Abstract
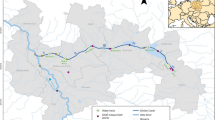
2-Methylisoborneol (2-MIB) is a cyanobacterial metabolite that is responsible for many taste and odor (T&O) complaints related to the aesthetics of drinking water and poses a problem for water authorities because it is recalcitrant during conventional water treatment. A numerical model was developed to simulate 2-MIB in the Qingcaosha Reservoir, an estuarine drinking water resource in the Changjiang estuary with known 2-MIB episodes. The objective of this study was to numerically simulate the generation and release processes of 2-MIB in the reservoir and to provide useful information for better management of drinking water resources experiencing T&O problems caused by cyanobacteria. The simulation results from 2009 to 2013 showed that the simulated 2-MIB concentrations corresponded well to the observational data. 2-MIB was released mainly during periods of low dissolved oxygen (DO) levels with an adequate potential sediment source. The temporal and spatial variations in nutrients, chlorophyll-a (Chl-a), Cyanophyta and 2-MIB were presented and analyzed during 2009 to 2013. According to the study results, high-concentration areas and peak levels of 2-MIB can be controlled by inhibiting algal growth and increasing oxygen levels in the water, which can be achieved via adequate water exchange and oxygen exposure in the reservoir, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blumberg A F, Krone R B. 2002. ECOMSED Manual. Academic Press, New York, USA. 194p.
Burgos L, Lehmann M, De Andrade H H R, de Abreu B R R, de Souza A P, Juliano V B, Dihl R R. 2014. In vivo and in vitro genotoxicity assessment of 2–methylisoborneol, causal agent of earthy–musty taste and odor in water. Ecotoxicology & Environmental Safety, 100: 282–286.
Chang P H, Isobe A, Kang K R, Ryoo S B, Kang H, Kim Y H. 2014. Summer behavior of the Changjiang diluted water to the East/Japan Sea: A modeling study in 2003. Continental Shelf Research, 81: 7–18.
Chen Y Z, Lin W Q, Zhu J R, Lu S Q. 2016. Numerical simulation of an algal bloom in Dianshan Lake. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 34(1): 231–244.
Christensen V G, Graham J L, Milligan C R, Pope L M, Zeigler A C. 2006. Water quality and relation to taste–and–odor compounds in the North Fork Ninnescah River and Cheney reservoir, Southcentral Kansas, 1997–2003. United States Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report, 2006–5095, 43p.
Codd G A. 2000. Cyanobacterial toxins, the perception of water quality, and the prioritisation of eutrophication control. Ecological Engineering, 16(1): 51–60.
Davies J M, Roxborough M, Mazumder A. 2004. Origins and implications of drinking water odours in lakes and reservoirs of British Columbia, Canada. Water Research, 38(7): 1 900–1 910.
Deng X W, Tao M, Zhang L, Xie P, Chen J, Zhang J. 2013. Relationships between Odors and Algae and Water Quality in Dongting Lake. Research of Environmental Sciences, 26(1): 16–21.(in Chinese with English abstract)
Downing J A, Watson S B, McCauley E. 1999. Predicting cyanobacteria dominance in lakes. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 58(10): 1 905–1 908.
Dzialowski A R, Smith V H, Huggins D G, Denoyelles F, Lim N C, Baker D S, Beury J H. 2009. Development of predictive models for geosmin–related taste and odor in Kansas, USA, drinking water reservoirs. Water Research, 43(11): 2 829–2 840.
Fizpartick J J. 2004. A user’s guide for RCA: release 3. 0. HydroQual Inc., New Jersey, USA. 217p.
Gao X L, Song J M. 2005. Phytoplankton distributions and their relationship with the environment in the Changjiang Estuary, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 50(3): 327–335.
Gregor J, Maršálek B, Šípková H. 2007. Detection and estimation of potentially toxic cyanobacteria in raw water at the drinking water treatment plant by in vivo fluorescence method. Water Research, 41(1): 228–234.
Ho L, Hoefel D, Bock F, Saint C P, Newcombe G. 2007. Biodegradation rates of 2–methylisoborneol(MIB) and geosmin through sand filters and in bioreactors. Chemosphere, 66(11): 2 210–2 218.
Hu J D, Zhang X H, Wan Z M, Wang Z J. 2009. Investigation on characteristics of odor compounds and bacterial community in a typical urban polluted river. Research of Environmental Sciences, 22(1): 47–51.(in Chinese with English abstract)
Izydorczyk K, Tarczynska M, Jurczak T, Mrowczynski J, Zalewski M. 2005. Measurement of phycocyanin fluorescence as an online early warning system for cyanobacteria in reservoir intake water. Environmental Toxicology, 20(4): 425–430.
Ji R P, Lu X W, Li X N. 2004. Removal of taste and odor compounds from eutrophic raw water. Water & Wastewater Engineering, 30(10): 8–13.(in Chinese with English abstract)
Mau D P, Ziegler A C, Porter S D, Pope L M. 2004. Surfacewater–quality conditions and relation to taste–and–odor occurrences in the Lake Olathe Watershed, Northeast Kansas, 2000–02. United States Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report, 2004–5047, 95p.
Parinet J, Rodriguez M J, Sérodes J. 2010. Influence of water quality on the presence of off–flavour compounds (geosmin and 2–methylisoborneol). Water Research, 44(20): 5 847–5 856.
Pei H P, Ma J Y. 2002. Study on the algal dynamic model for West Lake, Hangzhou. Ecological Modelling, 148(1): 67–77.
Qiu C, Zhu J R. 2013. Influence of seasonal runoffregulation by the Three Gorges Reservoir on saltwater intrusion in the Changjiang River Estuary. Continental Shelf Research, 71: 16–26.
Smith V H, Sieber–Denlinger J, de Noyelles F Jr, Campell S, Pan S G, Randtke S J, Blain G T, Strasser V A. 2002. Managing taste and odor problems in a eutrophic drinking water reservoir. Lake and Reservoir Management, 18(4): 319–323.
Sugiura N, Utsumi M, Wei B, Iwami N, Okano K, Kawauchi Y, Maekawa T. 2004. Assessment for the complicated occurrence of nuisance odours from phytoplankton and environmental factors in a eutrophic lake. Lakes & Reservoirs: Research and Management, 9(3–4): 195–201.
Watson S B, Charlton M, Rao Y R, Howell T, Ridal J, Brownlee B, Marvin C, Millard S. 2007. Offflavours in large waterbodies: physics, chemistry and biology in synchrony. Water Science & Technology, 55(5): 1–8.
Wu H, Zhu J R, Chen B R, Chen Y Z. 2006. Quantitative relationship of runoffand tide to saltwater spilling over from the North Branch in the Changjiang Estuary: A numerical study. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 69(1–2): 125–132.
Zhang Y C, Zhang N, Xu B B, Kumirska J, Qi F. 2016. Occurrence of earthy–musty taste and odor in Taihu Lake, China: spatial and seasonal patterns. RSC Advances, 6(83): 79 723–79 733.
Zhu C W, Zhang X H, Wang L Y. 2008. Coupled influence of algae and sediment on typical odor compound in water source. China Water & Waste Water, 24(5): 14–17.(in Chinese with English abstract)
Acknowledgement
We acknowledge the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2017YFC0405400), the Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Commission, China (Nos. 12231201603, 15YF1409900), and the Hangzhou Science and Technology Guidance Project in 2016 (No. 20163501Y54)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Zhu, J. Observation and simulation of 2-methylisoborneol in the Qingcaosha Reservoir, Changjiang estuary. J. Ocean. Limnol. 36, 1586–1596 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-018-7124-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-018-7124-7