Abstract
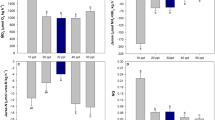
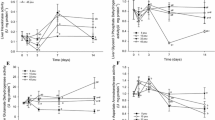
We evaluated the effects of salinity and body mass on the oxygen consumption rate and ammonia excretion rate of mudskipper Boleophthalmus pectinirostris under laboratory conditions. Salinity and body mass had highly significant effects on the oxygen consumption rate (R O) and ammonia excretion rate (R N) (P<0.01). The interactive effects between salinity and body mass on R O and R N were insignificant (P>0.05) and highly significant (P<0.01), respectively. R O and R N of B. pectinirostris decreased significantly as the individual body mass increased. The relationship between R O and body mass was represented by R O = aW b (R 2=0.956, P<0.01). The relationship between R N and the body mass of B. pectinirostris was represented by R N = cW d (R 2=0.966, P<0.01). The R O/R N (O:N) ratios increased significantly as the salinity increased from 12 to 27, but decreased as salinity increased from 27 to 32. The atomic O:N ratios were significantly higher at 27 than at other salinity levels. The average O:N ratio was 25.25. Lipid and carbohydrate were the primary energy sources and protein was the secondary energy source within the salinity range 12–32. R O and R N were significantly higher at 27 than at other salinity levels. Our results suggest that the optimum salinity level for B. pectinirostris is 27.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ana F A, Iker U, Jorge H, Soledad P, Cristina P, Claudia C, Pedro D, Carlos R. 2009. How size relates to oxygen consumption, ammonia excretion, and ingestion rates in cold (Enteroctopus megalocyathus) and tropical (Octopus maya) octopus species. Mar. Biol., 156: 1 547–1 558.
Aristizabal-Abud E O. 1992. Effects of salinity and weight on routine metabolism in the juvenile croaker, Micropogonias furnieri (Desmarest 1823). Fish Biology, 40: 471–472.
Bayne B L, Widdows J. 1978. The physiological ecology of two populations of Mytilus edulis L. Oecologia., 37: 137–162.
Claireaux G, Lagardere J P. 1999. Influence of temperature, oxygen and salinity on the metabolism of the European sea bass. Journal of Sea Research, 42: 157–168.
Conover R J, Corner E D S. 1968. Respiration and nitrogen excretion by some marine zooplankton in relation to their life cycles. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 48: 49–75.
Cui Y, Wootton R J. 1988. The metabolic rate of the minnow, Phoxinus phoxinus (L.) (Pisces: Cyrinidae), in relation to ration, body size and temperature. Functional Ecology, 2: 157–162.
Ding Y W, Li J E. 2000. A preliminary study on the oxygen consumption of fry of flat bream Rhabdosargus sarba (Forskal). Journal of Zhanjiang Ocean University, 20: 8–12. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Foster R P, Goldstein L. 1969. Formation of excretory products. In: Hoar W S, Randall D J eds. Fish Physiology, Vol. 1. Academic Press, New York. p.313–350.
Gracia-López V, Rosas-Vázquez C, Brito-Pérez R. 2006. Effects of salinity on physiological conditions in juvenile common snook Centropomus undecimalis. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A, 145: 340–345.
Gu R B, Xu G C, Wen H B. 2006. Studies on the oxygen consumption rate and asphyxiant point of Hemibarbus maculatus Bleeker. Journal of Shanghai Fisheries University, 15: 118–122. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Herrmann J P, Endel S E C. 2000. Effect of body size on the standard metabolism of horse mackerel. Journal of Fish Biology, 57: 746–760.
Hettler E F. 1976. Influence of temperature and salinity on routine metabolic rate and growth of young Atlantic menhaden. Fish Biology, 8: 55–65.
Hong W S, Dai Q N, Zhang Q Y. 1988. Observations on the early development of the mud skipper, Boleophthalmus pectinirostris (Linnaeus). Tropic Oceanology, 2: 1–8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Jiang L H, Zhu A Y. 2009. Effect of temperature on oxygen consumption rate and ammonia excretion of Sciaenops ocellatus. Journal of Aquaculture, 30: 27–30. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Jobling M. 1985. Growth and Metabolism. Fish Energetics: Perspectives. Croom Helm, London. p.257–281.
Jon A, Trygve S. 1997. A model for oxygen consumption of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) based on measurements of individual fish in a tunnel respirometer. Aquaculture Engineering, 17: 241–251.
Lei S J. 2002. Effect of salinity and body weight on the oxygen consumption of Oreochromis niloticus × O. mossambicus. Journal of Applied Ecology, 13: 739–742. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li J E. 1991. A preliminary study on the oxygen consumption of Lates calcarifer. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 13: 424–430. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li J E. 2008. A preliminary study on oxygen consumption rate, ammonia excretion rate and asphyxiation point of fry of chu’s croaker Nibea coibor. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 30: 165–170. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu H J, Yasunori S, Hiroyuki M. 1997. Effect of feeding time on oxygen consumption and ammonia excretion of Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Suisan Zoshoku, 45: 81–86.
Mayzaud P, Conover R J. 1988. O:N atomic ratio as a tool to describe zooplankton metabolism. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 45: 289–302.
Moser M L, Hettler W F. 1989. Routine metabolism of juvenile spot, Leiostomus xanthurus, as a function of temperature, salinity and weight. Journal of Fish Biology, 35: 703–707.
Navarro J M. 1988. The effects of salinity on the physiological ecology of Choromytilus chorus (Molina, 1782) (Bivalaia: Mytilidae). Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 122: 19–33.
Rocha A J S, Gomes V, Phan V N, Passos M J, Furia R R. 2005. Metabolic demand and growth of juveniles of Centropomus parallelus as function of salinity. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 316: 157–165.
Shumway S E. 1982. Oxygen consumption rate in oysters on overview. Marine Biology Letters, 3: 1–23.
Sun B Z, Huang H, Cao W X, Wang J W, Tan D Q. 2010. Studies on the oxygen consumption rate and asphyxiant point of Megalobrama pellegrini and Coreius guichcnoti. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 34: 88–93. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Via J D, Villani P, Gasteiger E, Niederstätter H. 1998. Oxygen consumption in sea bass fingerling Dicentrarchus labrax exposed to acute salinity and temperature changes: metabolic basis for maximum stocking density estimations. Aquaculture, 169: 303–313.
Wang B, Li J Q, Cao Z H, Sun Q X, Zuo Y M, Zhu M Y, Mao X H. 2003. Study on respiration and oxygen consumption rate of summer flounder (Paralichthys dentatus) juvenile. Advances in Marine Science, 21: 325–330. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang G J, Xie J, Pang D B. 2001. A preliminary study on the oxygen consumption of Japanese eel. Marine Fisheries Research, 22: 52–55. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang M, Qiu S Y. 2001. Study on excretion rate of endogenous, exogenous and total nitrogen of juvenile Plectorhy nchus cinctus temminck. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 20: 87–92. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Widdows J. 1978. Physiological in dices of stress in Mytilus edulis. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 58: 125–142.
Winberg G G. 1956. Rate of metabolism and food requirements of fishes. Journal of Fisheries Research Board of Canada, 194: 1–253.
Wu S. 2006. Artificial culturing technology of Boleophthalmus pectinirostris. Journal of Fujian Fisheries, 3: 48–50. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yamamoto K T A, Kao S. 1990. Relationship between oxygen consumption and body weight in 36 marine teleost fish under resting and noromoxic conditions. Suisan Zoshoku, 38: 41–45.
Yan M C, Shan L Z, Xie X L, Lin S Z, Shao X B, Liu W C, Huang X K. 2008. Influence of temperature, salinity and body weight on oxygen consumption and ammonia excretion of Oplegnathus fasciatus juvenile. Advances in Marine Science, 26: 486–496. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yan M C, Shan L Z, Shao X B, Hu L H, Cai X L, Lin Z H. 2007. Influence of salinity and pH on t he rates of oxygen consumption and ammonia excretion of Juvenile Miichthy miuy. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 26: 85–91. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang L Z, Yang J H, Liu J Y, Zhuang P, Zhang F, Qu L. 2009. Effects of water temperature, salinity, pH, and anaesthetics on oxygen consumption rate of juvenile Siganus canaliculatus. Journal of Ecology, 28: 1 494–1 498. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang Q, Yuan Z G, Yuan C X, Luo Q P. 2007. The oxygen consumption rate of Sebastiscusm armoratus in different circumstances of body weight, salinity and temperature. Journal of Fujian Fisheries, 4: 12–15. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang Z Q, Zhang M Z. 1997. Oxygen consumption and ammonia excretion of Paralichthys Olivaceus with different body weight s at different water temperature. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao, 27: 483–489. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zheng Z M, Jin C H, Li M Y, Bai P F, Dong S L. 2008. Effects of temperature and salinity on oxygen consumption and ammonia excretion of juvenile miiuy croaker, Miichthys miiuy (Basilewsky). Aquaculture International, 16: 581–589.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (No. 8152408801000015)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, F., Wang, H. Effects of salinity and body mass on oxygen consumption and ammonia excretion of mudskipper Boleophthalmus pectinirostris . Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 33, 92–98 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-015-4107-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-015-4107-9