Abstract
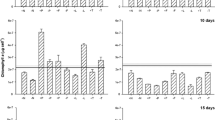
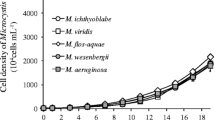
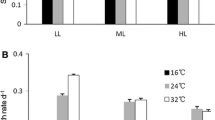
The effects of light, temperature, and coculture on the intracellular microcystin-LR (MC-LR) quota of Microcystis aeruginosa were evaluated based on coculture experiments with nontoxic Dolichospermum (Anabaena) flos-aquae. The MC-LR quota and transcription of mcyB and mcyD genes encoding MC synthetases in M. aeruginosa were evaluated on the basis of cell counts, high-performance liquid chromatography, and reverse-transcription quantitative real-time PCR. The MC-LR quotas of M. aeruginosa in coculture with a 1/1 ratio of inoculum of the two species were significantly lower relative to monocultures 6-d after inoculation. Decreased MC-LR quotas under coculture conditions were enhanced by increasing the D. flos-aquae to M. aeruginosa ratio in the inoculum and by environmental factors, such as temperature and light intensity. Moreover, the transcriptional concentrations of mcyB and mcyD genes in M. aeruginosa were significantly inhibited by D. flos-aquae competition in coculture (P <0.01), lowered to 20% of initial concentrations within 8 days. These data suggested that coculture eff ects by D. flos-aquae not only reduced M. aeruginosa’s intracellular MC-LR quota via inhibition of genes encoding MC synthetases, but also that this eff ect was regulated by environmental factors, including temperature and light intensities.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bittencourt-Oliveira M do C, Kujbida P, Cardozo K H M, Carvalho V M, Moura A do N, Colepicolo P, Pinto E. 2005. A novel rhythm of microcystin biosynthesis is described in the cyanobacterium Microcystis panniformis Komárek et al. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 326(3): 687–694.
Briand E, Bormans M, Quiblier C, Salencon M J, Humbert J F. 2012. Evidence of the cost of the production of microcystins by Microcystis aeruginosa under differing light and nitrate environmental conditions. PLoS One. 7 (1): e29981.
Briand E, Yéprémian C, Humbert J F, Quiblier C. 2008. Competition between microcystin-and non-microcystinproducing Planktothrix agardhii (cyanobacteria) strains under different environmental conditions. Environ. Microbiol., 10(12): 3337–3348.
Bustin S A. 2000. Absolute quantification of mRNA using realtime reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assays. J. Mol. Endocrinol., 25(2): 169–193.
Butler N, Carlisle J C, Linville R, Washburn B. 2009. Microcystins: a Brief Overview of Their Toxicity and Effects, with Special Reference to Fish, Wildlife, and Livestock. Ecotoxicology Program Integrated Risk Assessment Branch Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment California Environmental Protection Agency, Sacramento, CA, USA, p.1–17.
Carmichael W W. 1994. The toxins of cyanobacteria. Sci. Am., 2 70(1): 78–86.
Chen J, Hu L B, Zhou W, Yan S H, Yang J D, Xue Y F, Shi Z Q. 2010. Degradation of microcystin-LR and RR by a Stenotrophomonas sp. strain EMS isolated from Lake Taihu, China. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 11(3): 896–911.
Chen Y W, Qin B Q, Teubner K, Dokulil M T. 2003. Long-term dynamics of phytoplankton assemblages: microcystis -domination in Lake Taihu, a large shallow lake in China. J. Plankton Res., 25(4): 445–453.
Dawson R M. 1998. The toxicology of microcystins. Toxicon. 36(7): 953–962.
Fahnenstiel G L, Millie D F, Dyble J, Litaker R W, Tester P A, McCormick M J, Rediske R, Klarer D. 2008. Microcystin concentrations and cell quotas in Saginaw Bay, Lake Huron. Aquatic Ecosystem Health & Management. 11(2): 190–195.
Gan N Q, Xiao Y, Zhu L, Wu Z X, Liu J, Hu C L, Song L R. 2012. The role of microcystins in maintaining colonies of bloom-forming Microcystis spp. Environ. Microbiol., 14(3): 730–742.
Ginn H P, Pearson L A, Neilan B A. 2010. NtcA from Microcystis aeruginosa PCC 7806 is autoregulatory and binds to the microcystin promoter. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 76(13): 4362–4368.
Grosse Y, Baan R, Straif K, Secretan B, EI Ghissassi F, Cogliano V. 2006. Carcinogenicity of nitrate, nitrite, and cyanobacterial peptide toxins. Lancet Oncol., 7(8): 628–629.
Health Canada. 2002. Guidelines for Canadian drinking water quality: supporting documentation. Cyanobacterial Toxins-Microcystin-LR.
Horst G P, Sarnelle O, White J D, Hamilton S K, Kaul R B, Bressie J D. 2014. Nitrogen availability increases the toxin quota of a harmful cyanobacterium, Microcystis aeruginosa. Water Res., 54: 188–198.
Hu X, Liu Y G, Zeng G M, Hu X J, Wang Y Q, Zeng X X. 2014. Effects of limonene stress on the growth of and microcystin release by the fresh water cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa FACHB-905. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 105: 121–127.
Jang M H, Ha K, Joo G J, Takamura N. 2003. Toxin production of cyanobacteria is increased by exposure to zooplankton. Freshwater Biology. 48(9): 1540–1550.
Kaebernick M, Neilan B A, Börner T, Dittmann E. 2000. Light and the transcriptional response of the microcystin biosynthesis gene cluster. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 66(8): 3387–3392.
Karadžic V, Subakov-Simic G, Krizmanic J, Natic D. 2010. Phytoplankton and eutrophication development in the water supply reservoirs Garaši and Bukulja (Serbia). Desalination. 255(1-3): 91–96.
Krishnamurthy T, Carmichael W W, Sarver E W. 1986. Toxic peptides from freshwater cyanobacteria (blue-green algae). I. Isolation, purification and characterization of peptides from Microcystis aeruginosa and Anabaena flos-aquae. Toxicon. 24(9): 865–873.
Kuniyoshi T M, Sevilla E, Bes M T, Fillat M F, Peleato M L. 2013. Phosphate deficiency (N/P 40: 1) induces mcyD transcription and microcystin synthesis in Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806. Plant Physiol. Biochem., 65: 120–124.
Kurmayer R. 2011. The toxic cyanobacterium Nostoc sp. strain 152 produces highest amounts of microcystin and nostophycin under stress conditions. J. Phycol., 47(1): 200–207.
Laub J, Henriksen P, Brittain S M et al. 2002. [ADMAdda 5 ]-microcystins in Planktothrix agardhi i strain PH-123 (cyanobacteria)-importance for monitoring of microcystins in the environment. Environ. Toxicol., 17(4): 351–357.
LeBlanc S, Pick F R, Aranda-Rondriguze R. 2005. Allelopathic effects of the toxic cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa on duckweed, Lemma gibba L. Environ. Toxicol., 20(1): 67–73.
Lehman P W, Boyer G, Satchwell M, Waller S. 2008. The influence of environmental conditions on the seasonal variation of Microcystis cell density and microcystins concentration in San Francisco Estuary. Hydrobiologia. 600(1): 187–204.
Li Y X, Li D H. 2012. Competition between toxic Microcystics aeruginosa and nontoxic Microcystis wesenbergii with Anabaena PCC7120. J. Appl. Phycol., 24(1): 69–78.
Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-C T method. Methods. 25(4): 402–408.
Oh H M, Lee S J, Jang M H, Yoon B D. 2000. Microcystin production by Microcystis aeruginosa in a phosphorouslimited chemostat. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 66(1): 176–179.
Orr P Y, Jones G J. 1998. Relationship between microcystin production and cell division rates in nitrogen-limited Microcystis aeruginosa cultures. Lancet Oceanogr., 43(7): 1604–1614.
Papadimitriou T, Armeni E, Stalikas C D, Kagalou I, Leonardos I D. 2012. Detection of microcystins in Pamvotis lake water and assessment of cyanobacterial bloom toxicity. Environ mental Monit oring A nd Assess ment. 184(5): 3043–3052.
Pineda-Mendoza R M, Zúñiga G, Martínez-Jerónimo F. 2014. Infochemicals released by Daphnia magna fed on Microcystis aeruginosa affect mcyA gene expression. Toxicon. 80: 78–86.
Rantala A, Rajaniemi-Wacklin P, Lyra C, Lepistö L, Rintala J, Mankiewicz-Boczek J, Sivonen K. 2006. Detection of microcystin-producing cyanobacteria in Finnish Lakes with genus-specific microcystin synthetase gene E (mcyE) PCR and associations with environmental factors. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 72(9): 6101–6110.
Rinta-Kanto J M, Konopko E A, De Bruyn J M, Bourbonniere R A, Boyer G L, Wilhelm S W. 2009. Lake Erie Microcystis: relationship between microcystin production, dynamics of genotypes and environmental parameters in a large lake. Harmful Algae. 8(5): 665–673.
Ríos V, Moreno I, Prieto A I, Soria-Díaz M E, Frías J E, Cameán A M. 2014. Comparison of Microcystis aeruginosa (PCC7820 and PCC7806) growth and intracellular microcystins content determined by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay anti-Adda and phosphatase bioassay. J. Water Health. 12(1): 69–80.
Rouhiainen L, Vakkilainen T, Siemer B L, Buikema W, Haselkorn R, Sivonen K. 2004. Genes coding for hepatotoxic heptapeptides (microcystins) in the cyanobacterium Anabaena strain 90. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 70(2): 686–692.
Rzymski P, Poniedzialek B, Kokocinski M, Jurczak T, Lipski D, Wiktorowicz K. 2014. Interspecific allelopathy in cyanobacteria: Cylindrospermopsin and Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii effect on the growth and metabolism of Microcystis aeruginosa. Harmful Algae. 35: 1–8.
Saker M L, Welker M, Vasconcelos V M. 2007. Multiplex PCR for the detection of toxigenic cyanobacteria in dietary supplements produced for human consumption. Appl. Microbiol. Biot echnol., 73(5): 1136–1142.
Schatz D, Keren Y, Hadas O, Carmeli S, Sukenik A, Kaplan A. 2005. Ecological implications of the emergence of nontoxic subcultures from toxic Microcystis strains. Environ. Microbiol., 7(6): 798–805.
Schatz D, Keren Y, Vardi A, Sukenik A, Carmeli S, Berner T, Dittmann E, Kaplan A. 2007. Towards clarification of the biological role of microcystins, a family of cyanobacterial toxins. Environ. Microbiol., 9(4): 965–970.
Schmidt J R, Wilhelm S W, Boyer G L. 2014. The fate of Microcystins in the environment and challenges for monitoring. Toxins. 6(12): 3354–3387.
Scott L L, Downing S, Phelan R R, Downing T G. 2014. Environmental modulation of microcystin and ß-N-methylamino-L-alanine as a function of nitrogen availability. Toxicon. 87: 1–5.
Sevilla E, Martin-Luna B, Vela L, Bes M T, Fillat M F, Peleato M L. 2008. Iron availability affects mcyD expression and microcystin-LR synthesis in Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806. Environ. Microbiol., 10(10): 2476–2483.
Sevilla E, Martin-Luna B, Vela L, Bes M T, Peleato M L, Fillat M F. 2010. Microcystin-LR synthesis as response to nitrogen: transcriptional analysis of the mcyD gene in Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806. Ecotoxicology. 19(7): 1167–1173.
Song R F, Wang G X, Xu Y, Shao J H, Wang Z J, Liu Y, Li R H. 2011. Transcriptional response of microcystin biosynthesis gene cluster of Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806 under Daphnia stress using real-time RT-PCR technique. J. Lake Sci., 23(1): 150–154.
Te S H, Gin K Y H. 2011. The dynamics of cyanobacteria and microcystin production in a tropical reservoir of Singapore. Harmful Alage. 10(3): 319–329.
Tillett D, Dittmann E, Erhard M, von Döhren H, Börner T, Neilan B A. 2000. Structural organization of microcystin biosynthesis in Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806: an integrated peptide-polyketide synthetase system. Chem. Biol., 7(10): 753–764.
Wan L, Zhu W, Zhao L F. 2007. Effect of nitrogen and phosphorus on growth and competition of M. aeruginosa and S. quadricauda. Environ. Sci., 28(6): 1230–1235. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang J, Zhao F, Chen B H, Li Y N, Na P, Zhuo J. 2013. Small water clusters stimulate microcystin biosynthesis in cyanobacterial Microcystis aeruginosa. J. Appl. Phycol., 25(1): 329–336.
WHO. 2003. Cyanobacterial Toxins: Microcystin-LR in Drinking-Water. In: Background Document for Preparation of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality. World Health Organization (WHO/SDS/WSH/03. 04/57), Geneva.
Wiedner C, Visser P M, Fastner J, Metcalf J S, Codd G A, Mur L R. 2003. Effects of light on the microcystin content of Microcystis strain PC. 7806. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 69(3): 1475–1481.
Wood S A, Rueckert A, Hamilton D P, Cary S C, Dietrich D R. 2011. Swiching toxin production on and off: intermittent microcystin synthesis in a Microcystis bloom. Environ. Microbiol. Rep., 3(1): 118–124.
Wu X D, Kong F X. 2008. The determination of in situ growth rates of the bloomed Microcystis in Meiliang Bay, Lake Taihu. China Environ. Sci., 28(6): 552–555. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yen H K, Lin T F, Tseng I C. 2012. Detection and quantification of major toxigenic Microcystis genotypes in Moo-Tan reservoir and associated water treatment plant. J. Environ. Monitor., 14(2): 687–696.
Zhai C M, Song S, Zou S H, Liu C H, Xue Y R. 2013. The mechanism of competition between two bloom-forming Microcystis species. Freshwater Biology. 58(9): 1831–1839.
Zhang P, Zhai C M, Chen R Q, Liu C H, Xue Y R, Jiang J H. 2012. The dynamics of the water bloom-forming Microcystis aeruginosa and its relationship with biotic and abiotic factors in Lake Taihu, China. Ecol. Eng., 47: 274–277.
Zhang P, Zhai C M, Wang X X, Liu C H, Jiang J H, Xue Y R. 2013. Growth competition between Microcystis aeruginosa and Quadrigula chodatii under controlled conditions. J. Appl. Phycol., 25(2): 555–565.
Zhang T, Song L R. 2006. Allelopathic effect between Microcystis aeruginosa and three filamentous cyanobacteria. J. Lake Sci., 18(2): 150–156. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang X W, Fu J, Song S, Zhang P, Yang X H, Zhang L R, Luo Y, Liu C H, Zhu H L. 2014. Interspecific competition between Microcystis aeruginosa and Anabaena flos -aquae from Taihu Lake, China. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung C. 69(1-2): 53–60.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31471810, 31272081), the Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Treatment (No. 2012ZX07101-013-05(02)), and the Jiangsu Key Technology R&D Program (No. BE2012372)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, R., Li, F., Liu, J. et al. The combined effects of Dolichospermum flos-aquae, light, and temperature on microcystin production by Microcystis aeruginosa . Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 34, 1173–1182 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-016-5204-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-016-5204-0