Abstract
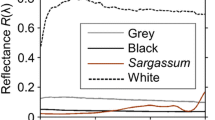
The camouflaging abilities of cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis) are remarkable and well known. It is commonly believed that cuttlefish—although color blind—actively match various colors of their immediate surroundings, yet no quantitative data support this notion. We assembled several natural substrates chosen to evoke the three basic types of camouflaged body patterns that cuttlefish express (uniform/stipple, mottle, and disruptive) and measured the spectral reflectance of the camouflaged pattern and the respective background using a fiber optic spectrometer. We demonstrate that the reflectance spectra of cuttlefish skin patterns correlate closely with the spectra of these natural substrates. Since pigmented chromatophores play a key role in cephalopod color change, we also measured the spectral reflectance of individual cuttlefish chromatophores under the microscope, and confirm the results from a previous publication reporting three distinct colors of chromatophores (yellow, orange, and dark brown) on the animals’ dorsal side. Taken together, our results show that the color variations in substrate and animal skin can be very similar and that this may facilitate color match on natural substrates in the absence of color vision.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aristotle (1910) Historia animalium. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Barbosa A, Florio CF, Chiao C-C, Hanlon RT (2004) Visual background features that elicit mottled body patterns in cuttlefish, Sepia officinalis. Biol Bull 207:154
Barbosa A, Mäthger LM, Chubb C, Florio C, Chiao C-C, Hanlon RT (2007) Disruptive coloration in cuttlefish: a visual perception mechanism that regulates ontogenetic adjustment of skin patterning. J Exp Biol 210:1139–1147
Brown PK, Brown PS (1958) Visual pigments of the octopus and cuttlefish. Nature 182:1288–1290
Chiao C-C, Hanlon RT (2001a) Cuttlefish camouflage: visual perception of size, contrast and number of white squares on artificial checkerboard substrata initiates disruptive coloration. J Exp Biol 204:2119–2125
Chiao C-C, Hanlon RT (2001b) Cuttlefish cue visually on area—not shape or aspect ratio—of light objects on the substrate to produce disruptive body patterns for camouflage. Biol Bull 201:269–270
Chiao C-C, Cronin TW, Osorio D (2000) Color signals in natural scenes: characteristics of reflectance spectra and effects of natural illuminants. J Opt Soc Am A 17:218–224
Chiao C-C, Kelman EJ, Hanlon RT (2005) Disruptive body pattern of cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis) requires visual information regarding edges and contrast of objects in natural substrate backgrounds. Biol Bull 208:7–11
Cott HB (1940) Adaptive coloration in animals. Methuen, London
Denton EJ, Nicol JAC (1966) A survey of reflectivity in silvery teleosts. J Mar Biolog Assoc UK 46:685–722
Endler JA (1990) On the measurement and classification of colour in studies of animal colour patterns. Biol J Linn Soc Lond 41:315–352
Froesch D, Messenger JB (1978) On leucophores and the chromatic unit of Octopus vulgaris. J Zool Lond 186:163–173
Hanlon RT (2007) Cephalopod dynamic camouflage. Curr Biol 17:R400–R404
Hanlon RT, Messenger JB (1988) Adaptive coloration in young cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis L.): the morphology and development of body patterns and their relation to behaviour. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 320:437–487
Hanlon RT, Messenger JB (1996) Cephalopod behaviour. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Hochberg EJ, Atkinson MJ (2000) Spectral discrimination of coral reef benthic communities. Coral Reefs 19:164–171
Hochberg EJ, Atkinson MJ, Apprill A, Andréfouët S (2004) Spectral reflectance of coral. Coral Reefs 23:84–95
Holmes W (1940) The colour changes and colour patterns of Sepia officinalis L Proc Zool Soc Lond A 110:2–35
Jerlov NG (1968) Optical oceanography. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Jerlov NG (1976) Marine optics. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Kelber A, Vorobyev M, Osorio D (2003) Animal colour vision—behavioural tests and physiological concepts. Biol Rev 78:81–118
Kelman EJ, Baddeley RJ, Shohet AJ, Osorio D (2007) Perception of visual texture and the expression of disruptive camouflage by the cuttlefish, Sepia officinalis. Proc R Soc B 274:1369–1375
Losey GS, McFarland WN, Loew ER, Zamzow JP, Nelson PA, Marshall NJ (2003) Visual biology of Hawaiian coral reef fishes. I. Ocular transmission and visual pigments. Copeia 3:433–454
Lythgoe JN (1979) The ecology of vision. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Lythgoe JN, Muntz WRA, Partridge JC, Shand J, Williams DM (1994) The ecology of the visual pigments of snappers (Lutjanidae) on the Great Barrier Reef. J Comp Physiol A 174:461–467
Marshall NJ, Messenger JB (1996) Colour-blind camouflage. Nature 382:408–409
Marshall NJ, Jennings KJ, McFarland WN, Loew ER, Losey GS (2003) Visual biology of Hawaiian coral reef fishes. III. Environmental light and an integrated approach to the ecology of reef fish vision. Copeia 3:467–480
Mäthger LM, Hanlon RT (2006) Anatomical basis for camouflaged polarized light communication in squid. Biol Lett 2:494–496
Mäthger LM, Hanlon RT (2007) Malleable skin coloration in cephalopods: selective reflectance, transmission and absorbance of light by chromatophores and iridophores. Cell Tiss Res 329:179–186
Mäthger LM, Barbosa A, Miner S, Hanlon RT (2006) Color blindness and contrast perception in cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis) determined by a visual sensorimotor assay. Vision Res 46:1746–1753
Mäthger LM, Chiao C-C, Barbosa A, Buresch KC, Kaye S, Hanlon RT (2007) Disruptive coloration elicited on controlled natural substrates in cuttlefish, Sepia officinalis. J Exp Biol 210:2657–2666
Shohet AJ, Baddeley RJ, Anderson JC, Kelman EJ, Osorio D (2006) Cuttlefish responses to visual orientation of substrates, water flow and a model of motion camouflage. J Exp Biol 209:4717–4723
Shohet AJ, Baddeley RJ, Anderson JC, Osorio D (2007) Cuttlefish camouflage: a quantitative study of patterning. Biol J Linn Soc Lond 92:335–345
Stuart-Fox D, Whiting MJ, Moussalli A (2006) Camouflage and colour change: antipredator responses to bird and snake predators across multiple populations in a dwarf chameleon. Biol J Linn Soc Lond 88:437–446
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the Sholley Foundation and to ONR grant N00014-06-1-0202 for support of this project. CCC was supported by the MBL summer research fellowship. AB is grateful for funding from POCI 2010 and Fundo Social Europeu through the Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia, Portugal (SFRH/BD/11303/2002). This paper fulfils partial requirements for a PhD degree at the University of Porto for AB. Special thanks to the Animal Care Staff of the Marine Resources Center of the MBL. Thanks also to Justin Marshall for valuable discussions, and Devi Stuart-Fox and Almut Kelber for their constructive comments on this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mäthger, L.M., Chiao, CC., Barbosa, A. et al. Color matching on natural substrates in cuttlefish, Sepia officinalis . J Comp Physiol A 194, 577–585 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-008-0332-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-008-0332-4