Abstract
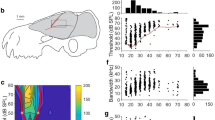
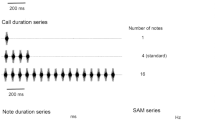
We examined the auditory response properties of neurons in the medial geniculate body of unanesthetized little brown bats (Myotis lucifugus). The units' selectivities to stimulus frequency, amplitude and duration were not significantly different from those of neurons in the inferior colliculus (Condon et al. 1994), which provides the primary excitatory input to the medial geniculate body, or in the auditory cortex (Condon et al. 1997) which receives primary input from the medial geniculate body. However, in response to trains of unmodulated tone pulses, the upper cutoff frequency for time-locked discharges (64 ± 46.9 pulses per second or pps) and the mean number of spikes per pulse (19.2 ± 12.2 pps), were intermediate to those for the inferior colliculus and auditory cortex. Further, in response to amplitude-modulated pulse trains, medial geniculate body units displayed a degree of response facilitation that was intermediate to that of the inferior colliculus and auditory cortex inferior colliculus: 1.32 ± 0.33; medial geniculate body: 1.75 ± 0.26; auditory cortex: 2.52 ± 0.96, P < 0.01). These data suggest that the representation of isolated tone pulses is not significantly altered along the colliculo-thalamo-cortical axis, but that the fidelity of representation of temporally patterned signals progressively degrades along this axis. The degradation in response fidelity allows the system to better extract the salient feature in complex amplitude-modulated signals.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted: 9 January 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Llano, D., Feng, A. Response characteristics of neurons in the medial geniculate body of the little brown bat to simple and temporally-patterned sounds. J Comp Physiol A 184, 371–385 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003590050336
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003590050336