Abstract
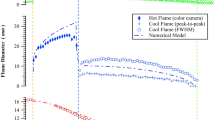
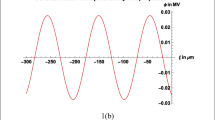
A two wavelength extinction technique is used to quantitatively measure the temporal fuel vapor field produced by pulsed automotive fuel injectors. Line-of-sight measurements are spatially deconvoluted to yield a picture of the overall, cycle-averaged, radial vapor concentration profiles. Vapor measurements are also given for single, consecutive, injection pulses, showing cycle-to-cycle variations in the vapor field. Methods to characterize the cyclic variability in the vapor field of a pulsed spray are discussed. As an illustrative example, the differences between an air assist and a non-air assist injector are shown as a function of duty cycle and axial location.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 11 August 1997/Accepted: 10 February 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wright, J., Drallmeier, J. Cyclic variability of pulsed spray vapor fields. Experiments in Fluids 25, 329–336 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003480050237
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003480050237