Abstract
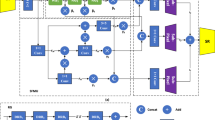
Due to the pixel limit of the polarization imaging detector and the object detection conditions, the spatial resolution of the object polarization image in actual imaging detection applications is generally low. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have been introduced to image super-resolution (SR). However, these methods rarely explore the internal connections between local spatial components and multi-scale feature maps in different receptive fields. To this end, we propose a multi-scale adaptive weighted network (MSAWN) for polarization computational imaging super-resolution to gain superior reconstruction performance. Computational imaging methods centered on information acquisition and interpretation can obtain high-resolution images that are superior to imaging systems. Specifically, we use a limited amount of memory and computational power even with multi-scale and multi-level polarization information. Second, a spatial pyramid structure based on the space-channel attention mechanism is designed to effectively adjust the feature weight of polarization information. Third, we adopt an adaptive weight unit to reduce redundant network branches and parameters. Particularly, we design an innovative reconstruction layer with inputs coming from multiple paths by means of sub-pixel convolution. The experimental results show that the proposed method achieves better reconstruction accuracy and visual effect, and the objective evaluation indexes such as PSNR and SSIM are significantly improved.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
V. Thilak, D.G. Voelz, C.D. Creusere, Polarization-based index of refraction and reflection angle estimation for remote sensing applications. Appl. Opt. 46(30), 7527–7536 (2007)
F. Cremer, W. De Jong, K. Schutte, Infrared polarization measurements and modelling applied to surface laid anti-personnel landmines. Opt. Eng. 41(5), 1021–1032 (2002)
N. Yadav, W. Wang, K. Ullah, X. Liu, Polarization parametric indirect microscopic imaging for patterned device line edge inspection. Appl. Phys. B 124(8), 1–8 (2018)
J. Wang, L. Dong, H. Chen, S. Huang, Birefringence measurement of biological tissue based on polarization-sensitive digital holographic microscopy. Appl. Phys. B 124(12), 1–9 (2018)
S. Wen, Y. Zheng, F. Lu, Q. Zhao, Convolutional demosaicing network for joint chromatic and polarimetric imagery. Opt. Lett. 44(22), 5646–5649 (2019)
W.A. Woźniak, P. Kurzynowski, S. Drobczyński, Adjustment method of an imaging stokes polarimeter based on liquid crystal variable retarders. Appl. Opt. 50(2), 203–212 (2011)
J. Zhang, C. Yuan, G. Huang, Y. Zhao, W. Ren, Q. Cao, J. Li, M. Jin, Acquisition of a full-resolution image and aliasing reduction for a spatially modulated imaging polarimeter with two snapshots. Appl. Opt. 57(10), 2376–2382 (2018)
L. Tong, X. Huang, P. Wang, L. Ye, M. Peng, L. An, Q. Sun, Y. Zhang, G. Yang, Z. Li et al., Stable mid-infrared polarization imaging based on quasi-2d tellurium at room temperature. Nat. Commun. 11(1), 1–10 (2020)
V. Durán, P. Clemente, M. Fernández-Alonso, E. Tajahuerce, J. Lancis, Single-pixel polarimetric imaging. Opt. Lett. 37(5), 824–826 (2012)
W. Treimer, R. Köhler, Determination of the spatial resolution in the case of imaging magnetic fields by polarized neutrons. Appl. Sci. 11(15), 6973 (2021)
K. Jiang, Z. Wang, P. Yi, J. Jiang, A progressively enhanced network for video satellite imagery superresolution. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 25(11), 1630–1634 (2018)
K. Zhang, W. Zuo, L. Zhang, Deep plug-and-play super-resolution for arbitrary blur kernels. In: Proc. IEEE/CVF Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., pp. 1671–1681 (2019)
Q. Xie, M. Zhou, Q. Zhao, D. Meng, W. Zuo, Z. Xu, Multispectral and hyperspectral image fusion by ms/hs fusion net. In: Proc. IEEE/CVF Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., pp. 1585–1594 (2019)
W. Wang, W. Zeng, Y. Huang, X. Ding, J. Paisley, Deep blind hyperspectral image fusion. In: Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Comput. Vis., pp. 4150–4159 (2019)
Y. Hu, J. Li, Y. Huang, X. Gao, Channel-wise and spatial feature modulation network for single image super-resolution. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 30(11), 3911–3927 (2019)
Z. Wang, J. Chen, S.C. Hoi, Deep learning for image super-resolution: a survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 43(10), 3365–3387 (2020)
Y. LeCun, Y. Bengio, G. Hinton, Deep learning. Nature 521(7553), 436–444 (2015)
D. Yuan, N. Fan, Z. He, Learning target-focusing convolutional regression model for visual object tracking. Knowl. Based Syst. 194, 105526 (2020)
W. Zhang, Y. Liu, C. Dong, Y. Qiao, Ranksrgan: Generative adversarial networks with ranker for image super-resolution. In: IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., pp. 3096–3105 (2019)
Z. Pan, W. Ma, J. Guo, B. Lei, Super-resolution of single remote sensing image based on residual dense backprojection networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 57(10), 7918–7933 (2019)
Y. Chen, H. Jiang, C. Li, X. Jia, P. Ghamisi, Deep feature extraction and classification of hyperspectral images based on convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 54(10), 6232–6251 (2016)
X. Hu, H. Mu, X. Zhang, Z. Wang, T. Tan, J. Sun, Meta-sr: A magnification-arbitrary network for super-resolution. In: Proc. IEEE/CVF Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., pp. 1575–1584 (2019)
J. Kim, J.K. Lee, K.M. Lee, Accurate image super-resolution using very deep convolutional networks. In: Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., pp. 1646–1654 (2016)
J.M. Haut, R. Fernandez-Beltran, M.E. Paoletti, J. Plaza, A. Plaza, F. Pla, A new deep generative network for unsupervised remote sensing single-image super-resolution. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 56(11), 6792–6810 (2018)
C. Dong, C.C. Loy, K. He, X. Tang, Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 38(2), 295–307 (2015)
C. Dong, C.C. Loy, X. Tang, Accelerating the super-resolution convolutional neural network. In: Proc. Comput. Vis.-ECCV, pp. 391–407 (2016)
J. Hu, L. Shen, G. Sun, Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: Proc. IEEE/CVF Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., pp. 7132–7141 (2018)
B. Lim, S. Son, H. Kim, S. Nah, K. Mu Lee, Enhanced deep residual networks for single image super-resolution. In: Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. Workshops, pp. 136–144 (2017)
Y. Zhang, Y. Tian, Y. Kong, B. Zhong, Y. Fu, Residual dense network for image super-resolution. In: Proc. IEEE/CVF Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., pp. 2472–2481 (2018)
J. Liu, W. Zhang, Y. Tang, J. Tang, G. Wu, Residual feature aggregation network for image super-resolution. In: Proc. IEEE/CVF Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., pp. 2359–2368 (2020)
Z. Li, C. Wang, J. Wang, S. Ying, J. Shi, Lightweight adaptive weighted network for single image super-resolution. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 211, 103254 (2021)
K.I. Kim, Y. Kwon, Single-image super-resolution using sparse regression and natural image prior. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 32(6), 1127–1133 (2010)
S. Dai, M. Han, W. Xu, Y. Wu, Y. Gong, A.K. Katsaggelos, Softcuts: a soft edge smoothness prior for color image super-resolution. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 18(5), 969–981 (2009)
Q. Yuan, Y. Wei, X. Meng, H. Shen, L. Zhang, A multiscale and multidepth convolutional neural network for remote sensing imagery pan-sharpening. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 11(3), 978–989 (2018)
W. Shi, J. Caballero, F. Huszár, J. Totz, A.P. Aitken, R. Bishop, D. Rueckert, Z. Wang, Real-time single image and video super-resolution using an efficient sub-pixel convolutional neural network. In: Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., pp. 1874–1883 (2016)
J. Kim, J.K. Lee, K.M. Lee, Deeply-recursive convolutional network for image super-resolution. In: Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., pp. 1637–1645 (2016)
Y. Tai, J. Yang, X. Liu, Image super-resolution via deep recursive residual network. In: Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., pp. 3147–3155 (2017)
W.-S. Lai, J.-B. Huang, N. Ahuja, M.-H. Yang, Deep laplacian pyramid networks for fast and accurate super-resolution. In: Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., pp. 624–632 (2017)
W. Han, S. Chang, D. Liu, M. Yu, M. Witbrock, T.S. Huang, Image super-resolution via dual-state recurrent networks. In: Proc. IEEE/CVF Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., pp. 1654–1663 (2018)
N. Ahn, B. Kang, K.-A. Sohn, Fast, accurate, and lightweight super-resolution with cascading residual network. In: Proc. Comput. Vis.-ECCV, pp. 252–268 (2018)
Z. Hui, X. Wang, X. Gao, Fast and accurate single image super-resolution via information distillation network. In: Proc. IEEE/CVF Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., pp. 723–731 (2018)
B. Zoph, V. Vasudevan, J. Shlens, Q.V. Le, Learning transferable architectures for scalable image recognition. In: Proc. IEEE/CVF Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., pp. 8697–8710 (2018)
X. Chu, B. Zhang, R. Xu, Multi-objective reinforced evolution in mobile neural architecture search. In: Proc. Comput. Vis.-ECCV, pp. 99–113 (2020)
X. Chu, B. Zhang, H. Ma, R. Xu, Q. Li, Fast, accurate and lightweight super-resolution with neural architecture search. In: Proc. 25th Int. Conf. Pattern Recognit., pp. 59–64 (2021)
C. Szegedy, W. Liu, Y. Jia, P. Sermanet, S. Reed, D. Anguelov, D. Erhan, V. Vanhoucke, A. Rabinovich, Going deeper with convolutions. In: Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., pp. 1–9 (2015)
S.-H. Gao, M.-M. Cheng, K. Zhao, X.-Y. Zhang, M.-H. Yang, P. Torr, Res2net: a new multi-scale backbone architecture. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 43(2), 652–662 (2019)
Y. Wang, X. Tao, X. Qi, X. Shen, J. Jia, Proc. 32nd int. conf. neural inf. process. syst. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 329–338 (2018)
T.R. Shaham, T. Dekel, T. Michaeli, Singan: Learning a generative model from a single natural image. In: Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Comput. Vis., pp. 4570–4580 (2019)
J. Li, F. Fang, K. Mei, G. Zhang, Multi-scale residual network for image super-resolution. In: Proc. Comput. Vis.-ECCV, pp. 517–532 (2018)
J.M. Haut, R. Fernandez-Beltran, M.E. Paoletti, J. Plaza, A. Plaza, Remote sensing image superresolution using deep residual channel attention. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 57(11), 9277–9289 (2019)
L. Wang, Y. Wang, Z. Liang, Z. Lin, Y. Guo, Learning parallax attention for stereo image super-resolution. In: Proc. IEEE/CVF Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., pp. 12242–12251 (2019)
A. Muqeet, M.T.B. Iqbal, S.-H. Bae, Hran: hybrid residual attention network for single image super-resolution. IEEE Access 7, 137020–137029 (2019)
W. Ren, J. Pan, H. Zhang, X. Cao, M.-H. Yang, Single image dehazing via multi-scale convolutional neural networks with holistic edges. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 128(1), 240–259 (2020)
H. Shen, Towards a mathematical understanding of the difficulty in learning with feedforward neural networks. In: Proc. IEEE/CVF Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., pp. 811–820 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 61906118 and Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province under Grant Nos. 1908085MF208 and 2108085MF230; Key Project of Natural Science Research in Colleges and Universities of Anhui Province (No. KJ2019A0906), and the Major Special Science and Technology Project of Anhui Province (No.202003A06020016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, G., Wang, J., Zhang, L. et al. Multi-scale adaptive weighted network for polarization computational imaging super-resolution. Appl. Phys. B 128, 200 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-022-07900-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-022-07900-0