Abstract
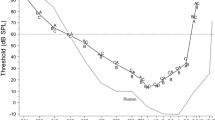
Northern saw-whet owls (Aegolius acadicus) are known for their unique asymmetrical ear structure and ability to localize prey acoustically, yet few attempts have been made to explore the auditory capabilities of this species. In this study, we evoked auditory brainstem responses (ABRs) with tonebursts to assess three main hypotheses regarding the evolution of auditory sensitivity: sender-receiver matching, ecological constraints, and phylogenetic/morphological constraints. We found that ABR amplitude increased with increasing stimulus level, which is consistent with results in other avian species. ABR amplitudes, latencies, and thresholds indicate that the hearing range of Northern saw-whet owls extends from 0.7 to 8.6 kHz, with an extended frequency range of best sensitivity between 1.6 and 7.1 kHz. Sensitivity fell off rapidly above and below these frequencies. The average audiogram was structurally similar to those found in other species of owls, suggesting that phylogeny or morphology may be constraining the frequency range of auditory sensitivity. However, ABR thresholds were 10–25 dB lower than those of Eastern screech-owls (Megascops asio), with thresholds below 0 dB SPL in some individuals. The lowest thresholds were at frequencies not found in the vocalizations of Northern saw-whet owls, suggesting ecological constraints rather than conspecific vocalizations are driving absolute sensitivity.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brinker DF (2000) Sex criteria for Northern saw-whet owls. http://www.projectowlnet.org. Accessed 25 Sept 2015
Brittan-Powell EF, Dooling RJ (2002) Auditory brainstem responses in adult budgerigars (Melopsittacus undulatus). J Acoust Soc Am 112:999–1008. doi:10.1121/1.1494807
Brittan-Powell EF, Lohr B, Hahn DC, Dooling RJ (2005) Auditory brainstem responses in the Eastern screech-owl: an estimate of auditory thresholds. J Acoust Soc Am 118:314–321. doi:10.1121/1.1928767
Dyson ML, Klump GM, Gauger B (1998) Absolute hearing thresholds and critical masking ratios in the European barn owl: a comparison with other owls. J Comp Physiol A 182:695–702. doi:10.1007/s003590050214
Ehret G (1989) Hearing in the mouse. In: Dooling RJ, Hulse SH (eds) The comparative psychology of audition: perceiving complex sounds. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc., Mahwah, pp 1–32
Ehret G, Bernecker C (1986) Low-frequency sound communication by mouse pups (Mus musculus): wriggling calls release maternal behaviour. Anim Behav 34:821–830. doi:10.18725/OPARU-1226
Erdman TC, Brinker DF (1997) Increasing mist net captures of migrant Northern saw-whet owls (Aegolius acadicus) with an audiolure. In: Duncan JR, Johnson DH, Nicholls TH (eds) Biology and conservation of owls of the Northern hemisphere: 2nd international symposium. USDA, Forest Service General Technical Report RM-142, St. Paul, Minnesota, pp 533–544
Evans DL, Rosenfield RN (1987) Remigial molt in fall migrant long-eared and Northern saw-whet owls. In: Nero RW, Clark RJ, Knapton RJ, Harme RH (eds) Biology and conservation of Northern forest owls: symposium proceedings. USDA Forest Service General Technical Report RM-142, Fort Collins, Colorado, pp 209–214
Fridolfsson A-K, Ellegren H (1999) A simple and universal method for molecular sexing of non-ratite birds. J Avian Biol 30:116–121. doi:10.2307/3677252
Frost BJ, Baldwin PJ, Csizy M (1989) Auditory localization in the Northern saw-whet owl, Aegolius acadicus. Can J Zool 67:1955–1959. doi:10.1139/z89-279
Gall MD, Brierley LE, Lucas JR (2011) Species and sex effects on auditory processing in brown-headed cowbirds and red-winged blackbirds. Anim Behav 81:973–982. doi:10.1016/j.anbehav.2011.01.032
Gall MD, Brierley LE, Lucas JR (2012) The sender–reciever matching hypothesis: support from peripheral coding of acoustic features in songbirds. J Exp Biol 215:3742–3751. doi:10.1242/jeb.072959
Gutiérrez-Ibáñez C, Iwaniuk AN, Wylie DR (2011) Relative size of auditory pathways in symmetrically and asymmetrically eared owls. Brain Behav Evol 78:286–301. doi:10.1159/000330359
Hall JW (2015) eHandbook of auditory evoked responses: principles, procedures, and protocols. Pearson Education Inc., London
Hall IC, Woolley SMN, Kwong-Brown U, Kelley DB (2016) Sex differences and endocrine regulation of auditory-evoked, neural responses in African clawed frogs (Xenopus). J Comp Physiol A 202:17–34. doi:10.1007/s00359-015-1049-9
Hazan Y, Kra Y, Yarin I, Wagner H, Gutfreund Y (2015) Visual-auditory integration for visual search: a behavioral study in barn owls. Front in Integr Neurosci 9:1–12. doi:10.3389/fnint.2015.00011
Henry KS, Lucas JR (2008) Coevolution of auditory sensitivity and temporal resolution with acoustic signal space in three songbirds. Anim Behav 76:1659–1671. doi:10.1016/j.anbehav.2008.08.003
Henry KS, Gall MD, Vélez A, Lucas JR (2017) Avian auditory processing at four different scales: variation among species, seasons, sexes, and individuals. In: Bee MA, Miller CT (eds) Psychological mechanisms in animal communication. Springer International Publishing, Cham
Holschuh CI, Otter KA (2005) Using vocal individuality to monitor Queen Charlotte saw-whet owls (Aegolius acadicus brooksi). J Raptor Res 39:134–141
Holt DW, Leroux LA (1996) Diets of Northern pygmy-owls and Northern saw-whet owls in west-central Montana. Wilson Bull 108:123–128
Houseknecht CR (1968) Sonographic analysis of vocalizations of three species of mice. J Mammal 49:555–560. doi:10.2307/1378232
Johnsgard PA (1988) North American owls: biology and natural history, 1st edn. Virginia, Washington DC
Jones KJ, Hill WL (2001) Auditory perception of hawks and owls for passerine alarm calls. Ethology 107:717–726. doi:10.1046/j.1439-0310.2001.00698.x
König C, Weick F, Becking JH (1999) Owls: a guide to the owls of the world. Yale University Press, New Haven
Konishi M (1973) How the owl tracks its prey: experiments with trained barn owls reveal how their acute sense of hearing enables them to catch prey in the dark. Am Sci 61:414–424
Köppl C, Gleich O (2007) Evoked cochlear potentials in the barn owl. J Comp Physiol A 193:601–612. doi:10.1007/s00359-007-0215-0
Lohr B, Brittan-Powell EF, Dooling RJ (2013) Auditory brainstem responses and auditory thresholds in woodpeckers. J Acoust Soc Am 133:337–342. doi: 10.1121/1.4770255
Longmire JL et al (1988) Isolation and molecular characterization of a highly polymorphic centromeric tandem repeat in the family Falconidae. Genomics 2:14–24
Mason JT, McClure CJW, Barber JR (2016) Anthropogenic noise impairs owl hunting behavior. Biol Cons 199:29–32. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2016.04.009
Mueller HC, Berger DD (1967) Observations on migrating saw-whet owls. Bird Band 38:120–125
Nieboer E, Van der Paardt M (1977) Hearing of the African woodowl, Strix woodforii. Neth J Zool 27:227–229
Norberg RA (1977) Occurrence and independent evolution of bilateral ear asymmetry in owls and implications on owl taxonomy. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 280:375–408. doi:10.1098/rstb.1977.0116
Norberg RA (2002) Independent evolution of outer ear asymmetry among five owl lineages; morphology, function and selection. In: Netwon I, Kavanagh R, Olsen J, Taylor I (eds) Ecology and conservation of owls. CSIRO Publishing Collingwood, Clayton, pp 329–342
Otter KA (1996) Individual variation in the advertising call of male Northern saw-whet owls. J Field Ornithol 67:398–405
Paxton BJ, Watts BD (2008) Mass variation in Northern saw-whet owls: implications for current sexing criteria. J Field Ornithol 79:53–57. doi:10.1111/j.1557-9263.2008.00145.x
Payne RS (1971) Acoustic location of prey by barn owls (Tyto alba). J Exp Biol 54:535–573
Rains C (1997) Comparison of food habits of the Northern saw-whet owl (Aegolius acadicus) and the Western screech-owl (Otus kennicottii) in Southwestern Idaho. In: Duncan JR, Johnson DH, Nicholls TH (eds) Biology and conservation of owls of the Northern hemisphere: 2nd international symposium. USDA, Forest Service General Technical Report NC190, St. Paul, Minnesota, pp 339–346
Rasmussen JL, Sealy SG, Cannings RJ (2008) Northern saw-whet owl (Aegolius acadicus). Cornell Lab of Ornithology. https://birdsna.org/Species-Account/bna/species/nswowl
Stapells DR, Oates P (1997) Estimation of the pure-tone audiogram by the auditory brainstem response: a review. Audiol Neurootol 2:257–280. doi: 10.1159/000259252
Swengel SR, Swengel AB (1992) Diet of Northern saw-whet owls in southern Wisconsin. Condor 94:707–711. doi:10.2307/1369255
Van Dijk T (1973) A comparative study of hearing in owls of the family Strigidae. Neth J Zool 23:131–167. doi:10.1163/002829673X00120
Vélez A, Gall MD, Lucas JR (2015) Seasonal plasticity in auditory processing of the envelope and temporal fine structure of sounds in three songbirds. Anim Behav 103:53–63. doi:10.1016/j.anbehav.2015.01.036
Young EI, Proudfoot GA (2014) Prevalence of haematozoa in migrating Northern saw-whet owls (Aegolius acadicus) of Eastern North America. Wilson J Ornithol 126:746–753. doi:10.1676/13-124.1
Acknowledgements
We thank the Mohonk Preserve, the Mohonk Mountain House, the Student Conservation Association, Wild Mountain Birds rehabilitation center, and the American Museum of Natural History for logistical support. We also thank Derek Arrowood, Luana Deng, Kirsten Denman, Maya Enriquez, Christine Guarino, Sandy Jiang, Steve Kovari, Colin Peros, and Aidan Wilcox for assistance with mist netting and banding of Northern saw-whet owls, and Alexander Koo for assistance in data processing. Funding was provided by Vassar College, The John Burroughs Natural History Society, and J.E. Walter. All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All experiments were approved under Vassar IACUC protocol #15-13B.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beatini, J.R., Proudfoot, G.A. & Gall, M.D. Frequency sensitivity in Northern saw-whet owls (Aegolius acadicus). J Comp Physiol A 204, 145–154 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-017-1216-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-017-1216-2