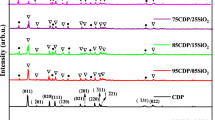
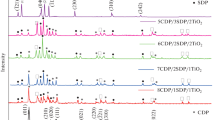
Abstract
This novel research focused on synthesizing a series of new proton conductive electrolytes of CsH2PO4 and CeP2O7 by chemical reaction method, in which phase purity, functional groups, thermal stability, and ionic conductivity were investigated. The composite electrolyte showed improvement in conductivity by about 4 orders of magnitude with oxide ion conduction observed with a value of 4.16 × 10–2 S cm–1. This work provides a comprehensive view of the underlying oxide ion migration mechanism for CsH2PO4 with tetravalent pyrophosphate-based composites. CsH2PO4 and pyrophosphate have gained significant interest as proton conductors for electrolyte application. The crystal growth approach developed here will prove useful for obtaining compounds that are thermodynamically favorable at temperatures close to ambient and the composite electrolytes confirm the practical suitability of the presented material to be used for intermediate-temperature fuel cells.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available upon request to the corresponding author.
References
S. Afroze, M.S. Reza, M.R. Somalu, A.K. Azad, Super–protonic conductors for solid acid fuel cells (SAFCs): a review. Eurasian J. Phys. Funct. Mater. 7, 6–37 (2023). https://doi.org/10.32523/ejpfm.2023070101
A.V. Nikonov, K.A. Kuterbekov, K.Z. Bekmyrza, N.B. Pavzderin, A brief review of conductivity and thermal expansion of perovskite-related oxides for SOFC cathode. Eurasian J. Phys. Funct. Mater. 2, 274–292 (2018). https://doi.org/10.29317/ejpfm.2018020309
G. Shen, J. Liu, H. Bin Wu, P. Xu, F. Liu, C. Tongsh, K. Jiao, J. Li, M. Liu, M. Cai, J.P. Lemmon, G. Soloveichik, H. Li, J. Zhu, Y. Lu, Multi-functional anodes boost the transient power and durability of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Nat. Commun. 11, 1–10 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-14822-y
M.K. Debe, Electrocatalyst approaches and challenges for automotive fuel cells. Nature 486, 43–51 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11115
V.V. Martsinkevich, V.G. Ponomareva, Double salts Cs1- xMxH2PO4 (M = Na, K, Rb) as proton conductors. Solid State Ionics 225, 236–240 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2012.04.016
M.R. Osafi, A. BakhshiAni, M. Kalbasi, Numerical modeling of solid acid fuel cell performance with CsH2PO4- AAM (anodic alumina membrane) composite electrolyte. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 129, 1086–1094 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2018.10.049
D.K. Lim, J. Liu, S.A. Pandey, H. Paik, C.R.I. Chisholm, J.T. Hupp, S.M. Haile, Atomic layer deposition of Pt@CsH2PO4 for the cathodes of solid acid fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 288, 12–19 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2018.07.076
A. Andrio, L.F. Castillo, Temperature dependence of anomalous protonic and superprotonic transport properties in mixed salts based on CsH2PO4. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 21, 12948–12960 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8cp07472k
S. Sanghvi, S.M. Haile, Crystal structure, conductivity, and phase stability of Cs3(H1.5PO4)2 under controlled humidity. Solid State Ionics 349, 115291 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2020.115291
H. Paik, A.V. Berenov, S.J. Skinner, S.M. Haile, Hydrogen oxidation kinetics on platinum-palladium bimetallic thin films for solid acid fuel cells. APL Mater. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5050093
I.N. Bagryantseva, V.G. Ponomareva, N.P. Lazareva, Proton-conductive membranes based on CsH2PO4 and ultra-dispersed polytetrafluoroethylene. Solid State Ionics 329, 61–66 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2018.11.010
B. Singh, H.N. Im, J.Y. Park, S.J. Song, Electrical behavior of CeP2O7 electrolyte for the application in low-temperature proton-conducting ceramic electrolyte fuel cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 159, 819–825 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1149/2.055212jes
L. Mathur, I. Kim, A. Bhardwaj, B. Singh, J. Park, S. Song, Structural and electrical properties of novel phosphate based composite electrolyte for low-temperature fuel cells. Compos Part B. 202, 108405 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2020.108405
B. Singh, J.H. Kim, H.N. Im, S.J. Song, Cerium pyrophosphate-based proton-conducting ceramic electrolytes for low temperature fuel cells. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 51, 248–259 (2014). https://doi.org/10.4191/kcers.2014.51.4.248
B. Singh, S.Y. Jeon, H.N. Im, J.Y. Park, S.J. Song, Electrical conductivity of M2+-doped (M = Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba) cerium pyrophosphate-based composite electrolytes for low-temperature proton conducting electrolyte fuel cells. J. Alloys Compd. 578, 279–285 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.06.017
S.K. Gautam, A. Singh, L. Mathur, N. Devi, R.K. Singh, S.J. Song, D. Henkensmeier, B. Singh, Sintering and electrical behavior of ZrP2O7–CeP2O7 solid solutions Zr1-xCexP2O7; x = 0–0.2 and (Zr0.92Y0.08) 1-yCeyP2O7; y = 0–0.1 for application as electrolyte in intermediate temperature fuel cells. Ionics (Kiel). 25, 155–162 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-018-2563-x
M.V. Le, D.S. Tsai, C.Y. Yang, W.H. Chung, H.Y. Lee, Proton conductors of cerium pyrophosphate for intermediate temperature fuel cell. Electrochim. Acta 56, 6654–6660 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2011.05.040
D. Veer, P. Kumar, D. Singh, R.S. Katiyar, Study of proton mobility and thermal stability of novel orthophosphate-based composite electrolyte for conductivity improvement. Ionics 28, 3357–3366 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-022-04576-6
D. Veer, D. Singh, D. Kumar, P. Kumar, R.S. Katiyar, Structural, thermal, and superprotonic behavior of a new phosphate NaH2PO4⋅2H2O/ZrO2. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 146, 110195 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2022.110195
D. Veer, P. Kumar, D. Singh, D. Kumar, R.S. Katiyar, Conduction and stability performance of CsH2PO4 with NaH2PO4/ZrO2 for fuel cell. Mater. Res. Express 8, 115501 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ac27d0
D. Singh, J. Singh, D. Veer, P. Kumar, R.S. Katiyar, Synergistic effect of SiO2 on proton conduction and thermal behavior for nanocomposite electrolyte CsH2PO4 fuel cells. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 33, 6524–6535 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-07827-4
G.V. Lavrova, V.G. Ponomareva, Intermediate-temperature composite proton electrolyte CsH5(PO4)2/SiO2: transport properties versus oxide characteristic. Solid State Ionics 179, 1170–1173 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2008.01.003
I.N. Bagryantseva, A.A. Gaydamaka, V.G. Ponomareva, Intermediate temperature proton electrolytes based on cesium dihydrogen phosphate and Butvar polymer. Ionics (Kiel). 26, 1813–1818 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-020-03505-9
J. Otomo, N. Minagawa, C.J. Wen, K. Eguchi, H. Takahashi, Protonic conduction of CsH2PO4 and its composite with silica in dry and humid atmospheres. Solid State Ionics 156, 357 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-2738(02)00746-4
X. Huang, Y. Deng, C. Xu, Y. Hu, L. Yang, P. Luo, Y. Lu, J. Cheng, Graphite oxide-incorporated CeP2O7/BPO4 solid composite electrolyte for high-temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Fuel 179, 299–304 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2016.03.089
H. Wang, J. Chen, C. Luo, R. Qiao, Electrical conduction of CeP2O7 and Ce095Yb005P2O7 at intermediate temperatures. Solid State Ionics 263, 71–74 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2014.02.015
P. Kumar, D. Veer, D. Singh, A. Kumar, R.S. Katiyar, Role of cerium pyrophosphate for improving protonic conduction and stabilization of SDP.2H2O composite electrolytes. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 158, 111614 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2023.111614
I.N. Bagryantseva, V.G. Ponomareva, Transport and structural properties of (1-X)CsHSO4-xKH2PO4 mixed compounds. Solid State Ionics 225, 250–254 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2012.02.032
V.G. Ponomareva, I.N. Bagryantseva, The influence of Cs2HPO4·H2O impurity on the proton conductivity and thermal properties of CsH2PO4. Solid State Ionics 329, 90–94 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2018.11.021
N. Mohammad, A.B. Mohamad, A.A.H. Kadhum, K.S. Loh, Effect of silica on the thermal behaviour and ionic conductivity of mixed salt solid acid composites. J. Alloys Compd. 690, 896–902 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.08.188
S. Hosseini, W.R. Wan Daud, M. Badiei, A.A.H. Kadhum, A.B. Mohammad, Effect of surfactants in synthesis of CsH2PO4 as protonic conductive membrane. Bull. Mater. Sci. 34, 759–765 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-011-0192-3
Z. Tao, W. Zhang, Y. Huang, D. Wei, H. Seo, A novel pyrophosphate BaCr2(P2O7)2 as green pigment with high NIR solar reflectance and durable chemical stability. Solid-State Sci 34, 78–84 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2014.05.016
V.G. Ponomareva, G.V. Lavrova, Effect of the excess protons on the electrotansport, structural and thermodynamic properties of CsH2PO4. Solid State Ionics 30, 90–95 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2017.03.026
E. Ortiz, R.A. Vargas, B.E. Mellander, On the high-temperature phase transitions of CsH2PO4: a polymorphic transition? A transition to a superprotonic conducting phase? J. Chem. Phys. 110, 4847–4853 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.478371
D. Veer, P. Kumar, D. Singh, D. Kumar, R.S. Katiyar, A synergistic approach to achieving the high conduction and stability performance of CsH2PO4/NaH2PO4/ZrO2 for fuel cell. Mater. Adv. 3, 409 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ma00612f
T. Anfimova, A.H. Jensen, E. Christensen, J.O. Jensen, N.J. Bjerrum, Q. Li, CsH2PO4/NdPO4 composites as proton conducting electrolytes for intermediate temperature fuel cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 162, 436–441 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0671504jes
X. Sun, S. Wang, Z. Wang, X. Ye, T. Wen, F. Huang, Proton conductivity of CeP2O7 for intermediate temperature fuel cells. Solid State Ionics 179, 1138–1141 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2008.01.046
X. Huang, G. Wang, M. Huang, Y. Deng, M.M. Fei, C. Xu, J. Cheng, Ce3+ doped CeP2O7 ceramic electrolyte for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cell. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 12, 2731–2740 (2017). https://doi.org/10.20964/2017.04.31
B. Singh, N. Devi, L. Mathur, S. Song, A. Kumar, R.K. Singh, M. Ashiq, D.P. Mondal, A new solution phase synthesis of cerium (IV) pyrophosphate compounds of different morphologies using cerium (III) precursor. J. Alloys Compd. 793, 686–694 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.04.221
K.M. White, P.L. Lee, P.J. Chupas, K.W. Chapman, E.A. Payzant, A.C. Jupe, W.A. Bassett, C.S. Zha, A.P. Wilkinson, Synthesis, symmetry, and physical properties of cerium pyrophosphate. Chem. Mater. 20, 3728–3734 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1021/cm702338h
D. Singh, J. Singh, D. Veer, P. Kumar, R.S. Katiyar, Structural, thermal, and transport properties of nanocomposite CsH2PO4/NaH2PO4/TiO2: a novel proton conducting electrolyte for fuel cells. Results Chem. 4, 100262 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rechem.2021.100262
V.G. Ponomareva, E.S. Shutova, K.A. Kovalenko, V.P. Fedin, New type of nanocomposite CsH2PO4-UiO-66 electrolyte with high proton conductivity. Molecules (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238387
D. Singh, J. Singh, D. Veer, P. Kumar, R.S. Katiyar, Influence of NaH2PO4 and TiO2 on the proton conduction and thermal properties of nanocomposite electrolyte CsH2PO4 for fuel cells. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 67, 598–607 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036023622050199
S. Wang, J. Otomo, M. Ogura, C.J. Wen, H. Nagamoto, H. Takahashi, Preparation and characterization of proton-conducting CsHSO4-SiO2 nanocomposite electrolyte membranes. Solid State Ionics 176, 755–760 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2004.10.013
C.E. Botez, I. Martinez, A. Price, H. Martinez, J.H. Leal, Superprotonic CsH2PO4 in dry air. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 129, 324–328 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2019.02.001
Y. Kungurtsev, I. Bagryantseva, V. Ponomareva, Copolymer of VDF/TFE as a promising polymer additive for CsH2PO4-based composite electrolytes. Membranes (Basel) (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13050520
Acknowledgements
We would like to support and thank the Material Science Laboratory, Gurukul Kangri (Deemed to be University) Haridwar, Uttarakhand, India.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Dharm Veer & Deshraj Singh: Conceptualization and experimentation. Pawan Kumar: Writing manuscript and taking correspondence.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, P., Veer, D., Singh, D. et al. A parametric study of crystal structure, phase stability, and conductivity of the novel phosphate-based composite electrolyte. Appl. Phys. A 130, 249 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-024-07414-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-024-07414-w