Abstract
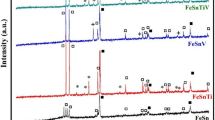
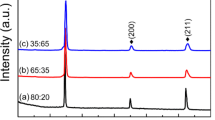
The synthesis of Fe/TiO2 nanocomposite soft magnetic materials, incorporating Cu, Fe2O3, and Cu/Fe2O3;, was achieved using the mechanical alloying technique. Advanced characterization methods, including Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS), X-ray Diffraction (XRD), and Vibrating Sample Magnetometer (VSM), were employed for a comprehensive investigation of structural, morphological, and magnetic properties of the nanocomposite at different synthesis stages. The crystallite size reaches its minimum value, while the lattice strain (ε) attains its maximum value in the FeCu/TiO2 nanocomposite, measuring 26.85 nm and 0.35%, respectively. Coercivity, magnetic remanence, and squareness ratio of Fe/TiO2 showed an upward trend with increasing milling time, reaching peak values after 5 h of milling. The FeTiO2 nanocomposite achieved maximum values for coercivity, magnetic remanence, and saturation magnetization. Notably, the squareness ratio demonstrated notable values for both FeTiO2 and FeCuTiO2.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data related to this study is available within the manuscript.
References
R.J. Álvaro, N.D. Diana, A.M. María, Impedance analysis of TiO2 nanoparticles prepared by green chemical mechanism. Cont. Eng. Sci. 11, 737–744 (2018)
S. Chavali, Murthy, P. Maria, Nikolova, Metal oxide nanoparticles and their applications in nanotechnology. SN Appl. Sci. 1, 607 (2019)
C. Karthikeyan, P. Arunachalam, K. Ramachandran, A.M. Al-Mayouf, S. Karuppuchamy, Recent advances in semiconductor metal oxides with enhanced methods for solar photocatalytic applications. J. Alloys Compd. 828, 154281 (2020)
P. Akhter, A. Arshad, A. Saleem, M. Hussain, Recent development in non-metal-doped titanium dioxide photocatalysts for different dyes degradation and the study of their strategic factors: a review. Catalysts. 12, 1331 (2022)
J. Bai, B. Zhou, Titanium dioxide nanomaterials for sensor applications. Chem. Rev. 114, 10131–10176 (2014)
X. Wu, Applications of titanium dioxide materials. Titanium Dioxide—Advances Appl. (2021)
X. Kang, S. Liu, Z. Dai, Y. He, X. Song, Z. Tan, Titanium dioxide: From engineering to applications, Catalysts 9,191 (2019)
J. Zhang, P. Zhou, J. Liu, J. Yu, New understanding of the difference of photocatalytic activity among anatase, rutile and brookite TiO2. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 16(38), 20382–20386 (2014)
K. Ellmer, R. Mientus, S. Seeger, Metallic oxides (ITO, ZnO, SnO2, TiO2). Transparent Conductive Materials (Materials, Synthesis, Characterization, Applications, 2018), pp. 31–80
M. Nasr, C. Eid, R. Habchi, P. Miele, M. Bechelany, Recent progress on titanium dioxide nanomaterials for photocatalytic applications. Chem. Sus Chem. 11, 3023–3047 (2018)
I. Mironyuk, T. Tatarchuk, M. Naushad, H. Vasylyeva, I. Mykytyn, Highly efficient adsorption of strontium ions by carbonated mesoporous TiO2. J. Mol. Liq. 285, 742–753 (2019)
M.L. Vera, H.D. Traid, A.N. Dwojak, M.R. Rosenberger, and C. E. Schvezov, Advances in nanostructured TiO2coatings for industrial applications (Industrial Applications of Nanoparticles, 2023), pp. 228–255
Z. Zahra, Z. Habib, Exposure route of TiO2 NPs from industrial applications to wastewater treatment and their impacts on the agro-environment. Nanomaterials. 10, 1469 (2020)
L.M. Anaya-Esparza, Z. Villagrán-de la, J.M. Mora, T. Romero-Toledo, S. Sandoval-Contreras, Aguilera-Aguirre, Pérez-Larios, Use of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles as reinforcement agent of polysaccharide-based materials. Processes. 8, 1395 (2020)
Q. Meng, T. Wang, E. Liu, X. Ma, Q. Ge, J. Gong, Understanding electronic and optical properties of anatase TiO2 photocatalysts co-doped with nitrogen and transition metals. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 15, 9549–9561 (2013)
A. Potbhare, P. Bhilkar, S. Yerpude, R. Madankar, S. Shingda, R. Adhikari, R. Chaudhary, Nanomaterials as Photocatalyst. Appl. Emerg. Nanomater Nanotechnol. 148, 304–333 (2023)
A. Chanda, K. Rout, M. Vasundhara, S.R. Joshi, J. Singh, Structural and magnetic study of undoped and cobalt doped TiO2 nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 8(20), 10939–10947 (2018)
E.T. Mombeshora, E. Muchuweni, M.L. Davies, V.O. Nyamori, B.S. Martincigh, Metal-organic chemical vapor deposition of Anatase Titania on multiwalled carbon nanotubes for electrochemical capacitors. Energy Sci. Eng. 10, 3493–3506 (2022)
O. Avciata, Y. Benli, S. Gorduk, O. Koyun, Ag doped TiO2 nanoparticles prepared by hydrothermal method and coating of the nanoparticles on the ceramic pellets for photocatalytic study: surface properties and photoactivity. J. Eng. Technol. Appl. Sci. 1(1), 34–50 (2016)
Y. Kissoum, D.E. Mekki, M. Bououdina, E. Sakher, S. Bellucci, Dependence of Fe doping and milling on TiO2 phase transformation: optical and magnetic studies. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 33, 427–440 (2020)
N. Nasralla, M. Yeganeh, Y. Astuti, S. Piticharoenphun, N. Shahtahmasebi, A. Kompanyb, M. Karimipour, B.G. Mendisd, N.R.J. Pooltone, L. Šiller, Structural and spectroscopic study of Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles prepared by sol–gel method. Scientia Iranica F. 20(3), 1018–1022 (2013)
B. Prajapati, S. Kumar, M. Kumar, S. Chatterjee, A.K. Ghosh, Investigation of the physical properties of Fe: TiO2-diluted magnetic semiconductor nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. C 5, 4257–4267 (2017)
T. Ali, P. Tripathi, A. Azam, W. Raza, A.S. Ahmed, A. Ahmed, M. Muneer, Photocatalytic performance of Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles under visible-light irradiation. Mater. Res. Express. 4, 015022 (2017)
T. Ahmad, S. Khatoon, R. Phul, A review on chemical synthesis, characterization and optical properties of nanocrystalline transition metal doped dilute magnetic semiconductors. Solid State Phenom. 201, 103–129 (2013)
A.N. Andriotis, M. Menon, Codoping induced enhanced ferromagnetism in diluted magnetic semiconductors. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter. 33, 393002 (2021)
H. Zhang, X. Ouyang, B. Yang, R. Lutes, Y. Ni, Synergistic effect of La and Co co-doping on room-temperature ferromagnetism enhancement of TiO2 nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 44, 6362–6369 (2018)
D. Kumar, P. Mandal, A. Singh, C. Pant, S. Sharma, Synthesis and characterization of Ni incorporated titanium dioxide thin films. J. Mater. Res. 33, 4165–4172 (2018)
O. Adedokun, P. Sivaprakash, A.S. Ajani, I.T. Bello, S. Arumugam, Structural, optical and magnetic studies of sol-gel synthesized Mg-doped pure anatase TiO2 nanoparticles for spintronic and optoelectronics applications. Phys. B: Condens. Matter. 667, 415199 (2023)
S. Zhang, Z. Zhou, R. Xiong, J. Shi, Z. Lu, H. Wang, The origin of ferromagnetism of co-doped TiO2 nanoparticles: experiments and theory investigation. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 30(32n33), 1650296 (2016)
Q. Wang, X. Liu, X. Wei, J. Dai, W. Li, Ferromagnetic property of co and Ni doped TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Nanomater. 1–5 (2015), Article ID 371582
N. Nithyaa, N.V. Jaya, Structural, optical, and magnetic properties of Gd-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Supercond Nov Magn. 31, 4117–4126 (2018)
S. Ahadi, N.S. Moalej, S. Sheibani, Characteristics and photocatalytic behavior of Fe and Cu doped TiO2 prepared by combined sol-gel and mechanical alloying. Solid State Sci. 96, 105975 (2019)
C. Suryanarayana, Mechanical alloying: a novel technique to synthesize advanced materials, Research 2019, 1–17 (2019), Article ID 4219812, https://doi.org/10.34133/2019/4219812
A. Dutta, N. Gayathri, R. Ranganathan, R., Effect of particle size on the magnetic and transport properties of La0.875Sr0.125MnO3. Phys. Rev. B 68, 054432 – Published 29 August 2003. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.68.054432
W. Su, G. He, X. Bao, C. He, Y. Li, L. Zhang, Y. Zhang, J. Liu, J. Chen, J. Chen, Y. Bai, S. Zhao, The practical doping principles of tuning antiferromagnetic state in BiMn2O5 ceramics. Appl. Phys. A 129, 108 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-06390-x
F. Scarpelli, T.F. Mastropietro, T. Poerio, N. Godbert, Mesoporous TiO2 thin films: state of the art, Titanium Dioxide-Material for a sustainable environment 508, 135–142 (2018)
K. Ashok Kumar, K. Subalakshmi, J. Senthilselvan, Effect of mixed valence state of titanium on reduced recombination for natural dye-sensitized solar cell applications. J. Solid State Electrochem. 20, 1921–1932 (2016)
A. Younes, M. Khorchef, A. Bouamer, H. Amar, Magnetic and structural behavior of Fe-CoO nanocomposites mechanically milled. Mater. Sci. Eng. 557, 1–12 (2019)
A. Younes, N. Kherrouba, Eddy current and magnetic evaluation of nanostructured iron–cobalt produced by ball-milling. Emerg. Mater. Res. 11(2), 268–275 (2022)
M. Cernea, M. Secu, C.E. Secu, M. Baibarac, B.S. Vasile, Structural and thermoluminescence properties of undoped and Fe-doped-TiO2 nanopowders processed by sol–gel method. J. Nanopart. Res. 13, 77–85 (2011)
S. Cynthia, S. Sagadevan, Physicochemical and magnetic properties of pure and Fe doped TiO2 nanoparticles synthesized by sol-gel method, Materials Today: Proceedings, 50, 2720–2724 (2022)
H.K. Kim, L.T. Schelhas, S. Keller, J.L. Hockel, S.H. Tolbert, G.P. Carman, Magnetoelectric control of superparamagnetism. Nano Lett. 13, 884–888 (2013)
M. Kooti, L. Matouri, Fabrication of nanosized cuprous oxide using fehling’s solution. Scientia Iranica. 17, 73–78 (2010)
D. Cui, Y. Li, K. Pan, J. Liu, Q. Wang, M. Liu, F. Yu, NO hydrogenation to NH3 over FeCu/TiO2 catalyst with improved activity. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng., 1–13 (2023)
H.M. Alghamdi, M.M. Abutalib, A. Rajeh, M.A. Mannaa, O. Nur, E.M. Abdelrazek, Effect of the Fe2O3/TiO2 nanoparticles on the structural, mechanical, electrical properties and antibacterial activity of the biodegradable chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol blend for food packaging. J. Polym. Environ. 30, 3865–3874 (2022)
M. Sołtys-Mróz, K. Syrek, Ł. Pięta, K. Malek, G.D. Sulka, Photoelectrochemical Performance of Nanotubular Fe2O3–TiO2 electrodes under Solar Radiation. Nanomaterials. 12, 1546 (2022)
A. Younes, R. Amraoui, A. Manseri, F. Smaili, The impact of Cu, Ni and Fe2O3 on the magnetic behavior and structural properties of FeSiO2 nanocomposite synthesized through ball milling. Phys. Scr. 98, 115536 (2023)
L. Lin, H. Wang, W. Jiang et al., Comparison study on photocatalytic oxidation of pharmaceuticals by TiO2-Fe and TiO2-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites immobilized on optical fibers. J. Hazard. Mater. 333, 162–168 (2017)
A. Realpe Jimenez, D. Nunez, N. Rojas, Y. Ramirez, M. Acevedo, Effect of Fe–N codoping on the optical properties of TiO2 for use in photoelectrolysis of water. ACS Omega. 6, 4932–4938 (2021)
L. Seid, O. Belgherbi, A. Younes, H. Amar, D. Chouder, Synthesis and characterization of ferromagnetic polyaniline-cobalt chloride composite through in situ oxidative polymerization technique. J. Solid State Electrochem. 27, 2713–2725 (2023)
A.I. Kokorin, R. Amal, W.Y. Teoh, A.I. Kulak, Studies of nanosized iron-doped TiO2 photocatalysts by spectroscopic methods. Appl. Magn. Reson. 48, 447–459 (2017)
S. Sood, A. Umar, S.K. Mehta et al., Highly effective Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles photocatalysts for visible-light driven photocatalytic degradation of toxic organic compounds. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 450, 213–223 (2015)
C. Lemire, S. Bertarione, A. Zecchina, D. Scarano, A. Chaka, S. Shaikhutdinov, H.J. Freund, C. Lemire et al., Ferryl (Fe = O) termination of the Hematite α – Fe2O3. Surf. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94(0001), 166101 (2005)
M.A. Kumar, B. Abebe, H.P. Nagaswarupa, H.A. Murthy, C.R. Ravikumar, F.K. Sabir, Enhanced photocatalytic and electrochemical performance of TiO2-Fe2O3 nanocomposite: its applications in dye decolorization and as supercapacitors. Sci. Rep. 10, 1249 (2020)
C.V. Tran, P.T.H. Nguyen, D.D. Nguyen, H.T. Pham, D.T. Do, D.D. La, Facile fabrication of Fe2O3/TiO2 composite from Titanium Slag as Adsorbent for as (V) removal from aqueous media. Sustainability. 15, 7253 (2023)
E.T. Helmy, U.A. Soliman, A.M. Elbasiony, B.S. Nguyen, CuCe-Ferrite/TiO2 nanocomposite as an efficient magnetically Separable Photocatalyst for Dye pollutants Decolorization. Top. Catal. 66, 53–63 (2023)
T. Raguram, K.S. Rajni, Synthesis and analysing the structural, optical, morphological, photocatalytic and magnetic properties of TiO2 and doped (Ni and Cu) TiO2 nanoparticles by sol–gel technique. Appl. Phys. A 125, 1–11 (2019)
J. Joy, A. Krishnamoorthy, A. Tanna, V. Kamathe, R. Nagar, S. Srinivasan, Recent developments on the synthesis of nanocomposite materials via ball milling approach for energy storage applications. Appl. Sci. 12, 9312 (2022)
M.M. Ahmad, S. Mushtaq, H.S. Al Qahtani, A. Sedky, M.W. Alam, Investigation of TiO2 nanoparticles synthesized by sol-gel method for effectual photodegradation, oxidation and reduction reaction. Crystals. 11, 1456 (2021)
C.R. Shyniya, K.A. Bhabu, T.R. Rajasekaran, Enhanced electrochemical behavior of novel acceptor doped titanium dioxide catalysts for photocatalytic applications. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28, 6959–6970 (2017)
R. Huang, R. Liang, H. Fan, S. Ying, L. Wu, X. Wang, G. Yan, Enhanced photocatalytic fuel denitrification over TiO2/α-Fe2O3 nanocomposites under visible light irradiation. Sci. Rep. 7, 7858 (2017)
R. Wang, X. Wang, X. Xi, R. Hu, G. Jiang, Preparation and photocatalytic activity of magnetic Fe3O4/SiO2/TiO2 composites, Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng.(2012)
X.J. Yang, W.A.N.G. Shu, H.M. Sun, X.B. Wang, J.S. Lian, Preparation and photocatalytic performance of Cu-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China. 25, 504–509 (2015)
X. Bao, J. Wang, X. Wu, C. He, H. Luo, Q. Bai, V. Bao, The symmetry aspect of magnetocaloric effect in LaxBi0.3-xCa0.7MnO3 manganites. Phys. B: Condens. Matter. 671, 415410 (2023)
X. Zhou, X. Li, K. Lu, Size Dependence of Grain Boundary Migration in Metals under Mechanical Loading. Phys. Rev. Lett. 122, 126101 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.122.126101
B. Santara, P.K. Giri, S. Dhara, K. Imakita, M. Fujii, Oxygen vacancy-mediated enhanced ferromagnetism in undoped and fedoped TiO2 nanoribbons. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 47(23), 235304 (2014)
J.O. Carneiro, S. Azevedo, F. Fernandes, E. Freitas, M. Pereira, C.J. Tavares, V. Teixeira, Synthesis of iron-doped TiO2 nanoparticles by ball-milling process: the influence of process parameters on the structural, optical, magnetic, and photocatalytic properties. J. Mater. Sci. 49(21), 7476–7488 (2014)
R. Amade, P. Heitjans, S. Indris, M. Finger, A. Haeger, D. Hesse, Defect formation during high-energy ball milling in TiO2 and its relation to the photocatalytic activity. J. Photochem. Photobiol Chem. 207(2–3), 231–235 (2009)
F. Tolea, M.N. Grecu, V. Kuncser, S.G. Constantinescu, D. Ghica, On the role of Fe ions on magnetic properties of doped TiO2 nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 106(14), 142404 (2015)
S. Bhullar, N. Goyal, S. Gupta, Synthesizing and optimizing Rutile TiO2 nanoparticles for magnetically guided drug delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 3147–3161 (2022)
B. Santara, B. Pal, P.K. Giri, Signature of strong ferromagnetism and optical properties of Co doped TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 110(11), 114322 (2011)
E. Xie, L. Zheng, X. Li, Y. Wang, J. Dou, A. Ding, D. Zhang, One-step synthesis of magnetic-TiO2-nanocomposites with high iron oxide-composing ratio for photocatalysis of rhodamine 6G. Plos One 14, e0221221 (2019)
F. Heidarinejad, H. Kamani, A. Khtibi, Magnetic Fe-doped TiO2@ Fe3O4 for metronidazole degradation in aqueous solutions: characteristics and efficacy assessment. Heliyon 9, (2023)
W. Liu, W. Zhong, Y.W. Du, Magnetic nanoparticles with core/shell structures. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 8(6), 2781–2792 (2008)
A.G. Kolhatkar, A.C. Jamison, D. Litvinov, R.C. Willson, T.R. Lee, Tuning the magnetic properties of nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 14, 15977–16009 (2013)
L. Yang, S. Han, X. Ma, W. Qin, S. Xie, Ferromagnetic mechanism in organic photovoltaic cells with closed-shell structures. Sci. Rep. 7, 8384 (2017)
P. Kuivalainen, J. Sinkkonen, K. Kaski, T. Stubb, Bound magnetic polaron in magnetic semiconductors. Phys. Status Solidi (b). 94(1), 181–190 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1002/pssb.2220940119
F. Ostovari, Coexistence of paramagnetism and ferromagnetism in Fe-TiO2 nanoparticle. Chin. J. Phys. 56(1), 86–90 (2018)
M. Abbas, B. Parvatheeswara Rao, V. Reddy, C. Kim, Fe3O4/TiO2 core/shell nanocubes: single-batch surfactantless synthesis, characterization and efficient catalysts for methylene blue degradation. Ceram. Int. 40, 11177–11186 (2014)
E. Norabadi, A. Jahantiq, H. Kamani, Synthesis of Fe-TiO2@ Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles as a recyclable sonocatalyst for the degradation of 2, 4-dichlorophenol. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30, 31446–31460 (2023)
T.A. Hameed, A.A. Azab, R.S. Ibrahim, K.E. Rady, Optimization, structural, optical and magnetic properties of TiO2/CoFe2O4 nanocomposites. Ceram. Int. 48, 20418–20425 (2022)
H. Zhang, Y. Wang, W. Zhong, B. Long, Y. Wu, Z. Xie, Tailoring the room temperature ferromagnetism in TiO2 nanoparticles by modulating the concentration of surface oxygen vacancy via La incorporating. Ceram. Int. 45(10), 12949–12956 (2019)
J. Sort, S. Suriñach, J.S. Muñoz, M.D. Baró, J. Nogués, G. Chouteau, G.C. Hadjipanayis, Improving the energy product of hard magnetic materials. Phys. Rev. B 65, 174420 (2002)
N. Nishimura, T. Hirai, A. Koganei, T. Ikeda, K. Okano, Y. Sekiguchi, Y. Osada, Magnetic tunnel junction device with perpendicular magnetization films for high-density magnetic random access memory. J. Appl. Phys. 91, 5246–5249 (2002)
N. Rani, B.S. Dehiya, Magnetic core-shell Fe3O4@ TiO2 nanocomposites for broad spectrum antibacterial applications. IET Nanobiotechnol. 15, 301–308 (2021)
Funding
The authors assert that no financial support, grants, or other forms of assistance were obtained during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare the absence of any pertinent financial or non-financial interests that could potentially influence the content disclosed in this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Younes, A., Amraoui, R., Amar, H. et al. Impact of Cu, Fe2O3, and Cu/Fe2O3 on the magnetic and structural characteristics of FeTiO2 nanocomposite synthesized through mechanical alloying processes. Appl. Phys. A 130, 407 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-024-07570-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-024-07570-z