Abstract
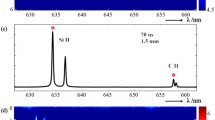
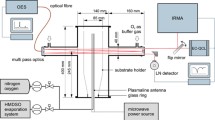
In this paper, experimental results obtained with laser-induced plasma spectroscopy to retrieve local compositions are presented for an ambient pressure up to 5.0 MPa in a still cell. Well-controlled mixtures of gases are introduced and plasma is obtained with the fundamental emission of a pulsed Nd:YAG laser. Simultaneously, plasma shape and spectrally resolved data are taken with a temporal resolution down to 2 ns. First, the temporal evolutions of a high-pressure nitrogen plasma are analyzed as function of spark energy. It is shown that plasma changes orientation from an elongated shape parallel to the laser line to a perpendicular one in a very short time. Results are reported for both spatial and spectral variations. Afterward, the effects of increased carbon concentration are discussed in both shape and spectra. It is seen that strong intensity due to the atomic carbon emissions appear for the high-pressure case. From those experiments, calibration strategies are proposed to get equivalence ratio under high-pressure conditions with a ratio of carbon versus nitrogen and oxygen. The delay between plasma and measurements is set to 2,000 ns and the signal is integrated for 5,000 ns, so as to yield a good signal to noise ratio and a good sensitivity of the technique to changes in mixture fraction. Calibration curves are reported for equivalence ratio up to 1.00 and for pressure from 1.0 to 5.0 MPa. It is shown that typical uncertainties are limited to 7.5% regardless the equivalence ratio in a single shot approach using a spectral fit procedure, whereas it accounts to two times more in a more classical peak ratio approach. Increasing the pressure tends to increase the precision as lower pressure had higher uncertainties.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acquaviva S (2004) Simulation of emission molecular spectra by a semi-automatic programme package: the case of c2 and cn diatomic molecules emitting during laser ablation of a graphite target in nitrogen environment. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 60(8–9): 2079–2086, 7
Arp ZA, Cremers DA, Harris RD, Oschwald DM, Parker GR, Wayne DM (2004) Feasibility of generating a useful laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy plasma on rocks at high pressure: preliminary study for a venus mission. Spectrochim Acta Part B At Spectrosc 59(7):987–999
Bradley D, Sheppard CGW, Suardjaja IM, Woolley R (2004) Fundamentals of high-energy spark ignition with lasers. Combust Flame 138(1–2):55–77
Devillers R, Bruneaux G, Schulz C (2009) Investigation of toluene lif at high pressure and high temperature in an optical engine. Appl Phys B Laser Opt 96(4):735–739
Ferioli F, Buckley SG (2006) Measurements of hydrocarbons using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Combust Flame 144(3):435–447
Hanson RK (2011) Applications of quantitative laser sensors to kinetics, propulsion and practical combustion system. Proc Combust Inst 33:1–40
Kojima J, Nguyen Q-V (2004) Measurement and simulation of spontaneous raman scattering in high-pressure fuel-rich h2-air flames. Meas Sci Technol 15(3):565–580
Orain M, Grisch F, Jourdanneau E, Rossow B, Guin C, Trétout B (2009) Simultaneous measurements of equivalence ratio and flame structure in multipoint injectors using plif. Comptes Rendus Mécanique 337(6–7):373–384
Phuoc TX, White FP (2002) Laser-induced spark for measurements of the fuel-to-air ratio of a combustible mixture. Fuel 81(13):1761–1765
Schmieder RW (1981) Combustion applications of laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. Technical Report Report No. SAND81–8886, Sandia National Laboratories, Livermore, Calif
Schulz C, Sick V (2005) Tracer-lif diagnostics: quantitative measurement of fuel concentration, temperature and fuel/air ratio in practical combustion systems. Progr Energy Combust Sci 31(1):75–121
Stavropoulos P, Michalakou A, Skevis G, Couris S (2005) Quantitative local equivalence ratio determination in laminar premixed methane-air flames by laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (libs). Chem Phys Lett 404(4–6):309–314
Sturm V, Noll R (2003) Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy of gas mixtures of air, co2, n2, and c3h8 for simultaneous c, h, o, and n measurement. Appl Opt 42(30):6221–6225
Vors E, Gallou C, Salmon L (2008) Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy of carbon in helium and nitrogen at high pressure. Spectrochim Acta Part B At Spectrosc 63(10):1198–1204
Zimmer L, Tachibana S (2007) Laser induced plasma spectroscopy for local equivalence ratio measurements in an oscillating combustion environment. Proc Combust Inst 31(1):737–745
Zimmer L, Yoshida S (2008) Measurements of mixture fraction with laser induced plasma spectroscopy. J Combust Soc Jpn 50:317–324
Zimmer L, Okai K, Kurosawa Y (2007) Combined laser induced ignition and plasma spectroscopy: fundamentals and application to a hydrogen-air combustor. Spectrochim Acta Part B At Spectrosc 62:1484–1495
Acknowledgments
The first author wishes to acknowledge the financial support of the CNRS for providing the grants to travel through the Programme International de Collaboration Scientifique, number 4979.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zimmer, L., Yoshida, S. Feasibility of laser-induced plasma spectroscopy for measurements of equivalence ratio in high-pressure conditions. Exp Fluids 52, 891–904 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-011-1151-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-011-1151-x