Abstact.
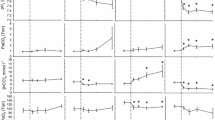
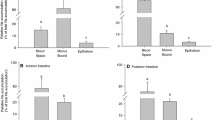
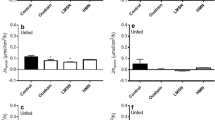
This study investigated whether urea transport mechanisms were present in the gills of the ammoniotelic plainfin midshipman (Porichthys notatus), similar to those recently documented in its ureotelic relative (family Batrachoididae), the gulf toadfish (Opsanus beta). Midshipmen were fitted with internal urinary and caudal artery catheters for repetitive sampling of urine and blood in experiments and radiolabeled urea analogues ([14C]-thiourea and [14C]-acetamide) were used to evaluate the handling of these substances. Isosmotically balanced infusions of urea were used to raise plasma and urine urea concentrations to levels surpassing physiological levels by 8.5-fold and 6.4-fold, respectively. Despite these high urea levels, there was no observable transport maximum in either renal or branchial urea excretion rate, a result mirrored by the total uptake of fish exposed to a range of environmental urea concentrations. Permeability to urea appeared to be symmetrical in the two directions. At comparable plasma concentrations the branchial clearance rate of acetamide was 74% that of urea while branchial clearance rate of thiourea was 55% that of urea. For influx, the comparable values were 60% and 36%, indicating the same pattern. In contrast, the secretion clearance rate of acetamide by the kidney was 56% that of urea while the rate of thiourea secretion clearance was 137% greater than that of urea, with both urea and thiourea being more concentrated in the urine than in the plasma. In addition, the secretion clearance rates of thiourea and urea were significantly greater than those of water and Cl–, whereas acetamide, water and Cl– were found equally in the plasma and urine, appearing to passively equilibrate between the two fluids. Based on our findings, there appear to be two distinct transport mechanisms involved in urea excretion in the plainfin midshipmen, one in the gill (a facilitated diffusion type transporter) and one in the kidney (an active transport mechanism), each of which does not saturate even at plasma urea concentrations that greatly exceed physiological levels. These transporters appear to be similar to those in the midshipman's ureotelic relative, the gulf toadfish.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McDonald, .M., Walsh, .P. & Wood, .C. Branchial and renal excretion of urea and urea analogues in the plainfin midshipman, Porichthys notatus . J Comp Physiol B 172, 699–712 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-002-0299-3
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-002-0299-3