Abstract
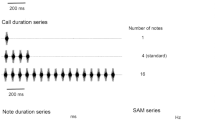
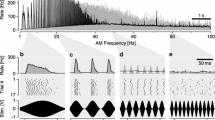
Responses of auditory neurons in the torus semicircularis (TS) of Pleurodema thaul, a leptodactylid from Chile, to synthetic stimuli having diverse temporal patterns and to digitized advertisement calls of P. thaul and three sympatric species, were recorded to investigate their temporal response selectivities. The advertisement call of this species consists of a long sequence of sound pulses (a pulse-amplitude-modulated, or PAM, signal) having a dominant frequency of about 2000 Hz. Each of the sound pulses contains intra-pulse sinusoidal-amplitude-modulations (SAMs). Synthetic stimuli consisted of six series in which the following acoustic parameters were systematically modified, one at a time: PAM rate, pulse duration, number of pulses, and intra-pulse SAM rate. The carrier frequency of these stimuli was set at the characteristic frequency (CF) of the isolated units (n = 47). Response patterns of TS units to synthetic call variants reveal different degrees of selectivities for each of the temporal variables, with populations of neurons responding maximally to specific values found in the advertisement call of this species. These selectivities are mainly shaped by neuronal responsiveness to the overall sound energy of the stimulus and by the inability of neurons to discharge to short inter-pulse gaps.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted: 30 October 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Penna, M., Lin, WY. & Feng, A. Temporal selectivity for complex signals by single neurons in the torus semicircularis of Pleurodema thaul (Amphibia: Leptodactylidae). J Comp Physiol A 180, 313–328 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003590050051
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003590050051