Abstract
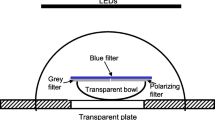
The influence of salt concentration in the seawater on solar orientation in Talitrus saltator and Talorchestia ugolinii was studied in a confined environment (transparent plexiglass bowls). Sodium and calcium concentrations strongly affect both sea–land orientation and the sun compass mechanism in T.saltator, whereas the behaviour of T. ugolinii is less influenced. The absence of Na+ does not influence the sun compass mechanism, but causes an inversion in the mean direction of orientation in T. saltator. In T. ugolinii, there was no influence on the compass mechanism for solar orientation and no inversion in the directional choice. In the absence of Ca2+, a photonegative tendency was observed for T saltator together with marked reduction in the capacity to go in any direction. However, the effect of Ca2+ absence on the orientation capacity of T. saltator is reversible and the orientation capacity can be reduced in a few minutes. The different behaviour of the two species of sandhoppers is discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alton SJ, Herzog ED (2005) Come together, right…now: synchronization of rhythms in a mammalian circadian clock. Neuron 48:531–534
Atkinson MJ, Bingman C (1998) Elemental composition of commercial seasalts. J Aquarium Aqua Sci 8:39–43
Batschelet E (1981) Circular statistics in biology. Academic Press, New York
Calosi P, Ugolini A, Morritt D (2005) Physiological responses to hyposmotic stress in the supralittoral amphipod Talitrus saltator (Crustacea: Amphipoda). Comp Biochem Physiol A 142:267–275
Calosi P, Morritt D, Chelazzi G, Ugolini A (2007) Physiological capacity and environmental tolerance in two sandhoppers species with contrasting geographical ranges: Talitrus saltator and Talorchestia ugolinii. Mar Biol 151:1647–1655
Debenedetti ET (1963) Preliminary observations on the orientation of Talitrus saltator in fresh and sea water. Naturwissenschaften 50:25–26
Hamasaka Y, Wegener C, Naessel DR (2005) GABA modulates Drosophila circadian clock neurons via GABAB receptors and decreases in calcium. J Neurobiol 65:225–240
Herzog ED, Block GD (1999) Keeping an eye on retinal clocks. Chronobiol Int 16:229–247
Mei Q (2014) Molecular evolution of cryptochrome (CRY) and PAS containing proteins in eukaryotic circadian clock. Ph.D. thesis, Hong Kong University
Morritt D (1988) Osmoregulation in littoral terrestrial talitroidean amphipods (Crustacea) from Britain. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 123:77–94
Morritt D (1989) Ionic regulation in littoral and terrestrial amphipods (Crustacea: Amphipoda: Talitridae). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 132:53–67
Morritt D, Spicer J (1998) The physiological ecology of talitrid amphipods: an update. Canad J Zool 76:1965–1982
Morritt D, Spicer J (1999) Developmental ecophysiology of the beachflea Orchestia gammarellus (Pallas) (Crustacea: Amphipoda: Talitridae) III. Physiological competency as a possible explanation for timing of hatchling release. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 232:275–283
Pardi L, Ercolini A (1986) Zonal recovery mechanisms in talitrid crustaceans. Boll Zool 53:139–160
Scapini F (1979) Orientation of Talitrus saltator (Montagu) (Crustacea Amphipoda) in fresh, sea and diluted sea water. Monitore Zool Ital (NS) 13:71–76
Scholz NL (2001) NO/cGMP signaling and the flexible organization of motor behavior in crustaceans. Amer Zool 41:292–303
Spicer J, Moore PG, Taylor AC (1987) The physiological ecology of land invasion by the Talitridae (Crustacea: Amphipoda). Proc R Soc London B 232:95–124
Tafani B, Ugolini A, Bazzicalupo M, Mengoni A, Ruffo S (2004) Phylogenetic relationships among Mediterranean sandhoppers. J Nat Hist 38:499–508
Ugolini A, Macchi T (1988) Learned component in the solar orientation of Talitrus saltator Montagu (Amphipoda: Talitridae). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 121:79–87
Ugolini A, Ungherese G (2012) Sandhoppers as bioindicators of anthropogenic influence on Mediterranean sandy beaches. In: Stambler N (ed) Life in the Mediterranean Sea: A Look at Habitat Changes. Engineering and Technology Ser. Nova Science Publ, New York, pp 413–443
Ugolini A, Felicioni S, Ruffo S, Cipriani L (1995) Distribution of Talorchestia ugolinii and other sandhoppers in Corsica. Boll Zool 62:291–296
Ugolini A, Boddi V, Mercatelli L, Castellini C (2005a) Moon orientation in adult and young sandhoppers under artificial light. Proc R Soc London B 272:2189–2194
Ugolini A, Borghini F, Focardi S, Chelazzi G (2005b) Heavy metals accumulation in two syntopic sandhopper species: Talitrus saltator (Montagu) and Talorchestia ugolinii Bellan Santini and Ruffo. Mar Pollut Bull 50:1328–1334
Ugolini A, Somigli S, Mercatelli L (2006) Green land and blue sea: a coloured landscape in the orientation of the sandhopper Talitrus saltator (Montagu) (Amphipoda, Talitridae). J Exp Biol 209:2509–2514
Ugolini A, Somigli S, Pasquali V, Renzi P (2007) Locomotor activity rhythm and sun compass orientation in the sandhopper Talitrus saltator are related. J Comp Physiol A 193:1259–1263
Ugolini A, Ungherese G, Somigli S, Galanti G, Baroni D, Borghini F, Cipriani N, Nebbiai M, Passaporti M, Focardi S (2008) The amphipod Talitrus saltator as bioindicator of human trampling on sandy beaches. Mar Environ Res 65:349–357
Ugolini A, Ungherese G, Mercatelli L, Saer D, Lepri L (2009) Seawater Ca2+ concentration influences solar orientation in Talitrus saltator (Crustacea, Amphipoda). J Exp Biol 212:797–801
Ugolini A, Galanti G, Mercatelli L (2012a) The skylight gradient of luminance helps sandhoppers in sun and moon identification. J Exp Biol 215:2814–2819
Ugolini A, Pasquali V, Baroni D, Ungherese G (2012b) Behavioural responses of the supralittoral amphipod Talitrus saltator (Montagu) to trace metals contamination. Ecotoxicology 21:139–147
Ugolini A, Ungherese G, Ciofini M, Lapucci A, Camaiti M (2013) Microplastic debris in sandhoppers. Est Coast Shelf Sci 129:19–22
Ugolini A, Nistri A, Schintu M, Abdelrhman KFA, Mengoni A (2015) New data on the distribution of Talorchestia ugolinii Bellan Santini and Ruffo 1991 and Sardorchestia pelecaniformis (Bellan Santini e Ruffo 1985). Biol Mar Medit 22 (in press)
Ungherese G, Ugolini A (2009) Sandhopper solar orientation as a behavioural biomarker of trace metals contamination. Environ Pollut 157:1360–1364
Ungherese G, Mengoni A, Somigli S, Baroni D, Focardi S, Ugolini A (2010) Relationship between heavy metals pollution and genetic diversity in Mediterranean populations of the sandhopper Talitrus saltator (Montagu) (Crustacea, Amphipoda). Environ Pollut 158:1638–1643
Ungherese G, Cincinelli A, Martellini T, Ugolini A (2012) PBDEs in the supralittoral environment: The sandhopper Talitrus saltator (Montagu) as biomonitor? Chemosphere 86:223–227
Wilkins RG, Wilkins PC (2002) The role of calcium and comparable cations in animal behavior. R Soc Chem, Cambridge
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank the Ente Parco Regionale Migliarino San Rossore Massaciuccoli (Pisa, Italy) for the authorization for sampling. Financial support was provided by the Università di Firenze (local funds ex-60 % assigned to A. Ugolini).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ugolini, A., Cincinelli, A., Martellini, T. et al. Salt concentration and solar orientation in two supralittoral sandhoppers: Talitrus saltator (Montagu) and Talorchestia ugolinii Bellan Santini and Ruffo. J Comp Physiol A 201, 455–460 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-015-0992-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-015-0992-9