Abstract
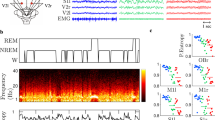
Dramatic changes in neocortical electroencephalogram (EEG) rhythms are associated with the sleep–waking cycle in mammals. Although amphibians are thought to lack a neocortical homologue, changes in rest–activity states occur in these species. In the present study, EEG signals were recorded from the surface of the cerebral hemispheres and midbrain on both sides of the brain in an anuran species, Babina daunchina, using electrodes contacting the meninges in order to measure changes in mean EEG power across behavioral states. Functionally relevant frequency bands were identified using factor analysis. The results indicate that: (1) EEG power was concentrated in four frequency bands during the awake or active state and in three frequency bands during rest; (2) EEG bands in frogs differed substantially from humans, especially in the fast frequency band; (3) bursts similar to mammalian sleep spindles, which occur in non-rapid eye movement mammalian sleep, were observed when frogs were at rest suggesting sleep spindle-like EEG activity appeared prior to the evolution of mammals.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aristakesyan E, Karmanova I (2007) Effect of photostimulation on the wakefulness–sleep cycle in the common frog Rana temporaria. J Evol Biochem Physl Engl Transl 43(2):208–214
Bakalian MJ, Fernstrom JD (1990) Effects of l-tryptophan and other amino acids on electroencephalographic sleep in the rat. Brain Res 528(2):300–307
Balasandaram K, Ramalingam K, Selvarajan V (1997) Bioelectrical activity of brain in Rana tigrina (Daudin) in response to phosalone poisoning. Comp Biochem Physiol C: Pharmacol Toxicol Endocrinol 118(2):229–231
Basar E, Basar-Eroglu C, Karakas S, Schurmann M (2000) Brain oscillations in perception and memory. Int J Psychophysiol 35(2–3):95–124
Basar E, Basar-Eroglu C, Karakas S, Schurmann M (2001) Gamma, alpha, delta, and theta oscillations govern cognitive processes. Int J Psychophysiol 39(2–3):241–248
Bjorvatn B, Fagerland S, Ursin R (1998) EEG power densities (0.5–20 Hz) in different sleep–wake stages in rats. Physiol Behav 63(3):413–417
Blisard K, Fagin K, Falivena P, Privitera M, Olejniczak P, Harrington D, Taylor K, Scremin O (1994) Experimental seizures in the frog (Rana pipiens). Epilepsy Res 17(1):13–22
Buzsaki G, Draguhn A (2004) Neuronal oscillations in cortical networks. Science 304(5679):1926–1929
Cohen J (1992) A power primer. Psychol Bull 112(1):155–159
Corsi-Cabrera M, Guevara M, Del-Río-Portilla Y, Arce C, Villanueva-Hernández Y (2000) EEG bands during wakefulness, slow-wave and paradoxical sleep as a result of principal component analysis in man. Sleep 23(6):1–7
Corsi-Cabrera M, Pérez-Garci E, Del-Río-Portilla Y, Ugalde E, Guevara M (2001) EEG bands during wakefulness, slow-wave, and paradoxical sleep as a result of principal component analysis in the rat. Sleep 24(4):374–380
Csicsvari J, Jamieson B, Wise KD, Buzsaki G (2003) Mechanisms of gamma oscillations in the hippocampus of the behaving rat. Neuron 37(2):311–322
Cui J, Wang Y, Brauth S, Tang Y (2010) A novel female call incites male-female interaction and male–male competition in the Emei music frog, Babina daunchina. Anim Behav 80:181–187
Engel AK, Fries P, Singer W (2001) Dynamic predictions: oscillations and synchrony in top-down processing. Nat Rev Neurosci 2(10):704–716
Fang G, Xia Y, Lai Y, You Z, Yao D (2010) Long-range correlations of different EEG derivations in rats: sleep stage-dependent generators may play a key role. Physiol Meas 31:795–808
Grasing K, Szeto H (1992) Diurnal variation in continuous measures of the rat EEG power spectra. Physiol Behav 51(2):249–254
Hair J, Anderson R, Tatham R, Black W (1998) Multivariate data analysis. Prentice–Hall, Englewood
Hobson J (1967a) Electrographic correlates of behavior in the frog with special reference to sleep. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 22(2):113–121
Hobson J (1967b) Respiration and EEG synchronization in the frog. Nature 213:988–989
Hobson J, Goin O, Goin C (1968) Electrographic correlates of behaviour in tree frogs. Nature 220:386–387
Hoffmann A, Menescal De Oliveira L (1990) Changes in electric activity (EEG) of the telencephalon of conscious toads (Bufo paracnemis) caused by cholinergic stimulation of the mesencephalic tegmentum. Physiol Behav 47(5):857–861
Hoffmann A, Romero S, Menescal-de-Oliveira L (1994) The basal midbrain as a region modulating the level of alerting in the toad, Bufo paracnemis. Physiol Behav 55(2):301–306
Ismail K (2008) Unravelling factor analysis. Br Med J 11(4):99–102
Karmanova I (1996) Novel about peculiarities of sleep and organization of the wakefulness–sleep cycle in poikilothermal vertebrates. Zh Evol Biokhim Fiziol 32:511–535
Karmanova I, Aristakesyan E, Shilling N (1987) Neurophysiological analysis of hypothalamic mechanisms for the regulation of primary sleep and hypobiosis. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR 294:245–248
Klimesch W (1999) EEG alpha and theta oscillations reflect cognitive and memory performance: a review and analysis. Brain Res Rev 29(2–3):169–195
Kline P (1994) An easy guide to factor analysis. Routledge, London
Kopell N, Ermentrout G, Whittington M, Traub R (2000) Gamma rhythms and beta rhythms have different synchronization properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(4):1867–1872
Kostowski W (1967) Pharmacological analysis of bioelectrical activity of the central nervous system of amphibia. I. The effect of some cholinergic and anticholinergic drugs on the frog’s EEG. Brain Res 6(4):783–785
Laming P (1982) Electroencephalographic correlates of behavior in the anurans Bufo regularis and Rana temporaria. Behav Neural Biol 34(3):296–306
Lancel M, Kerkhof GA (1989) Effects of repeated sleep deprivation in the dark-or light-period on sleep in rats. Physiol Behav 45(2):289–297
Merica H, Fortune R (2004) State transitions between wake and sleep, and within the ultradian cycle, with focus on the link to neuronal activity. Sleep Med Rev 8(6):473–485
Nunez PL, Cutillo BA (1995) Neocortical dynamics and human EEG rhythms. Oxford University Press, New York
Ono K, Baba H, Mori K, Sato K (1980) EEG activities during kindling in frog. Int J Neurosci 11(1):9–15
Pan WX, McNaughton N (1997) The medial supramammillary nucleus, spatial learning and the frequency of hippocampal theta activity. Brain Res 764(1–2):101–108
Pletzer B, Kerschbaum H, Klimesch W (2010) When frequencies never synchronize: the golden mean and the resting EEG. Brain Res 1335:91–102
Rechtschaffen A, Kales A (1968) A manual of standardized terminology, technique and scoring system for sleep stages of human subjects. UCLA Brain Information Service, Los Angeles
Saastamoinen A, Huupponen E, Varri A, Hasan J, Himanen S (2007) Systematic performance evaluation of a continuous-scale sleep depth measure. Med Eng Phys 29(10):1119–1131
Sato K (1969) On the effects of cutaneous stimulations upon EEG, respiratory and muscular activities of frog. Acta Med Nagasaki 13:14–27
Segura E, De Juan A (1966) Electroencephalographic studies in toads. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 21(4):373–380
Servít Z, Machek J, Fischer J (1965) Electrical activity of the frog brain during electrically induced seizures. A comparative study of the spike and wave complex. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 19(2):162–171
Smolin L (1962) The origin of the “spontaneous” electrical activity of the frog brain. Bull Exp Biol Med 52(6):1359–1362
Tauber E (1974) The phylogeny of sleep. In: Weitzman ED (ed) Advances in sleep research. Wiley, New York, pp 133–172
Thut G, Miniussi C (2009) New insights into rhythmic brain activity from TMS–EEG studies. Trends Cogn Sci 13(4):182–189
Whishaw I, Vanderwolf C (1971) Hippocampal EEG and behavior: effects of variation in body temperature and relation of EEG to vibrissae movement, swimming and shivering. Physiol Behav 6(4):391–397
Young C, McNaughton N (2009) Coupling of theta oscillations between anterior and posterior midline cortex and with the hippocampus in freely behaving rats. Cereb Cortex 19:24–40
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by grants from the Chinese Academy of Sciences ‘Bairenjihua’ (KSCX2-YW-R-077) to Yezhong Tang and Chinese Academy of Sciences ‘Xibuzhi-guang’ (09C302) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30900141) to Jianguo Cui. Permits for capturing animals were obtained from the local environmental department and all experiments were approved by Chengdu Institute of Biology and carried out according to international standards of animal care and use.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, G., Chen, Q., Cui, J. et al. Electroencephalogram bands modulated by vigilance states in an anuran species: a factor analytic approach. J Comp Physiol A 198, 119–127 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-011-0693-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-011-0693-y