Abstract
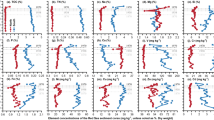
The content and distribution pattern of rare earth elements (REEs) in surface sediments from the Eastern and Western Pacific Ocean, the Northern and Southern Atlantic Ocean, and the Southwestern Indian Ocean were explored and the resources and geochemical characteristics of REEs in deep-ocean sediments from different oceans were studied. The total REE abundances (ΣREE) in the different oceans ranged as follows: Eastern Pacific, 56.88–500.02 µg/g; Western Pacific, 290.68–439.94 µg/g; NorthernAtlantic, 55.33–154.90 µg/g; Southern Atlantic, 40.83–69.30 µg/g; and Southwestern Indian Ocean, 20.24–64.76 µg/g. Their corresponding LREE (La-Eu)/HREE (Gd-Lu) average values were 5.18, 5.86, 9.01, 5.21, and 4.59, which indicated that the light REEs were all evidently enriched. δEu and δCe showed slight Eu-negative anomalies and significant Ce-positive anomalies in all sediments. Although the contents of REEs in the sediments varied among the different oceans, the distribution patterns of REEs were similar, and the correlation coefficient was greater than 0.929 0. In the Eastern Pacific sediments, ΣREE showed a significantly positive correlation with Co, Cu, Zn, Mn, Mo and a weak correlation with Fe. In the Western Pacific and Southern Atlantic sediments, ΣREE presented no obvious correlation and a weakly negative correlation with Co, Cu, Zn, Mn, Mo and Fe, respectively. ΣREE in the Southwestern Indian Ocean sediments positively correlated with Cu, Zn, Mn, Mo, Fe, and had a weakly negative correlation with Co.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott A N, Haley B A, McManus J. 2015. Bottoms up: sedimentary control of the deep North Pacific Ocean’s εNd signature. Geology, 43(11): 1 035–1 038.
Akagi T, Fu F F, Hongo Y, Takahashi K. 2011. Composition of rare earth elements in settling particles collected in the highly productive North Pacific Ocean and Bering Sea: implications for siliceous-matter dissolution kinetics and formation of two REE-enriched phases. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 75(17): 4 857–4 876.
Algeo T J, Maynard J B. 2004. Trace-element behavior and redox facies in core shales of Upper Pennsylvanian Kansas-type cyclothems. Chemical Geology, 206(3–4): 289–318.
Bai Y Y, Liu Z J, Sun P C, Liu R, Hu X F, Zhao H Q, Xu Y B. 2015. Rare earth and major element geochemistry of Eocene fine-grained sediments in oil shale- and coal- bearing layers of the Meihe Basin, Northeast China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 97: 89–101.
Balaram V, Banakar V K, Subramanyam K S V, Roy P, Satyanarayan M, RamMohan M, Sawant S S. 2012. Yttrium and rare earth element contents in seamount cobalt crusts in the Indian Ocean. Current Science, 103: 1 334–1 338.
Basak C, Pahnke K, Frank M, Lamy F, Gersonde R. 2015. Neodymium isotopic characterization of Ross Sea Bottom Water and its advection through the southern South Pacific. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 419: 211–221.
Bau M, Schmidt K, Koschinsky A, Hein J, Kuhn T, Usui A. 2014. Discriminating between different genetic types of marine ferro-manganese crusts and nodules based on rare earth elements and yttrium. Chemical Geology, 381: 1–9.
Dubinin A V, Sval’nov V N. 2000. Geochemistry of rare earth elements in ferromanganese micro- and macronodules from the Pacific nonproductive zone. Lithology and Mineral Resources, 35(6): 520–537.
Dubinin A V. 2000. Geochemistry of rare earth elements in oceanic phillipsites. Lithology and Mineral Resources, 35(2): 101–108.
German C R, Hergt J, Palmer M R, Edmond J M. 1999. Geochemistry of a hydrothermal sediment core from the OBS vent-field, 21°N East Pacific Rise. Chemical Geology, 155(1–2): 65–75.
German C R, Klinkhammer G P, Edmond J M, Mitra A, Elderfield H. 1990. Hydrothermal scavenging of rare-earth elements in the ocean. Nature, 345(6275): 516–518.
Guo Q J, Deng Y N, Hippler D, Franz G, Zhang J M. 2016. REE and trace element patterns from organic-rich rocks of the Ediacaran-Cambrian transitional interval. Gondwana Research, 36: 94–106.
Hara Y, Obata H, Doi T, Hongo Y, Gamo T, Takeda S, Tsuda A. 2009. Rare earth elements in seawater during an iron-induced phytoplankton bloom of the western subarctic Pacific (SEEDS-II). Deep-Sea Research Part II. Topical Studies in Oceanography, 56(26): 2 839–2 851.
Hathorne E C, Stichel T, Brück B, Frank M. 2015. Rare earth element distribution in the Atlantic sector of the Southern Ocean: the balance between particle scavenging and vertical supply. Marine Chemistry, 177: 157–171.
Hein J R, Mizell K, Koschinsky A, Conrad T A. 2013. Deep-ocean mineral deposits as a source of critical metals for high- and green-technology applications: comparison with land-based resources. Ore Geology Reviews, 51: 1–14.
Himmler T, Haley B A, Torres M E, Klinkhammer G P, Bohrmann G, Peckmann J. 2013. Rare earth element geochemistry in cold-seep pore waters of Hydrate Ridge, Northeast Pacific Ocean. Geo-Marine Letters, 33(5): 369–379.
Kato Y, Fujinaga K, Nakamura K, Takaya Y, Kitamura K, Ohta J, Toda R, Nakashima T, Iwamori H. 2011. Deep-sea mud in the Pacific Ocean as a potential resource for rare-earth elements. Nature Geoscience, 4(8): 535–539.
Lan X H, Shen S X. 2002. Geochemical characteristics of rare earth elements of sediment cores from the Central South Yellow Sea. Marine Science Bulletin, 21(5): 46–53. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li J R, Liu S F, Feng X L, Sun X Q, Shi X F. 2016. Rare earth element geochemistry of surface sediments in mid-bengal bay and implications for provenance. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 36(4): 41–50. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li J X, Zhu Z W, Yin X F, Han B, Zheng L, Wang J T, Wang X R. 2015. Analysis of contents and distribution patterns of rare earth elements in the surface sediments of the South Mid-Atlantic ridge. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 43(1): 21–26.
Li X H, Chu F Y, Zhang P P, Lei J J, Yu X, Zhao H Q. 2014. Characteristics of composition and source of rare earth elements in the seafloor hydrothermal products from the southwest Indian ridge. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 36(6): 33–41. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu F W, Miao L, Cai G Q, Yan W. 2015. The rare earth element geochemistry of surface sediments in four transects in the South China Sea and its geological significance. Environmental Earth Sciences, 74(3): 2 511–2 522.
Liu J H. 1982. Geochemistry of REE of deep sea sediments in the east Pacific Ocean. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 12(2): 33–42. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Mills R A, Elderfield H. 1995. Rare earth element geochemistry of hydrothermal deposits from the active TAG Mound, 26°N Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 59(17): 3 511–3 524.
Mondal M E A, Wani H, Mondal B. 2012. Geochemical signature of provenance, tectonics and chemical weathering in the Quaternary flood plain sediments of the Hindon River, Gangetic plain, India. Tectonophysics, 566–567: 87–94.
Munksgaard N C, Lim K, Parry D L. 2003. Rare earth elements as provenance indicators in North Australian estuarine and coastal marine sediments. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 57(3): 399–409.
Nozaki Y, Alibo D S. 2003. Importance of vertical geochemical processes in controlling the oceanic profiles of dissolved rare earth elements in the northeastern Indian Ocean. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 205(3–4): 155–172.
Ren J B, Yao H Q, Zhu K C, He G W, Deng X G, Wang H F, Liu J Y, Fu P E, Yang S X. 2015. Enrichment mechanism of rare earth elements and yttrium in deep-sea mud of Clarion-Clipperton Region. Earth Science Frontiers, 22(4): 200–211. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Shen H T. 1990. Rare earth elements in deep-sea sediments. Geochimica, (4): 340–348. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Singh P. 2009. Major, trace and REE geochemistry of the Ganga River sediments: influence of provenance and sedimentary processes. Chemical Geology, 266(3–4): 242–255.
Soyol-Erdene T O, Huh Y. 2013. Rare earth element cycling in the pore waters of the Bering Sea Slope (IODP Exp. 323). Chemical Geology, 358: 75–89.
Szamalek K, Konopka G, Zglinicki K, Marciniak-Maliszewska B. 2013. New potential source of rare earth elements. Gospodarka Surowcami Mineralnymi, 29(4): 59–76.
Tribovillard N, Algeo T J, Lyons T, Riboulleau A. 2006. Trace metals as paleoredox and paleoproductivity proxies: an update. Chemical Geology, 232(1–2): 12–32.
Wang S H, Zhang N, Chen H, Li L, Yan W. 2014. The surface sediment types and their rare earth element characteristics from the continental shelf of the northern South China Sea. Continental Shelf Research, 88: 185–202.
Yasukawa K, Liu H J, Fujinaga K, Machida S, Haraguchi S, Ishii T, Nakamura K, Kato Y. 2014. Geochemistry and mineralogy of REY-rich mud in the eastern Indian Ocean. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 93: 25–36.
Zhang C S, Wang L J. 2001. Multi-element geochemistry of sediments from the Pearl River system, China. Applied Geochemistry, 16(9–10): 1 251–1 259.
Zhuang K L, Bi S P, Su D P. 2005. Rare earth elements of surface sediments in the subaqueous Yangtze delta. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 25(4): 15–22. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Acknowledgment
We would like to thank the Project for Overseas Innovative Talents of the Taishan Scholars, China. We were also very grateful for the great support of the oceanic voyage.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Supported by the Basic Scientific Fund for National Public Research Institutes of China (No. 2020Q10) and the China Ocean Mineral Resources R&D Association (Nos. DY135-E2-1-07, DY135-E2-4)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Sun, C., Jiang, F. et al. Distribution pattern and geochemical analysis of rare earth elements in deep-ocean sediments. J. Ocean. Limnol. 39, 79–88 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-020-9249-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-020-9249-8