Abstract
Temporally resolved observation of microscopic structural dynamics of solids with ultrafast electron diffraction (UED) requires extremely short pulsed, highly charged, monoenergetic electron beams with sufficient transverse coherence length of several unit cells of the investigated samples. However, Coulomb repulsion defeats these parameters in free propagation of an electron pulse initially bright on the photo cathode. We demonstrate a new electron pulse compressor design based on a simple and compact RF structure incorporating a pair of gallium arsenide photoconductive semiconductor switches that are triggered by femtosecond laser pulses, thereby providing a longitudinal voltage gradient of up to 20 V/ps. Our proof of principle experiment achieved compression of bunches containing 26,000 electrons to a duration of below 750 fs and a beam diameter of 300 μm in the temporal and spatial focus of the device while maintaining the good beam collimation required for time resolved electron diffraction experiments. The simplicity of the compressor provides a strong incentive for its further development toward practical implementation in sub-relativistic UED experiments requiring the highest possible source brightness.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Eichberger, H. Schäfer, M. Krumova, M. Beyer, J. Demsar, H. Berger, G. Moriena, G. Sciaini, R.J.D. Miller, Snapshots of cooperative atomic motions in the optical suppression of charge density waves. Nature 468, 799–802 (2010)
E. Möhr-Vorobeva, S. Johnson, P. Beaud, U. Staub, R. De Souza, C. Milne, G. Ingold, J. Demsar, H. Schaefer, A. Titov, Nonthermal melting of a charge density wave in TiSe2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 117(036403), 1–4 (2011)
M. Woerner, F. Zamponi, Z. Ansari, J. Dreyer, B. Freyer, M. Prémont-Schwarz, T. Elsaesser, Concerted electron and proton transfer in ionic crystals mapped by femtosecond X-ray powder diffraction. J. Chem. Phys. 133, 064509 (2010)
K. Sokolowski-Tinten, C. Blome, J. Blums, A. Cavalleri, C. Dietrich, A. Tarasevitch, I. Uschmann, E. Förster, M. Kammler, M. Horn- von Hoegen, D. von der Linde, Femtosecond X-ray measurement of coherent lattice vibrations near the Lindemann stability limit. Nature 422, 287–289 (2003)
A. Morak, T. Kämpfer, I. Uschmann, A. Lübcke, E. Förster, R. Sauerbrey, Acoustic phonons in InSb probed by time-resolved X-ray diffraction. Phys. Status Solidi B 12, 2728–2744 (2006)
C. Reich, P. Gibbon, I.E.F. Uschmann Yield optimization and time structure of femtosecond laser plasma Kα sources, Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 4846–4849 (2000)
M. Hagedorn, J. Kutzner, G. Tsimilis, H. Zacharias, High-repetition-rate hard X-ray generation with sub-milliJoule femtosecond laser pulses. Appl. Phys. B 77, 49–57 (2003)
www.desy.de/~mpyflo/. Accessed 1 Apr 2012
B.J. Siwick, R.J.D. Miller, Femtosecond electron diffraction studies of strongly driven structural phase transitions. Chem. Phys. 299, 285 (2004)
C.T. Hebeisen, G. Sciaini, M. Harb, R. Ernstorfer, T. Dartigalongue, S.G. Kruglik, R.J.D. Miller, Grating enhanced ponderomotive scattering for visualization and full characterization of femtosecond electron pulses. Opt. Express 16, 3335 (2008)
B. Siwick, J. Dwyer, R. Jordan, D. Miller, An atomic view of melting using femtosecond electron diffraction. Science 302, 1382–1385 (2003)
H. Park, X. Wang, S. Nie, R. Clinite, J. Cao, Direct and real-time probing of both coherent and thermal lattice motions. Solid State Commun. 136(9–10), 559–563 (2005)
P. Baum, D.-S. Yang, A. Zewail, 4D visualization of transitional structures in phase transformations by electron diffraction. Science 318, 788–792 (2007)
P. Musumeci, J.T. Moody, C.M. Scoby, M.S. Gutierrez, H.A. Bender, N.S. Wilcox, High quality single shot diffraction patterns using ultrashort megaelectronvolt electron beams from a radio frequency photoinjector. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 81, 013306 (2010)
B.J. Siwick, J.R. Dwyer, R.E. Jordan, R.J.D. Miller, Ultrafast electron optics: propagation dynamics of femtosecond electron packets. J. Appl. Phys. 92, 1643 (2002)
T. van Oudheusden, E.F. de Jong, S.B. van der Geer, W.P.E.M. Root, O.J. Luiten, B.J. Siwick, Electron source concept for single-shot sub-100 fs electron diffraction in the 100 keV range. J. Appl. Phys. 102(9), 093501 (2007)
E. Fill, L. Veisz, A. Apolonski, F. Krausz, Sub-fs electron pulses for ultrafast electron diffraction. New J. Phys. 8, 272 (2006)
T. van Oudheusden, P.L.E.M. Pasmans, S.B. van der Geer, M.J. de Loos, M.J. van der Wiel, O.J. Luiten, Compression of subrelativistic space-charge-dominated electron bunches for single-shot femtosecond electron diffraction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105(26), 264801 (2010)
G. Kassier, K. Haupt, N. Erasmus, E. Rohwer, H. Schwoerer, Achromatic reflectron compressor design for bright pulses in femtosecond electron diffraction. J. Appl. Phys. 105, 113111 (2009)
Y. Wang, N. Gedik Electron pulse compression with a practical reflectron design for ultrafast electron diffraction, IEEE J. Sel. Topics Quantum Electron. (2011)
S. Tokita, M. Hashida, S. Inoue, T. Nishoji, K. Otani, S. Sakabe, Single-shot femtosecond electron diffraction with laser-accelerated electrons: experimental demonstration of electron pulse compression. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 215004 (2010)
J. Faure, C. Rechatin, A. Norlin, A. Lifschitz, Y. Glinec, V. Malka, Controlled injection and acceleration of electrons in plasma wakefields by colliding laser pulses. Nature 444, 737–739 (2006)
G. H. Kassier Ultrafast electron diffraction: source development, diffractometer design and pulse characterisation. PhD Thesis, Chapter 6, University of Stellenbosch, Stellenbosch (2010)
A. Janzen, B. Krenzer, O. Heinz, P. Zhou, D. Thien, A. Hanisch, F. Heringdorf, D. von der Linde, M. von Horn Hoegen, A pulsed electron gun for ultrafast electron diffraction at surfaces. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 78, 13906 (2007)
G. Kassier, K. Haupt, N. Erasmus, E. Rohwer, H. von Bergmann, H. Schwoerer, S. Coelho, D. Auret, A compact streak camera for 150 fs time resolved measurement of bright pulses in ultrafast electron diffraction. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 81(105103), 1–5 (2010)
http://laacg1.lanl.gov/laacg/. Accessed 1 Apr 2012
O.J. Luiten, S.B. van der Geer, M.J. de Loos, F.B. Kiewiet, M.J. van der Wiel, Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 94802 (2004)
Acknowledgments
This work is based upon research supported by the South African Research Chair Initiative of the Department of Science and Technology and the National Research Foundation. We would like to thank Paul Papka for his help with the electron current measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix: A formula for pulsed compressor performance
Appendix: A formula for pulsed compressor performance
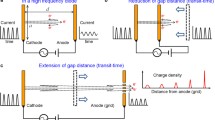
The compressor described in this paper can be approximated by a parallel plate capacitor with a harmonically ramped axial electric field between the plates separated by distance d, complete with apertures for electron pulses to pass through in the axial direction (see figure and Fig. 6.7 in Ref. 23). Subject to the assumption that the electron pulse transit time through the compressor is less than T/3, where T is the oscillation period of the harmonic electric field dependence, the latter can be considered approximately linear. Furthermore, if the electron pulse duration σt is much smaller than T/3, it can be shown that the rms energy spread ΔE k that is imparted on an electron pulse of rms pulse duration σt, is given by [23]
where γ is the Lorentz factor, β = v z/c with v z the electron velocity, and ΔE the electric field difference between the time at which the bunch enters and exits the compressor field respectively. Now, assuming a linear electric field ramp dE/dt such that ΔE = dE/dt × d/v z, using the fact that the voltage gradient dV/dt = dE/dt × d, and re-writing in terms of the relative rms energy spread ΔE k,r = ΔE k/E k, Eq. 1 yields
In the subrelativistic regime, γ/(β2γ2 + 1) varies slowly with energy E k, and consequently the required compressor voltage to achieve a desired ΔE k,r at fixed compressor frequency and injected pulse duration scales roughly linearly with E k.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kassier, G.H., Erasmus, N., Haupt, K. et al. Photo-triggered pulsed cavity compressor for bright electron bunches in ultrafast electron diffraction. Appl. Phys. B 109, 249–257 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-012-5207-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-012-5207-2