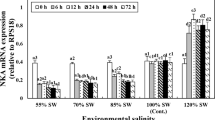
Abstract
NaCl-rich rock salt dissolved in natural water source leads to salinity fluctuation that profoundly affects freshwater ecosystem and aquatic fauna. The snakehead (Channa striata) can live in saline water, but the osmoregulatory mechanisms underlying this ability remain unclear. Herein, we found that exposure to salinities ≥10 ‰ NaCl markedly elevated plasma cortisol and glucose levels, and caused muscle dehydration. In a study of time-dependent response after being transferred from fresh water (0 ‰ NaCl, FW) to salt-dissolved brackish water (10 ‰ NaCl, SW), FW–SW, cortisol increased rapidly along with elevations of plasma glucose and lactate. Interestingly, plasma cortisol returned to baseline after prolonged exposure, followed by a second peak that probably enhanced the branchial Na+/K+-ATPase activity. Under SW–FW condition, Na+/K+-ATPase activity was not altered as compared to SW-adapted fish. In conclusion, salinity change, especially FW–SW, induced a stress response and hence cortisol release in C. striata, which might increase plasma glucose and lactate to energize the branchial Na+/K+-ATPase.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altinok I, Grizzle JM (2001) Effects of low salinities on Flavobacterium columnare infection of euryhaline and freshwater stenohaline fishes. J Fish Dis 24:361–367
Barcellos LJG, Volpato GL, Barreto RE, Coldebella I, Ferreira D (2011) Chemical communication of handling stress in fish. Physiol Behav 103:372–375
Barton BA (2002) Stress in fishes: a diversity of responses with particular reference to changes in circulating corticosteroids. Integr Comp Biol 42:517–525
Björnsson BT, Yamauchi K, Nishioka RS, Deftos LJ, Bern HA (1987) Effects of hypophysectomy and subsequent hormonal replacement therapy on hormonal and osmoregulatory status of coho salmon, Oncorhynchus kisutch. Gen Comp Endocrinol 68:421–430
Bringolf RB, Kwak TJ, Cope WG, Larimore MS (2005) Salinity tolerance of the Flathead Catfish: implications for dispersal of introduced populations. T Am Fish Soc 134:927–936
Butler DG, Carmichael J (1972) (Na+, K+)-ATPase activity in eel (Anguilla rostrata) gills in relation to change in environmental salinity: role of adrenocortical steroids. Gen Comp Endocrinol 19:421–427
Chang EWY, Loong AM, Wong WP, Chew SF, Wilson JM, Ip YK (2007) Changes in tissue free amino acid contents, branchial Na+/K+-ATPase activity and bimodal breathing pattern in the freshwater climbing perch, Anabas testudineus (Bloch), during seawater acclimation. J Exp Zool 307A:708–723
Ciccotti E, Marino G, Pucci P, Cataldi E, Cataudella S (1994) Acclimation trial of Mugil cephalus juveniles to freshwater: morphological and biochemical aspects. Environ Biol Fish 43:163–170
Dang Z, Balm PHM, Flik G, Wendelaar Bonga SE, Lock RAC (2000) Cortisol increases Na+/K+-ATPase density in plasma membranes of gill chloride cells in the freshwater tilapia Oreochromis mossambicus. J Exp Biol 203:2349–2355
Dange AD (1986) Brachial Na+, K+-ATPase activity in freshwater or saltwater acclimated tilapia Oreochromis (Sarotherodon) mossambicus: effects of cortisol and thyroxine. Gen Comp Endocrinol 62:341–343
De Boeck G, Vlaeminck A, Van der Linden A, Blust R (2000) The energy metabolism of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) when exposed to salt stress: an increase in energy expenditure or effects of starvation? Physiol Biochem Zool 73:102–111
De Silva SS (2008) Market chains of non-high value cultured aquatic commodities: case studies from Asia. FAO fisheries and aquaculture circular, no 1032, Rome, FAO, p 46
Eckert SM, Yada T, Shepherd BS, Stetson MH, Hirano T, Grau EG (2001) Hormonal control of osmoregulation in the channel catfish Ictalurus punctatus. Gen Comp Endocrinol 122:270–286
Eddy FB (1985) Uptake and loss of potassium by rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) in fresh water and dilute sea water. J Exp Biol 118:277–286
Ehrenfeld J, Klein U (1997) The key role of the H+ V-ATPase in acid-base balance and Na+ transport processes in frog skin. J Exp Biol 200:247–256
El Tabakh M, Utha-Aroon C, Schreiber C (1999) Sedimentology of the Cretaceous Maha Sarakham evaporites in the Khorat Plateau of northeastern Thailand. Sediment Geol 123:31–62
Evans DH (2008) Teleost fish osmoregulation: what have we learned since August Krogh, Homer Smith, and Ancel Keys. Am J Physiol 295:R704–R713
Gomez-Munoz A, Hales P, Brindley DN, Sancho MJ (1989) Rapid activation of glycogen phosphorylase by steroid hormones in cultured rat hepatocytes. Biochem J 262:417–423
Jacob WF, Taylor MH (1983) The time course of seawater acclimation in Fundulus heteroclitus L. J Exp Zool 228:33–39
Kammerer BD, Cech JJ Jr, Kültz D (2010) Rapid changes in plasma cortisol, osmolality, and respiration in response to salinity stress in tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus). Comp Biochem Physiol 157A:260–265
Kaneko T, Watanabe S, Lee KM (2008) Functional morphology of mitochondrion-rich cells in euryhaline and stenohaline teleosts. Aqua-BioSci Monogr 1:1–62
Kelly SP, Chow INK, Woo NYS (1999) Haloplasticity of black seabream (Mylio macrocephalus): hypersaline to freshwater acclimation. J Exp Zool 282:226–241
Kirschner LB (2004) The mechanism of sodium chloride uptake in hyperregulating aquatic animals. J Exp Biol 207:1439–1452
Laurent P, Perry SF (1990) Effects of cortisol on gill chloride cell morphology and ionic uptake in the freshwater trout, Salmo gairdneri. Cell Tissue Res 259:429–442
Lin YM, Chen CN, Lee TH (2003) The expression of gill Na, K-ATPase in milkfish, Chanos chanos, acclimated to seawater, brackish water and freshwater. Comp Biochem Physiol A 135:489–497
Luz RK, Martínez-Álvarez RM, De Pedro N, Delgado MJ (2008) Growth, food intake regulation and metabolic adaptation in goldfish (Carassius auratus) exposed to different salinities. Aquaculture 276:171–178
Maceina MJ, Shireman JV (1979) Grass carp: effects of salinity on survival, weight loss, and muscle tissue water content. Prog Fish Cult 41:69–73
Madsen SS, Bern HA (1993) In vitro effects of insulin-like growth factor-I on gill Na+/K+-ATPase in coho salmon, Oncorhynchus kisutch. J Endocrinol 138:23–30
Madsen SS, Jensen MK, Nhr J, Kristiansen K (1995) Expression of Na+/K+-ATPase in the brown trout, Salmo trutta: in vivo modulation by hormones and seawater. Am J Physiol 269:R1339–R1345
Marshall WS, Emberley TR, Singer TD, Bryson SE, McCormick SD (1999) Time course of salinity adaptation in a strongly euryhaline estuarine teleost, Fundulus heteroclitus: a multivariable approach. J Exp Biol 202:1535–1544
McCormick SD (1993) Methods for non-lethal gill biopsy and measurement of Na+, K+-ATPase activity. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 50:656–658
McCormick SD (1996) Effects of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor I on salinity tolerance and gill Na+/K+-ATPase in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar): interaction with cortisol. Gen Comp Endocrinol 101:3–11
McCormick SD, Bern HA (1989) In vitro stimulation of Na+-K+-ATPase activity and ouabain binding by cortisol in coho salmon gill. Am J Physiol 256:707–715
Mommsen TP (1984) Biochemical characterization of the rainbow trout gill. J Comp Physiol B 154:191–198
Mommsen TP, Vijayan MM, Moon TW (1999) Cortisol in teleosts: dynamics, mechanisms of action, and metabolic regulation. Rev Fish Biol Fish 9:211–268
Morgan JD, Iwama GK (1996) Cortisol-induced changes in oxygen consumption and ionic regulation in coastal cutthroat trout (Oncorhynchus clarki clarki) parr. Fish Physiol Biochem 15:385–394
Morgan JD, Sakamoto T, Grau EG, Iwama GK (1997) Physiological and respiratory responses of the Mozambique tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) to salinity acclimation. Comp Biochem Physiol 117A:391–398
Musikasinthorn P (2003) Channoidei (snakeheads). In: Hutchins M, Thoney A, Loiselle PV, Schlager N (eds) Grzimek’s animal life encyclopedia, 2nd edn, vols 4, 5. Fishes I–II. Gale Group, Farmington Hills, pp 437–447
Pedersen PBM, Hansen K, Huong DTT, Bayley M, Wang T (2014) Effects of salinity on osmoregulation, growth and survival in Asian swamp eel (Monopterus albus) (Zuiew 1793). Aquacul Res 45:427–438
Pickford GE, Pang PK, Weinstein E, Torretti J, Hendler E, Epstein FH (1970) The response of the hypophysectomized Cyprinodont, Fundulus heteroclitus, to replacement therapy with cortisol: effects on blood serum and sodium–potassium activated adenosine triphosphatase in the gills, kidney, and intestinal mucosa. Gen Comp Endocrinol 14:524–534
Sarma K, Prabakaran K, Kishnan P, Grinson G, Kumar AA (2013) Response of a freshwater air-breathing fish, Clarias batrachus to salinity stress: an experimental case for their farming in brackishwater area in Andaman, India. Aquacul Int 21:183–196
Scott GR, Richards JG, Forbush B, Isenring P, Schulte PM (2004) Changes in gene expression in gills of the euryhaline killifish Fundulus heteroclitus after abrupt salinity transfer. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 287:C300–C309
Serrano X, Serafy J, Grosell M (2011) Osmoregulatory capabilities of the gray snapper, Lutjanus griseus: salinity challenges and field observations. Mar Freshw Behav Physiol 44:185–196
Soivio A, Nikinmaa M, Nyholm K, Westman K (1981) The role of gills in the responses of Salmo gairdneri to moderate hypoxia. Comp Biochem Physiol 70A:133–139
Suwannatrai A, Suwannatrai K, Haruay S, Piratae S, Thammasiri C, Khampoosa P, Kulsantiwong J, Prasopdee S, Tarbsripair P, Suwanwerakamtorn R, Sukchan S, Boonmars T, Malone JB, Kearney MT, Tesana S (2011) Effect of soil surface salt on the density and distribution of the snail Bithynia siamensis goniomphalos in northeast Thailand. Geospatial Health 5:183–190
Tam WL, Wong WP, Loong AM, Hiong KC, Chew SF, Ballantyne JS (2003) The osmotic response of the Asian freshwater stingray (Himantura signifer) to increased salinity: a comparison with marine (Taeniura lymma) and amazonian freshwater (Potamotrygon motoro) stingrays. J Exp Biol 206:2931–2940
Tseng YC, Huang CJ, Chang JCH, Teng WY, Baba O, Fann MJ, Hwang PP (2007) Glycogen phosphorylase in glycogen rich cells is involved in the energy supply for ion regulation in fish gill epithelia. Am J Physiol 293:R482–R491
van der Boon J, van den Thillart GEEJM, Addink ADF (1991) The effects of cortisol administration on intermediary metabolism in teleost fish. Comp Biochem Physiol 100A:47–53
Van der Linden A, Vanaudenhove M, Verhoye M, De Boeck G, Blust R (1999) Osmoregulation of the common carp (Cyprinus carpio) when exposed to an osmotic challenge assessed in vivo and non-invasively by diffusion- and T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Comp Biochem Physiol 124A:343–352
Vidthayanon C (2002) Peat swamp fishes of Thailand. Office of Environmental Policy and Planning, Bangkok
Vijayan MM, Morgan JD, Sakamoto T, Grau EG, Iwama GK (1996) Food-deprivation affects seawater acclimation in tilapia: hormonal and metabolic changes. J Exp Biol 199:2467–2475
Vijayan MM, Pereira C, Forsyth RB, Kennedy CJ, Iwama GK (1997) Handling stress does not affect the expression of hepatic heat shock protein 70 and conjugation enzymes in rainbow trout treated with β-naphtoflvone. Life Sci 61:117–127
Wang JQ, Lui H, Po H, Fan L (1997) Influence of salinity on food consumption, growth and energy conversion efficiency of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) fingerlings. Aquaculture 148:115–124
Wendelaar Bonga SE (1997) The stress response in fish. Physiol Rev 7:591–625
Wendelaar Bonga SE, Lock RAC (1992) Toxicants and osmoregulations in fish. Neth J Zool 42:478–493
Wilkes PRH, McMahon BR (1986) Responses of a stenohaline freshwater teleost (Catostomus commersoni) to hypersaline exposure. J Exp Biol 121:77–94
Woo NYS, Chung KC (1995) Tolerance of Pomacanthus imperator to hypoosmotic salinities: changes in body composition and hepatic enzyme activities. J Fish Biol 47:70–81
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Prof. Nateetip Krishnamra for proofreading of the manuscript, and Dr. Panan Suntornsaratoon for the excellent technical assistance. This work was supported by a grant from the Thailand Research Fund (TRF), the Office of the Higher Education Commission, and Khon Kaen University (MRG5580008 to L. Nakkrasae). N. Charoenphandhu is the TRF Senior Research Scholar (RTA5780001) awarded by Thailand Research Fund and Mahidol University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by G. Heldmaier.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakkrasae, Li., Wisetdee, K. & Charoenphandhu, N. Osmoregulatory adaptations of freshwater air-breathing snakehead fish (Channa striata) after exposure to brackish water. J Comp Physiol B 185, 527–537 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-015-0902-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-015-0902-z