Abstract
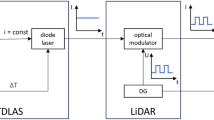
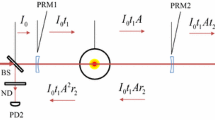
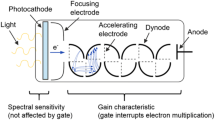
A novel concept for remote in situ detection of soot emissions by a combination of laser-induced incandescence (LII) and light detection and ranging (lidar) is presented. A lidar setup based on a picosecond Nd:YAG laser and time-resolved signal detection in the backward direction was used for LII measurements in sooty premixed ethylene–air flames. Measurements of LII–lidar signal versus laser fluence and flame equivalence ratio showed good qualitative agreement with data reported in literature. The LII–lidar signal showed a decay consisting of two components, with lifetimes of typically 20 and 70 ns, attributed to soot sublimation and conductive cooling, respectively. Theoretical considerations and analysis of the LII–lidar signal showed that the derivative was proportional to the maximum value, which is an established measure of soot volume fraction. Utilizing this, differentiation of LII–lidar data gave profiles representing soot volume fraction with a range resolution of ~16 cm along the laser beam propagation axis. The accuracy of the evaluated LII-profiles was confirmed by comparison with LII-data measured simultaneously employing conventional right-angle detection. Thus, LII–lidar provides range-resolved single-ended detection, resourceful when optical access is restricted, extending the LII technique and opening up new possibilities for laser-based diagnostics of soot and other carbonaceous particles.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Bockhorn, Soot Formation in Combustion—Mechanisms and Models (Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 1994), p. 606
A. D’Anna, Proc. Combust. Inst. 32, 593 (2009)
G. Shrestha, S.J. Traina, C.W. Swanston, Sustainability 2, 294 (2010)
B. Nowack, T.D. Bucheli, Environ. Pollut. 150(1), 5 (2007)
P.H. McMurry, Atmos. Environ. 34(12–14), 1959 (2000)
H. Moosmuller, R.K. Chakrabarty, W.P. Arnott, J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. 110(11), 844 (2009)
C. Schulz, B.F. Kock, M. Hofmann, H. Michelsen, S. Will, B. Bougie, R. Suntz, G. Smallwood, Appl. Phys. B 83, 333 (2006)
R.J. Santoro, C.R. Shaddix, in Applied Combustion Diagnostics, ed. by K. Kohse-Köinghaus, J.B. Jeffries (Taylor & Francis, London, 2002), pp. 252–286
L.A. Melton, Appl. Opt. 23, 2201 (1984)
H. Bladh, J. Johnsson, P.-E. Bengtsson, Appl. Phys. B 90, 109 (2008)
H. Bladh, P.-E. Bengtsson, J. Delhay, Y. Bouvier, E. Therssen, P. Desgroux, Appl. Phys. B 83, 423 (2006)
J.D. Black, Laser-induced Incandescence Measurements of Particles in Aero-Engine Exhausts, EOS/SPIE Meeting, Munich, June 14–18, Paper 3821-38 (1999)
K. Schäfer, J. Heland, D.H. Lister, C.W. Wilson, R.J. Howes, R.S. Falk, E. Lindermeir, M. Birk, G. Wagner, P. Haschberger, M. Bernard, O. Legras, P. Wiesen, R. Kurtenbach, K.J. Brockkmann, V. Kriesche, M. Hilton, G. Bishop, R. Clarke, J. Workman, M. Caola, R. Geatches, R. Burrows, J.D. Black, P. Hervé, J. Vally, Appl. Opt. 39, 441 (2000)
J. Delhay, P. Desgroux, E. Therssen, H. Bladh, P.-E. Bengtsson, H. Hönen, J.D. Black, I. Vallet, Appl. Phys. B 95, 825 (2009)
T.P. Jenkins, J.L. Bartholomew, P.A. DeBarber, P. Yang, J.M. Seitzman, R.P. Howard, AIAA, Paper 2002-3736 (2002)
C. Weitkamp (ed.), Lidar Range-Resolved Optical Remote Sensing of the Atmosphere (Springer, Berlin, 2005)
T. Fujii, T. Fukuchi (eds.), Laser Remote Sensing (Taylor & Francis, London, 2005)
B. Kaldvee, A. Ehn, J. Bood, M. Aldén, Appl. Opt. 48, B65 (2009)
B. Kaldvee, J. Bood, M. Aldén, Meas. Sci. Technol. 22, 125302 (2011)
D.J. Bradley, B. Liddy, W.E. Sleat, Opt. Commun. 2, 391 (1971)
M.Ya. Schelev, M.C. Richardson, A.J. Alcock, Appl. Phys. Lett. 18, 354 (1971)
H.A. Michelsen, J. Chem. Phys. 118, 7012 (2003)
H.A. Michelsen, Appl. Phys. B 83, 443 (2006)
R. Hadef, K.P. Geigle, W. Meier, M. Aigner, Int. J. Therm. Sci. 49, 1457 (2010)
S. Maffi, S. De Iuliis, F. Cignoli, G. Zizak, Appl. Phys. B 104(2), 357 (2011)
B. Kaldvee, C. Brackmann, J. Bood, M. Aldén, Opt. Express 20, 20688 (2012)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Centre of Combustion Science and Technology (CECOST) and the European Research Council Advanced Grant DALDECS for financial support. Moreover, Henrik Bladh, Per-Erik Bengtsson, and Jonathan Jonsson should be acknowledged for their input when planning the experiments and their valuable and helpful information regarding LII reference work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaldvee, B., Brackmann, C., Aldén, M. et al. LII–lidar: range-resolved backward picosecond laser-induced incandescence. Appl. Phys. B 115, 111–121 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-013-5581-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-013-5581-4