Abstract
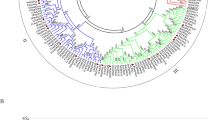
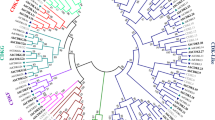
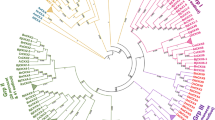
Cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK), the pivotal controller of cell cycle progression, is involved in stress resistance and plant growth. Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) with surprisingly rapid growth depends on continuous cell division, but the CDK gene family information is still lacking. Here, we performed the systematic identification and analysis of the CDK genes in moso bamboo. 40 PeCDK genes were identified and divided into eight subgroups via phylogeny. The same subgroup possessed extremely conserved sequences and similar gene structure. In addition, evolutionary analysis suggested that the PeCDK gene family may have experienced extensive duplication events primarily 6.85–13.71 million years ago (MYA), with segmental duplication dominating. Furthermore, the multiple promoter cis-elements determined in PeCDK genes indicated their potential functions. The expression patterns revealed that most PeCDK genes participated in responses to drought, salt, ABA and SA signals, cell wall synthesis, organ developmental processes and callus growth. The insights gained provide beneficial reference for clarifying the functions of PeCDKs as well as exploring the growth mechanism in bamboo.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The original data presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary material; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
References
Anders S, Huber W (2010) Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol 11:R106. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2010-11-10-r106
Banerjee G, Singh D, Sinha AK (2020) Plant cell cycle regulators: mitogen-activated protein kinase, a new regulating switch? Plant Sci 301:110660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2020.110660
Brookbank BP, Patel J, Gazzarrini S, Nambara E (2021) Role of basal ABA in plant growth and development. Genes 12:1936. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12121936
Cannon SB, Mitra A, Baumgarten A, Young ND, May G (2004) The roles of segmental and tandem gene duplication in the evolution of large gene families in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol 4:10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-4-10
Carneiro AK, Montessoro PDF, Fusaro AF, Araújo BG, Hemerly AS (2021) Plant CDKs-driving the cell cycle through climate change. Plants 10:1804. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10091804
Chen C, Chen H, Zhang Y, Thomas HR, Frank MH, He Y, Xia R (2020) TBtools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol Plant 13:1194–1202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009
Chen M, Guo L, Ramakrishnan M, Fei Z, Vinod KK, Ding Y, Jiao C, Gao Z, Zha R, Wang C, Gao Z, Yu F, Ren G, Wei Q (2022) Rapid growth of Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis): Cellular roadmaps, transcriptome dynamics, and environmental factors. Plant Cell 34:3577–3610. https://doi.org/10.1093/plcell/koac193
Elizabeth MN, Tampubolon K, Alridiwirsah BM, Al-Taey DKA, Jawad KAJH, Mehdizadeh M (2023) Drought stress induced by polyethylene glycol (PEG) in local maize at the early seedling stage. Heliyon 9(9):e20209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20209
Fabian T, Lorbiecke R, Umeda M, Sauter M (2000) The cell cycle genes cycA1;1 and cdc2Os-3 are coordinately regulated by gibberellin in planta. Planta 211:376–383. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004250000295
Gendreau E, Cayla T, Corbineau F (2012) S phase of the cell cycle: a key phase for the regulation of thermodormancy in barley grain. J Exp Bot 63:5535–5543. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ers204
Geng X, Ge B, Liu Y, Wang X, Dong K, Zhang Y, Chen Y, Lu C (2022) Genome-wide identification and functional analysis of silicon transporter family genes in moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). Int J Biol Macromol 223:1705–1719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.10.099
Guo J, Song J, Wang F, Zhang XS (2007) Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of rice cell cycle genes. Plant Mol Biol 64:349–360. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-007-9154-y
Guo ZH, Ma PF, Yang GQ, Hu JY, Liu YL, Xia EH, Zhong MC, Zhao L, Sun GL, Xu YX, Zhao YJ, Zhang YC, Zhang YX, Zhang XM, Zhou MY, Guo Y, Guo C, Liu JX, Ye XY, Chen YM, Li DZ (2019) Genome sequences provide insights into the reticulate origin and unique traits of woody bamboos. Mol Plant 12:1353–1365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2019.05.009
Guo L, Wang C, Chen J, Ju Y, Yu F, Jiao C, Fei Z, Ding Y, Wei Q (2022) Cellular differentiation, hormonal gradient, and molecular alternation between the division zone and the elongation zone of bamboo internodes. Physiol Plant 174:e13774. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.13774
He C, Liang J, Wu Z, Zhuge X, Xu N, Yang H (2022) Study on the interaction preference between CYCD subclass and CDK family members at the poplar genome level. Sci Rep 12:16805. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-20800-9
Hurles M (2004) Gene duplication: the genomic trade in spare parts. PLoS Biol 2:E206. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0020206
Jin G, Ma PF, Wu X, Gu L, Long M, Zhang C, Li DZ (2021) New genes interacted with recent whole-genome duplicates in the fast stem growth of bamboos. Mol Biol Evol 38:5752–5768. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msab288
Kamal KY, Khodaeiaminjan M, Yahya G, El-Tantawy AA, Abdel El-Moneim D, El-Esawi MA, Abd-Elaziz MAA, Nassrallah AA (2021) Modulation of cell cycle progression and chromatin dynamic as tolerance mechanisms to salinity and drought stress in maize. Physiol Plant 172:684–695. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.13260
Li N, Teranishi M, Yamaguchi H, Matsushita T, Watahiki MK, Tsuge T, Li SS, Hidema J (2015) UV-B-induced CPD photolyase gene expression is regulated by UVR8-dependent and -independent pathways in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol 56:2014–2023. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcv121
Liu H, Lyu HM, Zhu K, Van de Peer Y, Max Cheng ZM (2021) The emergence and evolution of intron-poor and intronless genes in intron-rich plant gene families. Plant J 105:1072–1082. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.15088
Liu R, Vasupalli N, Hou D, Stalin A, Wei H, Zhang H, Lin X (2022) Genome-wide identification and evolution of WNK kinases in Bambusoideae and transcriptional profiling during abiotic stress in Phyllostachys edulis. PeerJ 10:e12718. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.12718
Luo X, Xu J, Zheng C, Yang Y, Wang L, Zhang R, Ren X, Wei S, Aziz U, Du J, Liu W, Tan W, Shu K (2023) Abscisic acid inhibits primary root growth by impairing ABI4-mediated cell cycle and auxin biosynthesis. Plant Physiol 191:265–279. https://doi.org/10.1093/plphys/kiac407
Magwanga RO, Lu P, Kirungu JN, Cai X, Zhou Z, Wang X, Diouf L, Xu Y, Hou Y, Hu Y, Dong Q, Wang K, Liu F (2018) Whole genome analysis of cyclin dependent kinase (CDK) gene family in cotton and functional evaluation of the role of CDKF4 gene in drought and salt stress tolerance in plants. Int J Mol Sci 19:2625. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092625
Meguro A, Sato Y (2014) Salicylic acid antagonizes abscisic acid inhibition of shoot growth and cell cycle progression in rice. Sci Rep 4:4555. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep04555
Menges M, de Jager SM, Gruissem W, Murray JA (2005) Global analysis of the core cell cycle regulators of Arabidopsis identifies novel genes, reveals multiple and highly specific profiles of expression and provides a coherent model for plant cell cycle control. Plant J 40:546–566. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313x.2004.02319.x
Min XJ, Powell B, Braessler J, Meinken J, Yu F, Sablok G (2015) Genome-wide cataloging and analysis of alternatively spliced genes in cereal crops. BMC Genom 16:721. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-015-1914-5
Negishi T, Ohya Y (2010) The cell wall integrity checkpoint: coordination between cell wall synthesis and the cell cycle. Yeast 27:513–519. https://doi.org/10.1002/yea.1795
Nisa MU, Huang Y, Benhamed M, Raynaud C (2019) The plant DNA damage response: Signaling pathways leading to growth inhibition and putative role in response to stress conditions. Front Plant Sci 10:653. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00653
Peng Z, Lu Y, Li L, Zhao Q, Feng Q, Gao Z, Lu H, Hu T, Yao N, Liu K, Li Y, Fan D, Guo Y, Li W, Lu Y, Weng Q, Zhou C, Zhang L, Huang T, Zhao Y, Zhu C, Liu X, Yang X, Wang T, Miao K, Zhuang C, Cao X, Tang W, Liu G, Liu Y, Chen J, Liu Z, Yuan L, Liu Z, Huang X, Lu T, Fei B, Ning Z, Han B, Jiang Z (2013) The draft genome of the fast-growing non-timber forest species moso bamboo (Phyllostachys heterocycla). Nat Genet 45:456–461. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2569
Price MN, Dehal PS, Arkin AP (2009) FastTree: computing large minimum evolution trees with profiles instead of a distance matrix. Mol Biol Evol 26:1640–1650. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msp077
Qi F, Zhang F (2020) Cell cycle regulation in the plant response to stress. Front Plant Sci 10:1765. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.01765
Roy SW, Penny D (2007) Patterns of intron loss and gain in plants: intron loss-dominated evolution and genome-wide comparison of O. sativa and A. thaliana. Mol Biol Evol 24:171–181. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msl159
S GB, Gohil DS, Choudhury SR (2023) Genome-wide identification, evolutionary and expression analysis of the cyclin-dependent kinase gene family in peanut. BMC Plant Biol 23:43. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-023-04045-w
Schumacher I, Ndinyanka Fabrice T, Abdou MT, Kuhn BM, Voxeur A, Herger A, Roffler S, Bigler L, Wicker T, Ringli C (2021) Defects in cell wall differentiation of the Arabidopsis mutant rol1-2 is dependent on cyclin-dependent kinase CDK8. Cells 10:685. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10030685
Shabalina SA, Ogurtsov AY, Spiridonov AN, Novichkov PS, Spiridonov NA, Koonin EV (2010) Distinct patterns of expression and evolution of intronless and intron-containing mammalian genes. Mol Biol Evol 27:1745–1749. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msq086
Shi WJ, Li Z, Dong K, Ge BH, Lu CF, Chen YZ (2023) Genome-wide identification, classification and expression analysis of the JmjC domain-containing histone demethylase gene family in Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). S Afr J Botn 157:335–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2023.04.002
Shimotohno A, Aki SS, Takahashi N, Umeda M (2021) Regulation of the plant cell cycle in response to hormones and the environment. Annu Rev Plant Biol 72:273–296. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-080720-103739
Sukegawa Y, Negishi T, Kikuchi Y, Ishii K, Imanari M, Ghanegolmohammadi F, Nogami S, Ohya Y (2018) Genetic dissection of the signaling pathway required for the cell wall integrity checkpoint. J Cell Sci 131:219063. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.219063
Takatsuka H, Ohno R, Umeda M (2009) The Arabidopsis cyclin-dependent kinase-activating kinase CDKF;1 is a major regulator of cell proliferation and cell expansion but is dispensable for CDKA activation. Plant J 59:475–487. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313x.2009.03884.x
Tamirisa S, Vudem DR, Khareedu VR (2017) A cyclin dependent kinase regulatory subunit (CKS) gene of pigeonpea imparts abiotic stress tolerance and regulates plant growth and development in Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 8:165. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00165
Tank JG, Thaker VS (2011) Cyclin dependent kinases and their role in regulation of plant cell cycle. Biol Plant 55:201–212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-011-0031-9
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/25.24.4876
Uehara TN, Nonoyama T, Taki K, Kuwata K, Sato A, Fujimoto KJ, Hirota T, Matsuo H, Maeda AE, Ono A, Takahara TT, Tsutsui H, Suzuki T, Yanai T, Kay SA, Itami K, Kinoshita T, Yamaguchi J, Nakamichi N (2022) Phosphorylation of RNA Polymerase II by CDKC;2 maintains the Arabidopsis circadian clock period. Plant Cell Physiol 63:450–462. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcac011
Wang W, Chen X (2004) HUA ENHANCER3 reveals a role for a cyclin-dependent protein kinase in the specification of floral organ identity in Arabidopsis. Dev 131:3147–3156. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.01187
Wang D, Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Zhu J, Yu J (2010) KaKs_Calculator 2.0: a toolkit incorporating gamma-series methods and sliding window strategies. Genom Proteom Bioinf 8:77–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1672-0229(10)60008-3
Wang X, Geng X, Bi X, Li R, Chen Y, Lu C (2022a) Genome-wide identification of AOX family genes in Moso bamboo and functional analysis of PeAOX1b_2 in drought and salinity stress tolerance. Plant Cell Rep 40:2321–2339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-022-02923-5
Wang X, Geng X, Yang L, Chen Y, Zhao Z, Shi W, Kang L, Wu R, Lu C, Gao J (2022b) Total and mitochondrial transcriptomic and proteomic insights into regulation of bioenergetic processes for shoot fast-growth initiation in moso bamboo. Cells 11:1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11071240
Wang XJ, Yang LL, Geng X, Shi WJ, Chen YZ, Lu CF (2023) Integrative analysis of metabolome and transcriptome reveals the different metabolite biosynthesis profiles related to palatability in winter and spring shoot in moso bamboo. Plant Physiol Biochem 202:107973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2023.107973
Weimer AK, Biedermann S, Harashima H, Roodbarkelari F, Takahashi N, Foreman J, Guan Y, Pochon G, Heese M, Van Damme D, Sugimoto K, Koncz C, Doerner P, Umeda M, Schnittger A (2016) The plant-specific CDKB1-CYCB1 complex mediates homologous recombination repair in Arabidopsis. EMBO J 35:2068–2086. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.201593083
West G, Inzé D, Beemster GT (2004) Cell cycle modulation in the response of the primary root of Arabidopsis to salt stress. Plant Physiol 135:1050–1058. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.104.040022
Wolny E, Skalska A, Braszewska A, Mur LAJ, Hasterok R (2021) Defining the cell wall, cell cycle and chromatin landmarks in the responses of Brachypodium distachyon to salinity. Int J Mol Sci 22:949. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020949
Wood DJ, Endicott JA (2018) Structural insights into the functional diversity of the CDK-cyclin family. Open Biol 8:180112. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsob.180112
Xiao Q, Wei B, Wang Y, Li H, Huang HH, Ajayo BS, Hu YF (2021) Core cell cycle-related gene identification and expression analysis in maize. Plant Mol Biol Rep 39:72–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-020-01236-9
Zhang Y, Tang D, Lin X, Ding M, Tong Z (2018) Genome-wide identification of MADS-box family genes in moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) and a functional analysis of PeMADS5 in flowering. BMC Plant Biol 18:176. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-018-1394-2
Zhao H, Gao Z, Wang L, Wang J, Wang S, Fei B, Chen C, Shi C, Liu X, Zhang H, Lou Y, Chen L, Sun H, Zhou X, Wang S, Zhang C, Xu H, Li L, Yang Y, Wei Y, Jiang Z (2018) Chromosome-level reference genome and alternative splicing atlas of moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). GigaScience 7:115. https://doi.org/10.1093/gigascience/giy115
Zhao L, Li Y, Xie Q, Wu Y (2017) Loss of CDKC;2 increases both cell division and drought tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 91:816–828. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13609
Zhao L, Wang P, Hou H, Zhang H, Wang Y, Yan S, Huang Y, Li H, Tan J, Hu A, Gao F, Zhang Q, Li Y, Zhou H, Zhang W, Li L (2014) Transcriptional regulation of cell cycle genes in response to abiotic stresses correlates with dynamic changes in histone modifications in maize. PLoS ONE 9:e106070. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0106070
Zhao P, Zhang C, Song Y, Xu X, Wang J, Wang J, Zheng T, Lin Y, Lai Z (2022) Genome-wide identification, expression and functional analysis of the core cell cycle gene family during the early somatic embryogenesis of Dimocarpus longan Lour. Gene 821:146286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2022.146286
Zheng T, Nibau C, Phillips DW, Jenkins G, Armstrong SJ, Doonan JH (2014) CDKG1 protein kinase is essential for synapsis and male meiosis at high ambient temperature in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:2182–2187. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1318460111
Zhu Y, Wu N, Song W, Yin G, Qin Y, Yan Y, Hu Y (2014) Soybean (Glycine max) expansin gene superfamily origins: segmental and tandem duplication events followed by divergent selection among subfamilies. BMC Plant Biol 14:93. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-14-93
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2018 YFD0600101), and Beijing Forestry University Outstanding Postgraduate Mentoring Team Building (YJSY-DSTD2022005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K. D. wrote the original draft, performed the formal analysis, validation and data curation. L. L. and M. L. performed the experiments, processed raw data. B. G., X. B., Y. L. and X. G. gave bioinformatics analyses. Y. C. and C. L. designed the research, revised the manuscript and obtained funding acquisition and is responsible for this article. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Handling Author: Stefan de Folter.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, K., Lan, L., Liu, M. et al. Genome-Wide Identification, Evolutionary and Expression Analysis of Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Gene Family Members in Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). J Plant Growth Regul (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-024-11271-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-024-11271-5