Abstract
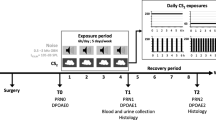
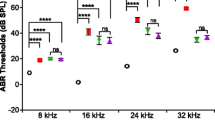
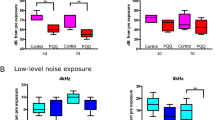
Brevetoxin-3 was shown previously to adversely affect central auditory function in goldfish. The present study evaluated the effects of exposure to this agent on cochlear function in mice using the 2f1-f2 distortion-product otoacoustic emission (DPOAE). Towards this end, inbred CBA/CaJ mice were exposed to a relatively high concentration of brevetoxin-3 (~400 μg/m3) by nose-only inhalation for a 2-h period. Further, a subset of these mice received a second exposure a day later that lasted for an additional 4 h. Mice exposed only once for 2 h did not exhibit any notable cochlear effects. Similarly, mice exposed two times, for a cumulative dose of 6 h, exhibited essentially no change in DPOAE levels.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABR:
-
Auditory brainstem response
- DP-gram:
-
Distortion-product otoacoustic emission gram
- DPOAE:
-
Distortion-product otoacoustic emission
- DSP:
-
Digital signal processor
- FFT:
-
Fast Fourier transform
- GM:
-
Geometric mean
- MMAD:
-
Mass median aerodynamic diameter
- NF:
-
Noise floor
- OHC:
-
Outer hair cell
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
References
Backer LC, Fleming LE, Rowan A, Cheng Y-S, Benson J, Pierce RH, Zaias J, Bean J, Bossart GD, Johnson D, Quimbo R, Baden DG (2003) Recreational exposure to aerosolized brevetoxins during Florida red tide events. Harmful Algae 2:19–28
Baden DG (1989) Brevetoxins: unique polyether dinoflagellate toxins. FASEB J 3:1807–1817
Benson JM, Tischler DL, Baden DG (1999) Uptake, tissue distribution, and excretion of Brevetoxin 3 administered to rats by intratracheal instillation. J Toxicol Environ Health A 57:345–355
Bossart GD, Baden DG, Ewing RY, Roberts B, Wright SD (1998): Brevetoxicosis in manatees (Trichechus manatus latirostris) from the 1996 epizootic: gross, histologic, and immunohistochemical features. Toxicol Pathol 26:276–282
Brownell WE (1990): Outer hair cell electromotility and otoacoustic emissions. Ear Hear 11:82–92
Candreia C, Martin GK, Stagner BB, Lonsbury-Martin BL (2004) distortion-product otoacoustic emissions show exceptional resistance to noise exposure in MOLF/Ei mice. Hear Res 194:109–117
Cattet M, Geraci JR (1993) Distribution and elimination of ingested Brevetoxin (PbTx3) in rats. Toxicon 31:1483–1486
Fleming LE, Backer L, Rowan A (2002) The epidemiology of human illnesses associated with harmful algal blooms. In: Baden D, Adams D (eds) Neurotoxicology Handbook, vol 1. Humana Press Inc, Totowa, pp 363–381
Henry KR, Chole RA, McGinn MD, Frush DP (1981) Increased ototoxicity in both young and old mice. Arch Otolaryngol 107:92–95
Hilton M, Chen J, Kakigi A, Hirakawa H, Mount RJ, Harrison RV (2002) Middle ear instillation of gentamicin and streptomycin in chinchillas: electrophysiological appraisal of selective ototoxicity. Clin Otolaryngol 27:529–535
Jimenez AM, Stagner BB, Martin GK, Lonsbury-Martin BL (1999) Age-related loss of distortion-product otoacoustic emissions in four mouse strains. Hear Res 138:91–105
Jimenez AM, Stagner BB, Martin GK, Lonsbury-Martin BL (2001) Susceptibility of DPOAEs to sound over-exposure in inbred mice with AHL. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 2:233–245
Lu Z, Tomchik SM (2002) Effects of a red-tide toxin on fish hearing. J Comp Physiol A 188:807–813
Naar J, Bourdelais A, Tomas C, Kubanek J, Whitney PL, Flewelling L, Steidinger K, Lancaster J, Baden DB (2002) A competitive ELISA to detect PbTxs from Karenia brevis (formerly Gymnodinium breve) in seawater, shellfish, and mammalian body fluid. Environ Health Perspect 110:179–185
Pierce RH, Henry MS, Blum PC, Lyons J, Cheng YS, Yazzie D, Zhou Y (2003) PbTx concentrations in marine aerosol: Human exposure levels during a Karenia brevis harmful algal bloom. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 70:161–165
Poli MA, Templeton CB, Thompson WL, Hewetson JF (1990) Distribution and elimination of Brevetoxin PbTx-3 in rats. Toxicon 28:903–910
Schlesinger RB (1985) Comparative deposition of inhaled aerosols in experimental animals and humans; a review. J. Toxicol Environ Health 15:197–214
Schlesinger RB (1989) Deposition and clearance of inhaled particles. In: McClelland RO, Henderson RF (eds) Concepts in Inhalation Toxicology. Hemisphere Publishing Co, New York, pp 163–192
Stavroulaki P, Apostolopoulos N, Segas J, Tsakanikos M, Adamopoulos G (2001) Evoked otoacoustic emissions–an approach for monitoring cisplatin induced ototoxicity in children. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 59:47–57
Sun XM, Kim DO (1999) Adaptation of 2f1-f2 distortion-product otoacoustic emission in young-adult and old CBA and C57 mice. J Acoust Soc Am 105:3399–3409
Vazquez AE, Lonsbury-Martin BL, Martin GK, Luebke AE (2001) Temporary and permanent noise-induced changes in distortion-product otoacoustic emissions in CBA/CAJ mouse. Hear Res 156:31–43
Vazquez AE, Jimenez AM, Martin GK, Luebke AE, Lonsbury-Martin BL (2004) Evaluating cochlear function and the effects of noise exposure in the B6.CAST+ahl mouse with distortion-product otoacoustic emissions. Hear Res 194:87–96
Wu WJ, Sha SH, McLaren JD, Kawamoto K, Raphael Y, Schacht J (2001) Aminoglycoside ototoxicity in adult CBA, C57BL and BALB mice and the Sprague-Dawley rat. Hear Res 158:165–178
Wu WJ, Sha, SH, Schacht J (2002) Recent advances in understanding aminoglycoside ototoxicity and its prevention. Audiol Neurootol 7:171–174
Acknowledgements
This research was funded in part by grants from the National Institutes of Health (ES10594, DC00613, DC03114). The authors thank Amber Dison, Carolyn Elliott, Dolores Esparza, Dean Kracko, Colleen Santistevan, and Thomas Argubright for technical assistance. The experiment was conducted in compliance with federal laws of the United States of America and guidance concerning the use of animals in scientific research
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benson, J.M., Stagner, B.B., Martin, G.K. et al. Cochlear function in mice following inhalation of brevetoxin-3. J Comp Physiol A 191, 619–626 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-005-0613-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-005-0613-0