Abstract.
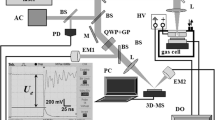
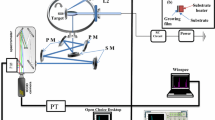
Monitoring the amplitude and the delay of arrival of the pressure waves generated during the interaction of laser pulses with YBCO in air, we can determine the vaporization and the ablation thresholds, the etching rate, the change of the acoustic wave velocity and the effect of plasma shielding on the etching rate. The steep increase of the amplitude and the order-of-magnitude increase of the etching rate above the ablation threshold, suggest that the laser–target coupling mechanism changes from (thermal) vaporization below threshold to a rapid solid-to-gas phase transition. The dumping of the acoustic waves following the ablation with successive laser pulses correlates with the evolution of the YBCO high-Tc superconductor surface morphology, which is known to relate to the deposition rate and the surface morphology of pulsed-laser-deposited high-Tc thin films.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 7 January 2000 / Accepted: 9 October 2000 / Published online: 25 July 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dogas, D., Efthimiopoulos, T., Andreouli, C. et al. Acoustic wave monitoring of the excimer laser ablation of YBCO high-Tc superconductor . Appl Phys A 73, 287–294 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003390100728
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003390100728