Abstract.
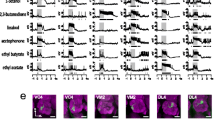
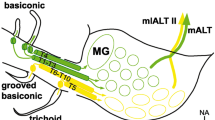
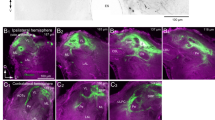
Two distinct neuronal pathways connect the first olfactory neuropil, the antennal lobe, with higher integration areas, such as the mushroom bodies, via antennal lobe projection neurons. Intracellular recordings were used to address the question whether neuroanatomical features affect odor-coding properties. We found that neurons in the median antennocerebral tract code odors by latency differences or specific inhibitory phases in combination with excitatory phases, have a more specific activity profile for different odors and convey the information with a delay. The neurons of the lateral antennocerebral tract code odors by spike rate differences, have a broader activity profile for different odors, and convey the information quickly. Thus, rather preliminary information about the olfactory stimulus first reaches the mushroom bodies and the lateral horn via neurons of the lateral antennocerebral tract and subsequently odor information becomes more specified by activities of neurons of the median antennocerebral tract. We conclude that this neuroanatomical feature is not related to the distinction between different odors, but rather reflects a dual coding of the same odor stimuli by two different neuronal strategies focusing different properties of the same stimulus.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Müller, .D., Abel, .R., Brandt, .R. et al. Differential parallel processing of olfactory information in the honeybee, Apis mellifera L.. J Comp Physiol A 188, 359–370 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-002-0310-1
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-002-0310-1