Abstract
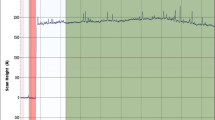
In the present work, gold nanoparticles/indium tin oxide (AuNPs/ITO) thin films were analyzed for pH sensing application based on extended gate field-effect transistor (EGFET). The AuNPs were synthesized through pulsed laser ablation in liquid (PLAL) technique. Afterwards, the AuNPs were deposited onto ITO thin film by electrospinning method. The AuNPs were characterized using transmission electron microscope (TEM) and UV–Vis spectroscope techniques. From the TEM analysis, the size of the spherical-shaped AuNPs was found to be in the range of 5–22 nm. The UV–Vis spectroscopy analysis revealed absorption peak at 518 nm, indicating purplish red color. The AuNPs/ITO thin films were also characterized using field emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM) and X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) technique. The depth of the films was 6.498 µm and the Au 4f doublet binding energy peaks of the photoelectrons at 83.79 and 87.45 eV. The current–voltage (I-V) curves indicated pH sensitivities values of 43.6 mV/pH and 0.6 μA1/2pH−1 with linear regression of 0.99 and 0.99 for pH voltage and current sensitivities, respectively. The hysteresis and drift characteristics of the prepared films were also done to investigate the stability and reliability of the films. The results of this work demonstrated that the AuNPs/ITO thin film is quite useful for the acidity and basicity detection.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pavlov I, Kaila K, Kullmann DM, Miles R. Cortical inhibition, pH and cell excitability in epilepsy: What are optimal targets for antiepileptic interventions? Vol. 591, J. Physiol. 2013. p. 765–74.
Manjakkal L, Szwagierczak D, Dahiya R. Progress in Materials Science Metal oxides based electrochemical pH sensors : Current progress and future perspectives. Prog. Mater. Sci. [Internet]. 2020;109(May 2019):100635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2019.100635
Jlassi K, Eid K, Sliem MH, Abdullah AM, Chehimi MM, Krupa I. Rational synthesis, characterization, and application of environmentally friendly (polymer–carbon dot) hybrid composite film for fast and efficient UV-assisted Cd2+ removal from water. Environ. Sci. Eur. [Internet]. 2020;32(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12302-020-0292-z
R. Buck, S. Rondinini, A. Covington, F. Baucke, C. Brett, M. Camões et al., Measurement of pH definition, standards, and procedures. Handb Biochem. Mol. Biol. Fourth Ed. 74(11), 675–692 (2010)
LANNA F. Drift and light characteristics of EGFET based on SnO2/ITO sensing gate. J Teknol [Internet]. 2013;1(1):69–73. Available from: https://www.bertelsmann-stiftung.de/fileadmin/files/BSt/Publikationen/GrauePublikationen/MT_Globalization_Report_2018.pdf%0Ahttp://eprints.lse.ac.uk/43447/1/India_globalisation%2C society and inequalities%28lsero%29.pdf%0Ahttps://www.quora.com/What-is-the
S. Liu, X. Guo, Carbon nanomaterials field-effect-transistor-based biosensors. NPG Asia Mater [Internet]. 4(8), e23–e10 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/am.2012.42
J. Jeon, W. Cho, field-effect transistors with multi-gate structure for transparent, flexible, and wearable biosensors. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. [Internet]. 21(1), 371–378 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/14686996.2020.1775477
P.D. Batista, M. Mulato, ZnO extended-gate field-effect transistors as pH sensors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87(14), 1–3 (2005)
Yao P, Chiang J, Lee M. Application of sol e gel TiO 2 fi lm for an extended-gate H þ ion-sensitive fi eld-effect transistor. 2014;28.
P. Sharma, V.S. Bhati, M. Kumar, R. Sharma, R. Mukhiya, K. Awasthi et al., Development of ZnO nanostructure film for pH sensing application. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process [Internet]. 126(4), 1–7 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-03466-w
N.H. Al-Hardan, M.A.A. Hamid, N.M. Ahmed, A. Jalar, R. Shamsudin, N.K. Othman et al., High sensitivity pH sensor based on porous silicon (PSi) extended gate field-effect transistor. Sensors (Switzerland). 16(6), 1–12 (2016)
J.L. Chiang, S.S. Jhan, S.C. Hsieh, A.L. Huang, Hydrogen ion sensors based on indium tin oxide thin film using radio frequency sputtering system. Thin Solid Films [Internet]. 517(17), 4805–4809 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2009.03.050
F.A. Sabah, N.M. Ahmed, Z. Hassan, N.H. Al-Hardan, Sensitivity of CuS and CuS/ITO EGFETs implemented as pH sensors. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 122(9), 1–6 (2016)
Das A, Ko DH, Chen CH, Chang LB, Lai CS, Chu FC, et al. Highly sensitive palladium oxide thin film extended gate FETs as pH sensor. Sensors Actuators, B. Chem. [Internet]. 2014;205:199–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.08.057
Megat Abdul Hedei PH, Alsaee SK, Omar AF, Hashim U, Mohd Kaus NH. Spectral aging of gold and silver nanoparticles synthesized by laser ablation in liquids. J. Nanophotonics. 2019;13(02):1.
M. Rafique, M.S. Rafique, U. Kalsoom, A. Afzal, S.H. Butt, A. Usman, Laser ablation synthesis of silver nanoparticles in water and dependence on laser nature. Opt. Quantum Electron. [Internet]. 51(6), 1–11 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-019-1902-0
Rao M, Ravindranadh K. Insight into Nanotechnology and Applications of Nanomaterials. IjapbcCom [Internet]. 2013;2(1):225–33. http://www.ijapbc.com/files/34-2163.pdf
S. Kutrovskaya, S. Arakelian, A. Kucherik, A. Osipov, A. Evlyukhin, A.V. Kavokin, The synthesis of hybrid gold-silicon nano particles in a liquid. Sci. Rep. [Internet]. 7(1), 3–8 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-09634-y
M. Vinod, R.S. Jayasree, K.G. Gopchandran, Synthesis of pure and biocompatible gold nanoparticles using laser ablation method for SERS and photothermal applications. Curr. Appl. Phys. [Internet]. 17(11), 1430–1438 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2017.08.004
Chanda N, Kan P, Watkinson LD, Shukla R, Zambre A, Carmack TL, et al. Radioactive gold nanoparticles in cancer therapy: therapeutic efficacy studies of GA-198AuNP nanoconstruct in prostate tumor-bearing mice. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. [Internet]. 2010;6(2):201–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2009.11.001
J.P. Sylvestre, S. Poulin, A.V. Kabashin, E. Sacher, M. Meunier, J.H.T. Luong, Surface chemistry of gold nanoparticles produced by laser ablation in aqueous media. J Phys Chem B. 108(43), 16864–16869 (2004)
H.K. Liao, L.L. Chi, J.C. Chou, W.Y. Chung, T.P. Sun, S.K. Hsiung, Study on pHpzc and surface potential of tin oxide gate ISFET. Mater. Chem. Phys. 59(1), 6–11 (1999)
Healy W. Site-binding Model of the Electrical Double Layer at the Oxide / Water Iiiterface. J Chem Soc. 1973;Faraday Tr:1807–18.
A.K. Mishra, D.K. Jarwal, B. Mukherjee, A. Kumar, S. Ratan, S. Jit, CuO nanowire-based extended-gate field-effect-transistor (FET) for pH sensing and enzyme-free/receptor-free glucose sensing applications. IEEE Sens. J. 20(9), 5039–5047 (2020)
Y.-H. Liao, J.-C. Chou, Fabrication and characterization of a ruthenium nitride membrane for electrochemical pH sensors. Sensors. 9(4), 2478–2490 (2009)
F.A. Sabah, N.M. Ahmed, Z. Hassan, M.A. Almessiere, Effect of light on the sensitivity of CuS thin film EGFET implemented as pH sensor. Int. J. Electrochem Sci. 11(6), 4380–4388 (2016)
Mokhtarifar N, Goldschmidtboeing F, Woias P. EGFET Differential Pair with ITO as the Extended-Gate Membrane for pH-Sensing. NEMS 2018—13th Annu. IEEE Int. Conf. Nano/Micro. Eng. Mol. Syst. 2018;60–3.
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the School of Physics (USM) for research assistance and support. The financial support from the RCMO (USM) via the short-term research grant (304/PFIZIK/6315514) is appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alsaee, S.K., Ahmed, N.M., Mzwd, E. et al. pH sensor based on AuNPs/ ITO membrane as extended gate field-effect transistor. Appl. Phys. B 128, 3 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-021-07727-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-021-07727-1