Abstract
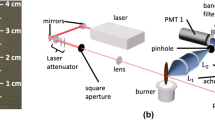
Multimode pulsed Nd:YAG lasers are commonly used in auto-compensating laser-induced incandescence (AC-LII) measurements of soot in flames and engine exhaust as well as black carbon in the atmosphere. Such lasers possess a certain degree of fluence non-uniformity across the laser beam even with the use of beam shaping optics. Recent research showed that the measured volume fraction of ambient-temperature soot using AC-LII increases significantly, by about a factor of 5–8, with increasing the laser fluence in the low-fluence regime from a very low fluence to a relatively high fluence of near sublimation. The causes of this so-called soot volume fraction anomaly are currently not understood. The effects of laser fluence non-uniformity on the measured soot volume fraction using AC-LII were investigated. Three sets of LII experiments were conducted in the exhaust of a MiniCAST soot generator under conditions of high elemental carbon using Nd:YAG lasers operated at 1064 nm. The laser beams were shaped and relay imaged to achieve a relatively uniform fluence distribution in the measurement volume. To further homogenize the laser fluence, one set of LII experiments was conducted by using a diffractive optical element. The measured soot volume fractions in all three sets of LII experiments increase strongly with increasing the laser fluence before a peak value is reached and then start to decrease at higher fluences. Numerical calculations were conducted using the experimental laser fluence histograms. Laser fluence non-uniformity is found partially responsible for the soot volume fraction anomaly, but is insufficient to explain the degree of soot volume fraction anomaly observed experimentally. Representing the laser fluence variations by a histogram derived from high-resolution images of the laser beam energy profile gives a more accurate definition of inhomogeneity than a simple averaged linear profile across the laser beam.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Oberdörster, Z. Sharp, V. Atudorei, A. Elder, R. Gelein, W. Kreyling, C. Cox, Translocation of inhaled ultrafine particles to the brain. Inhal. Toxicol. 16, 437–445 (2004)
M.Z. Jacobson, Strong radiative heating due to the mixing state of black carbon in atmospheric aerosols. Nature 409, 695–697 (2001)
T.C. Bond, S.J. Doherty, D.W. Fahey, P.M. Forster, T. Berntsen et al., Bounding the role of black carbon in the climate system: a scientific assessment. J. Geophys. Res. 118, 5380–5552 (2013)
M. Sato, J. Hansen, D. Koch, A. Lacis, R. Ruedy, O. Dubovik, B. Holben, M. Chin, T. Novakov, Global atmospheric black carbon inferred from AERONET. PNAS 100(11), 6319–6324 (2003)
D. Shindell, J.C.I. Kuylenstiema, E. Vignati, R. van Dingenen, M. Amann et al., Simultaneously mitigating near-term climate change and improving human health and food security. Science 335(13), 183–189 (2012)
C. Schulz, B.F. Kock, M. Hofmann, H. Michelsen, S. Will, B. Bougie, R. Suntz, G. Smallwood, Laser-induced incandescence: recent trends and current questions. Appl. Phys. B 83, 333–354 (2006)
H.A. Michelsen, C. Schulz, G.J. Smallwood, S. Will, Laser-induced incandescence: particulate diagnostics for combustion, atmospheric, and industrial applications. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 51, 2–48 (2015)
S. Will, S. Schraml, A. Leipertz, Two-dimensional soot-particle sizing by time-resolved laser-induced incandescence. Opt. Lett. 20(22), 2342–2344 (1995)
S. Pfadler, F. Beyrau, M. Löffler, A. Leipertz, Application of a beam homogenizer to planar laser diagnostics. Opt. Express 14(22), 10171–10180 (2006)
M.A. Dansson, M. Boisselle, M.A. Linne, H.A. Michelsen, Complications to optical measurements using a laser with an unstable resonator: a case study on laser-induced incandescence of soot. Appl. Opt. 46(33), 8095–8103 (2007)
D.R. Snelling, G.J. Smallwood, F. Liu, Ö.L. Gülder, W.D. Bachalo, A calibration-independent laser-induced incandescence technique for soot measurement by detecting absolute light intensity. Appl. Opt. 44(31), 6773–6785 (2005)
S. De Iuliis, F. Cignoli, G. Zizak, Two-color laser-induced incandescence (2C-LII) technique for absolute soot volume fraction measurement in flames. Appl. Opt. 44(34), 7414–7423 (2005)
A.R. Coderre, K.A. Thomson, D.R. Snelling, M.R. Johnson, Spectrally resolved light absorption properties of cooled soot from a methane flame. Appl. Phys. B 104, 175–188 (2011)
B.M. Crosland, M.R. Johnson, K.A. Thomson, Analysis of uncertainties in instantaneous soot volume fraction measurement using two-dimensional, auto-compensating, laser-induced incandescence (2D-AC-LII). Appl. Phys. B 102, 173–183 (2011)
G.J. Smallwood, A critique of laser-induced incandescence for the measurement of soot, Ph.D Thesis, Department of Automotive Engineering, School of Engineering (Cranfield University, 2008)
F. Migliorini, S. De Iuliis, S. Maffi, G. Zizak, Saturation curves of two-color laser-induced incandescence measurements for the investigation of soot optical properties. Appl. Phys. B 120, 417–427 (2015)
M. Saffaripour, K.-P. Geigle, D.R. Snelling, G.J. Smallwood, K.A. Thomson, Influence of rapid laser heating on the optical properties of in-flame soot. Appl. Phys. B 119, 621–642 (2015)
F. Liu, M. Yang, F.A. Hill, D.R. Snelling, G.J. Smallwood, Influence of polydisperse distributions of both primary particle and aggregate size on soot temperature in low-fluence LII. Appl. Phys. B 83, 383–395 (2006)
L. Jing, Standard combustion aerosol generator for calibration purposes. in 3rd ETH conference on combustion generated nanoparticles, Zurich, 9–10 Aug 1999. http://sootgenerator.com/documents/Pub-ETH-Workshop1999_Ji.pdf
M. Gysel, M. Laborde, A.A. Mensah, J.C. Corbin, A. Keller, J. Kim, A. Petzold, B. Sierau, The single particle soot photometer fails to reliably detect PALAS soot nanoparticles. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 5, 3099–3107 (2012)
A. Mamakos, I. Khalek, R. Giannelli, M. Spears, Characterization of combustion aerosol produced by a mini-CAST and treated in a catalytic stripper. Aerosol Sci. Tech. 47, 927–936 (2013)
B. Giechaskiel, M. Cresnoverh, H. Jorgl, A. Bergmann, Calibration and accuracy of a particle number measurement system. Meas. Sci. Technol. 21, 1–13 (2010)
R.H. Moore, L.D. Ziemba, D. Dutcher, A.J. Beyersdorf, K. Chan, S. Crumeyrolle, T.M. Raymond, K.L. Thornhill, E.L. Winstead, B.E. Anderson, Mapping the operation of the miniature combustion aerosol standard (Mini-CAST) soot generator. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 48, 467–479 (2014)
A.V. Filippov, D.E. Rosner, Energy transfer between an aerosol particle and gas at high temperature ratios in the Knudsen transition regime. Int. J. Hear Mass Transf. 43, 127–138 (2000)
F. Liu, K.J. Daun, D.R. Snelling, G.J. Smallwood, Heat conduction from a spherical nano-particle: status of modeling heat conduction in laser-induced incandescence. Appl. Phys. B 83, 355–382 (2006)
D.R. Snelling, F. Liu, G.J. Smallwood, Ö.L. Gülder, Determination of the soot absorption function and thermal accommodation coefficient using low-fluence LII in a laminar coflow ethylene diffusion flame. Combust. Flame 136, 180–190 (2004)
G.J. Smallwood, D.R. Snelling, F. Liu, Ö.L. Gülder, Clouds over soot evaporation: errors in modeling laser-induced incandescence of soot. ASME J. Heat Transf. 123, 814–818 (2001)
F. Liu, G.J. Smallwood, D.R. Snelling, Effects of primary particle diameter and aggregate size distribution on the temperature of soot particles heated by pulsed lasers. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 93, 301–312 (2005)
H. Bladh, J. Johnsson, P.-E. Bengtsson, Influence of spatial laser energy distribution on evaluated soot particle sizes using two-color laser-induced incandescence in a flat premixed ethylene/air flame. Appl. Phys. B 96, 645–656 (2009)
Acknowledgements
The financial support by NRCan PERD AFTER Project C23.006 is greatly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, F., Rogak, S., Snelling, D.R. et al. Effects of laser fluence non-uniformity on ambient-temperature soot measurements using the auto-compensating laser-induced incandescence technique. Appl. Phys. B 122, 286 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-016-6553-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-016-6553-2