Abstract
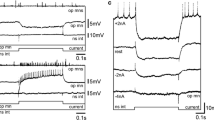
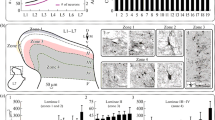
Using extracellular and intracellular stimulation, recording and dye-filling, we identified and studied the superficial extensor motor neurons of the crayfish, Cherax destructor. Functional associations of each neuron were characterised by recording its responses to sensory and abdominal cord inputs, its extensor muscle innervation pattern and its relationships with other neurons. Two clear associations were found among the six neurons of each segment. A medium-sized excitor (no. 3), that innervates a substantial percentage of extensor muscle fibres, and the largest excitor (no. 6), recruited during peak, excitation, were inhibited by input from unknown interneurons that excited the common inhibitor (no. 5). Likewise, these excitors received excitatory input when the inhibitor was silent. Another medium-sized neuron (no. 4) that innervates many muscle fibres was co-active with one of the small excitors (no. 2). The two medium-sized neurons were never active at the same time, and these two groupings may be determined by pre-motor interneurons. The implications of these findings for our understanding of motor control in this system are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted: 21 June 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Drummond, J., Macmillan, D. The abdominal motor system of the crayfish, Cherax destructor. I. Morphology and physiology of the superficial extensor motor neurons. J Comp Physiol A 183, 583–601 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003590050284
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003590050284