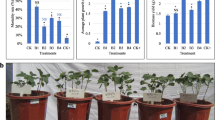
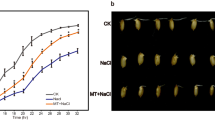
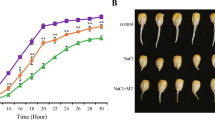
Abstract
Salt hazard is one of the major environmental stresses that seriously threaten world food security. Although melatonin has been proven to improve stress tolerance in plants, the metabolic changes and gene transcription affected by melatonin (MT) under salt stress remain uncertain, especially in maize. In the present study, we investigated the differences in the diurnal metabolism and transcription of maize seedlings to reveal the MT-mediated changes in diurnal metabolism in response to salt stress. Transcriptome analysis identified melatonin crosstalk with other hormones affecting their signal transduction pathways. The transcriptome and metabolome co-analysis revealed that MT maintained osmotic potential and regulated energy supply by regulating sucrose and starch metabolism. In addition, the regulatory network showed that MT and its metabolites were significantly correlated with a series of stress and hormone-related transcription factor (TF) genes, such as JAZ3-1, JAZ9, WRKY28, and ERF020. Taken together, our results indicated that MT alleviated salt stress-induced damage, influenced diurnal metabolic changes in maize under salt stress, and crosstalk with other endogenous hormones to improve salt tolerance in maize.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The RNA-seq dataset in this study has been uploaded to SRA database in NCBI (BioProject ID: PRJNA948831).
References
Abdallah MMS, Abdelgawad ZA, El-Bassiouny HMS (2016) Alleviation of the adverse effects of salinity stress using trehalose in two rice varieties. S Afr J Bot 103:275–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2015.09.019
Abdelrahman M, Nishiyama R, Tran CD, Kusano M, Nakabayashi R, Okazaki Y, Matsuda F et al (2021) Defective cytokinin signaling reprograms lipid and flavonoid gene-to-metabolite networks to mitigate high salinity in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 118:e2105021118. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2105021118
Ahmad S, Cui W, Kamran M, Ahmad I, Meng X, Wu X et al (2021) Exogenous application of melatonin induces tolerance to salt stress by improving the photosynthetic efficiency and antioxidant defense system of maize seedling. J Plant Growth Regul 40:1270–1283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-020-10187-0
Alharbi BM, Elhakem AH, Alnusairi GSH, Soliman MH, Hakeem KR, Hasan MM et al (2021) Exogenous application of melatonin alleviates salt stress-induced decline in growth and photosynthesis in Glycine max (L.) seedlings by improving mineral uptake, antioxidant and glyoxalase system. Plant Soil Environ 67:208–220. https://doi.org/10.17221/659/2020-PSE
Altaf MA, Shahid R, Ren MX, Altaf MM, Khan LU, Shahid S et al (2021) Melatonin alleviates salt damage in tomato seedling: a root architecture system, photosynthetic capacity, ion homeostasis, and antioxidant enzymes analysis. Sci Hortic 285:110145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2021.110145
Arnao MB, Hernández-Ruiz J (2019) Melatonin: a new plant hormone and/or a plant master regulator? Trends Plant Sci 24:38–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2018.10.010
Back K (2021) Melatonin metabolism, signaling and possible roles in plants. Plant J 105:376–391. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.14915
Byeon Y, Back K (2015) Molecular cloning of melatonin 2-hydroxylase responsible for 2-hydroxymelatonin production in rice (Oryza sativa). J Pineal Res 58:343–351. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12220
Cejudo FJ, Sandalio LM, Van BF (2021) Understanding plant responses to stress conditions: redox-based strategies. J Exp Bot 72:5785–5788. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erab324
Chen C, Liu H, Wang C, Liu Z, Liu X, Zou L et al (2019) Metabolomics characterizes metabolic changes of Apocyni Veneti Folium in response to salt stress. Plant Physiol Biochem 144:187–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2019.09.043
Chen L, Lu B, Liu L, Duan W, Jiang D, Li J et al (2021) Melatonin promotes seed germination under salt stress by regulating ABA and GA3 in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Plant Physiol Biochem 162:506–516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.03.029
Chen Y, Wang J, Yao L, Li B, Ma X, Si E et al (2022) Combined proteomic and metabolomic analysis of the molecular mechanism underlying the response to salt stress during seed germination in barley. Int J Mol Sci 23:10515. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810515
Du Z, Bramlage WJ (1992) Modified thiobarbituric acid assay for measuring lipid oxidation in sugar-rich plant tissue extracts. J Agric Food Chem 40:1566–1570. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf00021a018
Elstner EF, Heupel A (1976) Inhibition of nitrite formation from hydroxylammoniumchloride: a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. Anal Biochem 70:616–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90488-7
Galano A, Tan DX, Reiter RJ (2014) Cyclic 3-hydroxymelatonin, a key metabolite enhancing the peroxyl radical scavenging activity of melatonin. RSC Adv 4:5220–5227. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3RA44604B
Ghorbani Javid M, Sorooshzadeh A, Modarres Sanavy SAM, Allahdadi I, Moradi F (2011) Effects of the exogenous application of auxin and cytokinin on carbohydrate accumulation in grains of rice under salt stress. Plant Growth Regul 65:305–313. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-011-9602-1
Giannopolitis CN, Ries SK (1977) Superoxide dismutases: I. Occurrence in higher plants. Plant Physiol 59:309–314. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.59.2.309
Hamayun M, Khan SA, Khan AL, Shin JH, Ahmad B, Shin DH et al (2010) Exogenous gibberellic acid reprograms soybean to higher growth and salt stress tolerance. J Agric Food Chem 58:7226–7232. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf101221t
Hanin M, Ebel C, Ngom M, Laplaze L, Masmoudi K (2016) New insights on plant salt tolerance mechanisms and their potential use for breeding. Front Plant Sci 7:1787. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-0717(95)98611-Q
Hao S, Wang Y, Yan Y, Liu Y, Wang J, Chen S (2021) A review on plant responses to salt stress and their mechanisms of salt resistance. Horticulturae 7:132. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae7060132
Hasanuzzaman M, Hossain MA, Fujita M (2011) Nitric oxide modulates antioxidant defense and the methylglyoxal detoxification system and reduces salinity-induced damage of wheat seedlings. Plant Biotechnol Rep 5:353–365. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-011-0189-9
Hattori A, Migitaka H, Iigo M, Itoh M, Yamamoto K, Ohtani-Kaneko et al (1995) Identification of melatonin in plants and its effects on plasma melatonin levels and binding to melatonin receptors in vertebrates. Biochem Mol Biol Int 35:627–634
Hernández-Ruiz J, Cano A, Arnao MB (2005) Melatonin acts as a growth-stimulating compound in some monocot species. J Pineal Res 39:137–142. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2005.00226.x
Hu Z, Fu Q, Zheng J, Zhang A, Wang H (2020) Transcriptomic and metabolomic analyses reveal that melatonin promotes melon root development under copper stress by inhibiting jasmonic acid biosynthesis. Hortic Res 7:79. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41438-020-0293-5
Ismail A, Takeda S, Nick P (2014) Life and death under salt stress: same players, different timing? J Exp Bot 65:2963–2979. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eru159
Jing T, Liu K, Wang Y, Ai X, Bi H (2022) Melatonin positively regulates both dark- and age-induced leaf senescence by reducing ROS accumulation and modulating abscisic acid and auxin biosynthesis in cucumber plants. Int J Mol Sci 23:3576. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23073576
Keunen E, Peshev D, Vangronsveld J, Van Den Ende W, Cuypers A (2013) Plant sugars are crucial players in the oxidative challenge during abiotic stress: extending the traditional concept. Plant Cell Environ 36:1242–1255. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12061
Khadri M, Tejera NA, Lluch C (2006) Alleviation of salt stress in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) by exogenous abscisic acid supply. J Plant Growth Regul 25:110–119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-005-0004-3
Kolář J, Johnson CH, Macháčková I (2003) Exogenously applied melatonin (N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine) affects flowering of the short-day plant Chenopodium rubrum. Physiol Plant 118:605–612. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1399-3054.2003.00114.x
Kosar F, Akram NA, Sadiq M, Al-Qurainy F, Ashraf M (2019) Trehalose: a key organic osmolyte effectively involved in plant abiotic stress tolerance. J Plant Growth Regul 38:606–618. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-018-9876-x
Lee HJ, Back K (2016) 2-Hydroxymelatonin promotes the resistance of rice plant to multiple simultaneous abiotic stresses (combined cold and drought). J Pineal Res 61:303–316. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12347
Lee HY, Back K (2021) 2-Hydroxymelatonin, rather than melatonin, is responsible for RBOH-dependent reactive oxygen species production leading to premature senescence in plants. Antioxidants 10:1728. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10111728
Lee HY, Back K (2022) The antioxidant cyclic 3-hydroxymelatonin promotes the growth and flowering of Arabidopsis thaliana. Antioxidants 11:1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11061157
Lee HY, Byeon Y, Back K (2014) Melatonin as a signal molecule triggering defense responses against pathogen attack in Arabidopsis and tobacco. J Pineal Res 57:262–268. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12165
Lee HY, Byeon Y, Tan DX, Reiter RJ, Back K (2015) Arabidopsis serotonin N-acetyltransferase knockout mutant plants exhibit decreased melatonin and salicylic acid levels resulting in susceptibility to an avirulent pathogen. J Pineal Res 58:291–299. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12214
Lee K, Zawadzka A, Czarnocki Z, Reiter RJ, Back K (2016) Molecular cloning of melatonin 3-hydroxylase and its production of cyclic 3-hydroxymelatonin in rice (Oryza sativa). J Pineal Res 61:470–478. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12361
Li Y, Zhang Y, Feng F, Liang D, Cheng L, Ma F et al (2010) Overexpression of a Malus vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene (MdNHX1) in apple rootstock M.26 and its influence on salt tolerance. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult PCTOC 102:337–345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-010-9738-0
Li X, Wang C, Cheng J, Zhang J, da Silva JAT, Liu X et al (2014) Transcriptome analysis of carbohydrate metabolism during bulblet formation and development in Lilium davidii var. unicolor. BMC Plant Biol 14:358. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-014-0358-4
Li C, Tan D, Liang D, Chang C, Jia D, Ma F (2015) Melatonin mediates the regulation of ABA metabolism, free-radical scavenging, and stomatal behaviour in two Malus species under drought stress. J Exp Bot 66:669–680. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eru476
Li J, Liu J, Zhu T, Zhao C, Li L, Chen M (2019) The role of melatonin in salt stress responses. Int J Mol Sci 20:1735. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20071735
Li J, Xie J, Yu J, Lyv J, Zhang J, Ding D et al (2022) Melatonin enhanced low-temperature combined with low-light tolerance of pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) seedlings by regulating root growth, antioxidant defense system, and osmotic adjustment. Front Plant Sci 13:998293. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.998293
Liang C, Zheng G, Li W, Wang Y, Hu B, Wang H et al (2015) Melatonin delays leaf senescence and enhances salt stress tolerance in rice. J Pineal Res 59:91–101. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12243
Liang X, Liu S, Wang T, Li F, Cheng J, Lai J et al (2021) Metabolomics-driven gene mining and genetic improvement of tolerance to salt-induced osmotic stress in maize. New Phytol 230:2355–2370. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.17323
Liu Z, Ma C, Hou L, Wu X, Wang D, Zhang L et al (2022) Exogenous SA affects rice seed germination under salt stress by regulating Na+/K+ balance and Endogenous GAs and ABA homeostasis. Int J Mol Sci 23:3293. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23063293
Liu Y, Zhang W, Elango D, Liu H, Jin D, Wang X et al (2023) Metabolome and transcriptome analysis reveals molecular mechanisms of watermelon under salt stress. Environ Exp Bot 206:105200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2022.105200
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Lou J, Wu C, Wang H, Cao S, Wei Y, Chen Y et al (2023) Melatonin treatment delays postharvest senescence of broccoli with regulation of carotenoid metabolism. Food Chem 408:135185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.135185
Ludwig M, Wilmes P, Schrader S (2018) Measuring soil sustainability via soil resilience. Sci Total Environ 626:1484–1493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.043
Luo M, Wang D, Delaplace P, Pan Y, Zhou Y et al (2023) Melatonin enhances drought tolerance by affecting jasmonic acid and lignin biosynthesis in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Physiol Biochem 202:107974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2023.107974
Mahmoud LM, Stanton D, Amin BH, Grosser JW, Dutt M (2022) Overexpression of the Arabidopsis NPR1 gene confers enhanced salt tolerance by regulating antioxidant and starch accumulation in citrus. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult PCTOC 150:695–707. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-022-02323-3
Manchester LC, Coto-Montes A, Boga JA, Andersen LPH, Zhou Z et al (2015) Melatonin: an ancient molecule that makes oxygen metabolically tolerable. J Pineal Res 59:403–419. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12267
Nawaz M, Hassan MU, Chattha MU, Mahmood A, Shah AN, Hashem M et al (2022) Trehalose: a promising osmo-protectant against salinity stress—physiological and molecular mechanisms and future prospective. Mol Biol Rep 49:11255–11271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07681-x
Okuda T, Matsuda Y, Yamanaka A, Sagisaka S (1991) Abrupt increase in the level of hydrogen peroxide in leaves of winter wheat is caused by cold treatment. Plant Physiol 97:1265–1267. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.97.3.1265
Pan J, Li Z, Dai S, Ding H, Wang Q, Li X et al (2020) Integrative analyses of transcriptomics and metabolomics upon seed germination of foxtail millet in response to salinity. Sci Rep 10:13660. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-70520-1
Pleyerová I, Hamet J, Konrádová H, Lipavská H (2022) Versatile roles of sorbitol in higher plants: luxury resource, effective defender or something else? Planta 256:13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-022-03925-z
Polle A, Otter T, Seifert F (1994) Apoplastic peroxidases and lignification in needles of Norway spruce (Picea abies 1.). Plant Physiol 106:53–60. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.106.1.53
Punia H, Tokas J, Mor VS, Bhuker A, Malik A, Singh N et al (2021) Deciphering reserve mobilization, antioxidant potential, and expression analysis of starch synthesis in sorghum seedlings under salt stress. Plants 10:2463. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10112463
Qiu Z, Guo J, Zhu A, Zhang L, Zhang M (2014) Exogenous jasmonic acid can enhance tolerance of wheat seedlings to salt stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 104:202–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.03.014
Reiter RJ, Mayo JC, Tan DX, Sainz RM, Alatorre-Jimenez M, Qin L (2016) Melatonin as an antioxidant: under promises but over delivers. J Pineal Res 61:253–278. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12360
Shah AA, Ahmed S, Ali A, Yasin NA (2020) 2-Hydroxymelatonin mitigates cadmium stress in cucumis sativus seedlings: modulation of antioxidant enzymes and polyamines. Chemosphere 243:125308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125308
Shao Q, Han N, Ding T, Zhou F, Wang B, Shao Q et al (2014) SsHKT1;1 is a potassium transporter of the C3 halophyte Suaeda salsa that is involved in salt tolerance. Funct Plant Biol 41:790–802. https://doi.org/10.1071/FP13265
Shi H, Jiang C, Ye T, Tan D, Reiter RJ, Zhang H et al (2015a) Comparative physiological, metabolomic, and transcriptomic analyses reveal mechanisms of improved abiotic stress resistance in bermudagrass [Cynodon dactylon (L). Pers.] by exogenous melatonin. J Exp Bot 66:681–694. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eru373
Shi H, Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Chan Z (2015b) INDOLE-3-ACETIC ACID INDUCIBLE 17 positively modulates natural leaf senescence through melatonin-mediated pathway in Arabidopsis. J Pineal Res 58:26–33. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12188
Singh AP, Mani B, Giri J (2021) OsJAZ9 is involved in water-deficit stress tolerance by regulating leaf width and stomatal density in rice. Plant Physiol Biochem 162:161–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.02.042
Talaat NB, Todorova D (2022) Antioxidant machinery and glyoxalase system regulation confers salt stress tolerance to wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) plants treated with melatonin and salicylic acid. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 22:3527–3540. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-022-00907-8
Thalmann M, Santelia D (2017) Starch as a determinant of plant fitness under abiotic stress. New Phytol 214:943–951. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14491
Tripathi D, Nam A, Oldenburg DJ, Bendich AJ (2020) Reactive oxygen species, antioxidant agents, and DNA damage in developing maize mitochondria and plastids. Front Plant Sci 11:596. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00596
Tsugawa H, Rai A, Saito K, Nakabayashi R (2021) Metabolomics and complementary techniques to investigate the plant phytochemical cosmos. Nat Prod Rep 38:1729–1759. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1np00014d
Waadt R (2020) Phytohormone signaling mechanisms and genetic methods for their modulation and detection. Curr Opin Plant Biol Cell Signal Gene Regul 57:31–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2020.05.011
Wang J, Lv P, Yan D, Zhang Z, Xu X, Wang T et al (2022) Exogenous melatonin improves seed germination of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under salt stress. Int J Mol Sci 23:8436. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158436
Wang Y, Shi J, Ren Z, Fan X, Li R, Yu C et al (2023a) Physiological and transcriptomic analyses of the effects of coronatine on drought tolerance in Carex leucochlora. Environ Exp Bot 206:105184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2022.105184
Wang Y, Zhao H, Xu L, Zhang H, Xing H, Fu Y et al (2023b) PUB30-mediated downregulation of the HB24-SWEET11 module is involved in root growth inhibition under salt stress by attenuating sucrose supply in Arabidopsis. New Phytol 237:1667–1683. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.18635
Wei W, Li QT, Chu YN, Reiter RJ, Yu XM, Zhu DH et al (2015) Melatonin enhances plant growth and abiotic stress tolerance in soybean plants. J Exp Bot 66:695–707. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eru392
Wei W, Tao J, Yin C, Chen Y, Zhang S et al (2022) Melatonin regulates gene expressions through activating auxin synthesis and signaling pathways. Front Plant Sci 13:1057993. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.1057993
Wu H, Ye H, Yao R, Zhang T, Xiong L (2015) OsJAZ9 acts as a transcriptional regulator in jasmonate signaling and modulates salt stress tolerance in rice. Plant Sci 232:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2014.12.010
Xu T, Chen Y, Kang H (2019) Melatonin is a potential target for improving post-harvest preservation of fruits and vegetables. Front Plant Sci 10:1388. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.01388
Yang Y, Guo Y (2018) Elucidating the molecular mechanisms mediating plant salt-stress responses. New Phytol 217:523–539. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14920
Yang X, Zhang Y, Liu T, Shi J, Qi M, Liu Y et al (2022) Integrated physiological, transcriptomic, and proteomic analyses reveal the regulatory role of melatonin in tomato plants’ response to low night temperature. Antioxidants 11:2060. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11102060
Yu Y, Lv Y, Shi Y, Li T, Chen Y, Zhao D et al (2018) The role of phyto-melatonin and related metabolites in response to stress. Molecules 23:1887. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23081887
Zhang HJ, Zhang N, Yang RC, Wang L, Sun QQ, Li DB et al (2014) Melatonin promotes seed germination under high salinity by regulating antioxidant systems, ABA and GA4 interaction in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). J Pineal Res 57:269–279. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12167
Zhang X, Shi Z, Tian Y, Zhou Q, Cai J, Dai T et al (2016) Salt stress increases content and size of glutenin macropolymers in wheat grain. Food Chem 197:516–521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.11.008
Zhang N, Zhang HJ, Sun QQ, Cao YY, Li X, Zhao B et al (2017) Proteomic analysis reveals a role of melatonin in promoting cucumber seed germination under high salinity by regulating energy production. Sci Rep 7:503. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-00566-1
Zhang H, Zhu J, Gong Z, Zhu JK (2022) Abiotic stress responses in plants. Nat Rev Genet 23:104–119. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41576-021-00413-0
Zhao G, Yu X, Lou W, Wei S, Wang R, Wan Q et al (2019) Transgenic Arabidopsis overexpressing MsSNAT enhances salt tolerance via the increase in autophagy, and the reestablishment of redox and ion homeostasis. Environ Exp Bot 164:20–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2019.04.017
Zhao C, Zhang H, Song C, Zhu JK, Shabala S (2020) Mechanisms of Plant Responses and Adaptation to Soil Salinity. The Innovation 1:100017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xinn.2020.100017
Zhu D, Cai H, Luo X, Bai X, Deyholos MK, Chen Q et al (2012) Over-expression of a novel JAZ family gene from Glycine soja, increases salt and alkali stress tolerance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 426:273–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.08.086
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the General Plan for Scientific Research Projects of Beijing Education Commission (KM201910020009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RL: conceptualization, methodology, supervision, writing-reviewing and editing. LD: supervision, writing-reviewing and editing. JW: investigation, methodology, data curation, writing-original draft preparation. DY, ZL, RL, YH: investigation. YW, ZP, CY, YG, ZL: resources.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Tariq Aftab
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Yan, D., Lu, Z. et al. Integration of the Metabolome and Transcriptome Reveals Diurnal Variability in the Effects of Melatonin on Salt Tolerance in Maize Seedlings. J Plant Growth Regul 43, 1672–1688 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-023-11213-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-023-11213-7