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC), cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART), corticotrophin releasing factor (CRF), and agouti-related peptide (AgRP). In a first set of experiments, the injection of the 5-HT2C receptor agonists MK212 (60 μg kg−1 icv) and WAY 161503 (1 mg kg−1 ip), and of the 5-HT1A receptor agonist 8-OH-DPAT (1 mg kg−1 ip and 30 μg kg−1 icv) induced food intake inhibition. In a second set of experiments, we observed that the injection of MK212 or WAY 161503 (1 and 3 mg kg−1) significantly increased hypothalamic POMC mRNA abundance. CART mRNA abundance in hypothalamus was enhanced by treatment with MK212 and unaffected by WAY 161503. The administration of the 5-HT1A receptor agonist 8-OH-DPAT did not induce any significant variation in the hypothalamic POMC or CART mRNA levels. CRF mRNA abundance was only affected by MK212 that increased hypothalamic values. Finally, hypothalamic AgRP mRNA abundance was only evaluated with the agonist 5-HT2C MK212 resulting in no significant effects. The results show that the reduction in food intake mediated by 5-HT2C receptors is associated with increases in hypothalamic POMC, CART and CRF mRNA abundance.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldegunde M, Mancebo M (2006) Effects of neuropeptide Y on food intake and brain biogenic amines in the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Peptides 27:719–727
Anelli M, Bizzi A, Caccia S, Codegoni AM, Fracasso C, Garattini S (1992) Anorexigenic activity of fluoxetine and norfluoxetine in mice, rats and guinea-pigs. J Pharm Pharmacol 44:696–698
Arkle M, Ebenezer IS (2000) Ipsapirone suppresses food intake in food-deprived rats by an action at 5-HT receptors 1A. Eur J Pharmacol 408:273–276
Bernier NJ (2010) Food intake regulation and disorders. In: Leatherhead J, Woo PTK (eds) Fish diseases and disorders, Vol. 2, non-infectious disorders, 2nd edn. CABI, Wallingford, pp 238–266
Bernier NJ, Peter RE (2001) Appetite-suppressing effects of urotensin I and corticotropin-releasing hormone in goldfish (Carassius auratus). Neuroendocrinology 73:248–260
Bernier NJ, Alderman SL, Bristow EN (2008) Heads or tails? Stressor-specific expression of corticotropin-releasing factor and urotensin I in the preoptic area and caudal neurosecretory system of rainbow trout. J Endocrinol 196:637–648
Butt I, Hong A, Di J, Aracena S, Banerjee P, Shen Ch (2014) The effects of serotonin1A receptor on female mice body weight and food intake are associated with the differential expression of hypothalamic neuropeptides and the GABAA receptor. Neuropeptides 48:313–318
Cansell C, Denis RG, Joly-Amado A, Castel J, Luquet S (2012) Arcuate AgRP neurons and the regulation of energy balance. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 3:1–7
Cerdá-Reverter JM, Schiöth HB, Peter RE (2003) The central melanocortin system regulates food intake in goldfish. Regul Pept 115:101–113
Cerdá-Reverter JM, Agulleiro MJ, Guillot R, Sánchez E, Ceinos R, Rotllant J (2011) Fish melanocortin system. Eur J Pharmacol 660:53–60
Choi SH, Kwon BS, Lee S, Houpt TA, Lee HT, Kim DG, Jahng JW (2003) Systemic 5-hydroxy-l-tryptophan down-regulates the arcuate CART mRNA level in rats. Regul Pept 115:73–80
Choi S, Blake V, Cole S, Fernstrom JD (2006) Effects of chronic fenfluramine administration on hypothalamic neuropeptide mRNA expression. Brain Res 1087:83–86
Collin M, Bäckberg M, Onnestam K, Meister B (2002) 5-HT1A receptor immunoreactivity in hypothalamic neurons involved in body weight control. NeuroReport 13:945–951
Conde-Sieira M, Agulleiro MJ, Aguilar AJ, Míguez JM, Cerdá-Reverter JM, Soengas JL (2010) Effect of different glycaemic conditions on gene expression of neuropeptides involved in control of food intake in rainbow trout; interaction with stress. J Exp Biol 213:3858–3865
Cone RD, Lu D, Koppula S, Vage DI, Klungland H, Boston B, Chen W, Orth DN, Pouton C, Kesterson RA (1996) The melanocortin receptors: agonists, antagonists, and the hormonal control of pigmentation. Recent Prog Horm Res 51:287–317
Currie PJ (2003) Integration of hypothalamic feeding and metabolic signals: focus on neuropeptide Y. Appetite 41:335–337
Currie PJ, Coiro CD, Niyomchai T, Lira A, Farahmand F (2002) Hypothalamic paraventricular 5-hydroxytryptamine: receptor-specific inhibition of NPY-stimulated eating and energy metabolism. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 71:709–716
De Pedro N, Alonso-Gomez AL, Gancedo B, Delgado MJ, Alonso-Bedate M (1993) Role of corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) as a food intake regulator in goldfish. Physiol Behav 53:517–520
De Pedro N, Gancedo B, Alonso-Gómez AL, Delgado MJ, Alonso-Bedate M (1995) Alterations in food intake and thyroid tissue content by corticotropin-releasing factor in Tinca tinca. Rev Esp Fisiol 51:71–76
De Pedro N, Pinillos ML, Valenciano AI, Alonso-Bedate M, Delgado MJ (1998) Inhibitory effect of serotonin on feeding behavior in goldfish: involvement of CRF. Peptides 19:505–511
Donovan MH, Tecott LH (2013) Serotonin and the regulation of mammalian energy balance. Front Neurosci 7:1–15
Dryden S, Frankish HM, Wang Q, Pickavance L, Williams G (1996) The serotonergic agent fluoxetine reduces neuropeptide Y levels and neuropeptide Y secretion in the hypothalamus of lean and obese rats. Neuroscience 72:557–566
Dutia R, Kim AJ, Modes M, Rothlein R, Shen JM, Tian YE, Ihbais J, Victory SF, Valcarce C, Wardlaw SL (2013) Effects of AgRP inhibition on energy balance and metabolism in rodent models. PLoS One 8(6):e65317
Ebenezer IS, Arkle MJ, Tite RM (2007) 8-Hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)-tetralin inhibits food intake in fasted rats by (200an action at 5-HT1A receptors. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 29:269–272
Feijó FM, Bertoluci MC, Reis C (2011) Serotonin and hypothalamic control of hunger: a review. Rev Assoc Med Bras 57:74–77
Garfield AS, Heisler LK (2009) Pharmacological targeting of the serotonergic system for the treatment of obesity. J Physiol Lond 587:49–60
Geerling JJ, Wang Y, Havekes LM, Romijn JA, Rensen PCN (2013) Acute central neuropeptide Y administration increases food intake but does not affect hepatic very low-density lipoprotein (Vldl) production in mice. PLoS One 8(2):e55217
Gorissen MHAG, Flik G, Huising MO (2006) Peptides and proteins regulating food intake: a comparative view. Anim Biol 56:447–473
Hagan MM, Rushing PA, Pritchard LM, Schwartz MW, Strack AM, Van Der Ploeg LH, Woods SC, Seeley RJ (2000) Long-term orexigenic effects of AgRP-(83-132) involve mechanisms other than melanocortin receptor blockade. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 279:R47–R52
Heisler LK, Cowley MA, Tecott LH, Fan W, Low MJ, Smart JL, Rubinstein M, Tatro JB, Marcus JN, Holstege H et al (2002) Activation of central melanocortin pathways by fenfluramine. Science 297:609–611
Heisler LK, Jobst EE, Sutton GM, Zhou L, Borok E, Thornton-Jones Z, Liu HY, Zigman JM, Balthasar N, Kishi T et al (2006) Serotonin reciprocally regulates melanocortin neurons to modulate food intake. Neuron 51:239–249
Kask A, Rägo L, Harro J (1998) Evidence for involvement of neuropeptide Y receptors in the regulation of food intake: studies with Y1-selective antagonist BIBP3226. Br J Pharmacol 124:1507–1515
Lam DD, Przydzial MJ, Ridley SH, Yeo GSH, Rochford JJ, O’Rahilly S, Heisler LK (2008) Serotonin 5-HT2C receptor agonist promotes hypophagia via downstream activation of melanocortin 4 receptors. Endocrinology 149:1323–1328
Le Feuvre RA, Aisenthal L, Rothwell NJ (1991) Involvement of corticotrophin releasing factor (CRF) in the thermogenic and anorexic actions of serotonin (5-HT) and related compounds. Brain Res 555:245–250
Leder EH, Silverstein JT (2006) The pro-opiomelanocortin genes in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): duplications, splice variants, and differential expression. J Endocrinol 188:355–363
Librán-Pérez M, Polakof S, López-Patiño MA, Míguez JM, Soengas JL (2012) Evidence of a metabolic fatty acid-sensing system in the hypothalamus and Brockmann bodies of rainbow trout: implications in food intake regulation. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 302:R1340–R1350
Lim JE, Porteus CS, Bernier NJ (2013) Serotonin directly stimulates cortisol secretion from the interrenals in goldfish. Gen Comp Endocrinol 192:246–255
Lin X, Volkoff H, Narnaware Y, Bernier NJ, Peyon P, Peter RE (2000) Brain regulation of feeding behavior and food intake in fish. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 126:415–434
Lu X-Y, Barsh GS, Akil H, Watson SJ (2003) Interaction between α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone and corticotropin-releasing hormone in the regulation of feeding and hypothalamo pituitary-adrenal responses. J Neurosci 23:7863–7872
MacDonald LE, Alderman SL, Kramer S, Woo PTK, Bernier NJ (2014) Hypoxemia-induced leptin secretion: a mechanism for the control of food intake in diseased fish. J Endocrinol 221:441–445
Mancebo MJ, Ceballos FC, Pérez-Maceira J, Aldegunde M (2013) Hypothalamic neuropeptide Y (NPY) gene expression is not affected by central serotonin in the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 166:186–190
Marvin E, Scrogin K, Dudás B (2010) Morphology and distribution of neurons expressing serotonin 5-HT1A receptors in the rat hypothalamus and the surrounding diencephalic and telencephalic areas. J Chem Neuroanat 39:235–241
Matsuda K (2009) Recent advances in the regulation of feeding behavior by neuropeptides in fish. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1163:241–250
Matsuda K (2013) Regulation of feeding behavior and psychomotor activity by corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) in fish. Front Neurosci 7(91):1–5
Matsuda K, Kojima K, Shimakura S, Wada K, Maruyama K, Uchiyama M, Sakae Kikuyama S, Shioda S (2008) Corticotropin-releasing hormone mediates α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone-induced anorexigenic action in goldfish. Peptides 29:1930–1936
Mennigen JA, Harris EA, Chang JP, Moon TW, Trudeau VL (2009) Fluoxetine affects weight gain and expression of feeding peptides in the female goldfish brain. Regul Pept 155:99–104
Miryala CSJ, Maswood N, Uphouse L (2011) Fluoxetine prevents 8-OH-DPAT-induced hyperphagia in Fischer inbred rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 98:311–315
Murashita K, Jordal AE, Nilsen TO, Stefansson SO, Kurokawa T, Björnsson BT, Moen AG, Rønnestad I (2011) Leptin reduces Atlantic salmon growth through the central pro-opiomelanocortin pathway. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 158:79–86
Ni YG, Miledi R (1997) Blockage of 5HT2C serotonin receptors by fluoxetine (Prozac). Proc Natl Acad Sci 94:2036–2040
Ortega VA, Lovejoy DA, Bernier NJ (2013) Appetite-suppressing effects and interactions of centrally administered corticotropin-releasing factor, urotensin I and serotonin in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Front Neurosci 196:1–10
Pérez-Maceira JJ, Mancebo MJ, Aldegunde M (2012) Serotonin-induced brain glycogenolysis in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J Exp Biol 215:2969–2979
Pérez-Maceira JJ, Mancebo MJ, Aldegunde M (2014) The involvement of 5-HT-like receptors in the regulation of food intake in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 161:1–6
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:e45
Qiu J, Xue C, Bosch MA, Murphy JG, Fan W, Rønnekleiv OK, Kelly MJ (2007) Serotonin 5-hydroxytryptamine2C receptor signaling in hypothalamic proopiomelanocortin neurons: role in energy homeostasis in females. Mol Pharmacol 72:885–896
Rochester JA, Kirchner JT (1999) Ecstasy (3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine): history, neurochemistry, and toxicology. J Am Board Fam Pract 12:137–142
Ronnan PJ, Summers CH (2011) Molecular signalling and translational significance of the corticotrophin releasing factor system (2011). Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 98:235–292
Rossi M, Kim MS, Morgan DG, Small CJ, Edwards CM, Sunter D, Abusnana S, Goldstone AP, Russell SH, Stanley SA et al (1998) A C-terminal fragment of agouti-related protein increases feeding and antagonizes the effect of alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone in vivo. Endocrinology 139:4428–4431
Ruibal C, Soengas JL, Aldegunde M (2002) Brain serotonin and the control of food intake in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): effects of changes in plasma glucose levels. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol 188:479–484
Schjolden J, Schiöth HB, Larhammar D, Winberg S, Larson ET (2009) Melanocortin peptides affect the motivation to feed in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Gen Comp Endocrinol 160:134–138
Simansky KJ (1996) Serotonergic control of the organization of feeding and satiety. Behav Brain Res 73:37–42
Small CJ, Kim MS, Stanley SA, Mitchell JR, Murphy K, Morgan DG, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR (2001) Effects of chronic central nervous system administration of agouti-related protein in pairfed animals. Diabetes 50:248–254
Smith BK, York DA, Bray GA (1999) Activation of hypothalamic serotonin receptors reduced intake of dietary fat and protein but not carbohydrate. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 277:R802–R811
Soengas JL (2014) Contribution of glucose- and fatty acid sensing systems to the regulation of food intake in fish. A review. Gen Comp Endocrinol 205:36–48
Steffens SM, da Cunha IC, Beckman D, Lopes APF, Faria MS, Marino-Neto J, Paschoalini MA (2008) The effects of metergoline and 8-OH-DPAT injections into arcuate nucleus and lateral hypothalamic area on feeding in female rats during the estrous cycle. Physiol Behav 95:484–491
Steffens SM, Beckman D, Faria MS, Marino-Neto J, Paschoalini MA (2010) WAY100635 blocks the hypophagia induced by 8-OH-DPAT in the hypothalamic nuclei. Physiol Behav 99:632–637
Tecott LH (2007) Serotonin and the orchestration of energy balance. Cell Metab 6:352–361
Tubío RI, Pérez-Maceira J, Aldegunde M (2010) Homeostasis of glucose in the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum): the role of serotonin. J Exp Biol 213:1813–1821
Valassi E, Scacchi M, Cavagnini F (2008) Neuroendocrine control of food intake. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 18:158–168
Volkoff H, Canosa LF, Unniappan S, Cerdá-Reverter JM, Bernier NJ, Kelly SP, Peter RE (2005) Neuropeptides and the control of food intake in fish. Gen Comp Endocrinol 142:3–19
Volkoff H, Xu M, MacDonald E, Hoskins L (2009) Aspects of the hormonal regulation of appetite in fish with emphasis on goldfish, Atlantic cod and winter flounder: notes on actions and responses to nutritional, environmental and reproductive changes. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 153:8–12
Wurtman RJ, Wurtman JJ (1998) Serotonergic mechanisms and obesity. J Nutr Biochem 9:511–515
Xu Y, Jones JE, Kohno D, Williams KW, Lee CE, Choi MJ, Anderson JG, Heisler LK, Zigman JM, Lowell BB et al (2008) 5-HT2CRs expressed by pro-opiomelanocortin neurons regulate energy homeostasis. Neuron 60:582–589
Yeo G, Heisler L (2012) Unraveling the brain regulation of appetite: lessons from genetics. Nat Neurosci 15:1343–1349
Zhou L, Sutton GM, Rochford JJ, Semple RK, Lam DD, Oksanen LJ, Thornton-Jones ZD, Clifton PG, Yueh C-Y, Evans ML et al (2007) Serotonin 2C receptor agonists improve type 2 diabetes via melanocortin-4 receptor signaling pathways. Cell Metab 6:398–405
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a research grant from Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad and European Fund for Regional Development (AGL2013-46448-3-1-R and FEDER) to J.L.S. C.O.-R. was recipient of a predoctoral fellowship from Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad (BES‐2014‐068040).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by I. D. Hume.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pérez-Maceira, J.J., Otero-Rodiño, C., Mancebo, M.J. et al. Food intake inhibition in rainbow trout induced by activation of serotonin 5-HT2C receptors is associated with increases in POMC, CART and CRF mRNA abundance in hypothalamus. J Comp Physiol B 186, 313–321 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-016-0961-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-016-0961-9