Abstract.
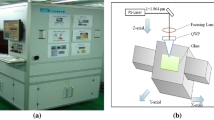
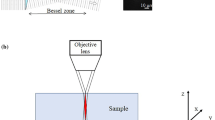
A novel microchannel fabrication technology for quartz using a Q-switched Nd:YAG laser is presented. Complex 3D channel systems inside quartz substrates can be constructed directly using a laser beam by controlled fracturing, and high-quality microchannels can be fabricated by melting quartz using a laser-induced plasma. The behavior of laser-induced plasmas in drilling microchannels is discussed. The diameter of the microchannels can be controlled from 25 to 200 μm. The average roughness of the interior channel wall is less than 0.2 μm. Currently, microchannels longer than 4 mm in fused-quartz cubes can be achieved using laser-induced plasmas.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 15 January 2001 / Accepted: 5 June 2001 / Published online: 30 October 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, SJ., Li, W. Micromachining of complex channel systems in 3D quartz substrates using Q-switched Nd:YAG laser . Appl Phys A 74, 773–777 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003390100943
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003390100943