Abstract
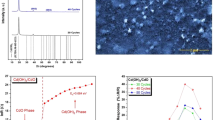
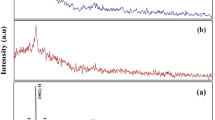
By employing a nebulizer spray pyrolysis approach, thin films of CdS, Al, La, and Al–La co-doped CdS thin films have been effectively formed on glass substrates, and their physical characteristics have been examined. The structural investigations confirmed the hexagonal structure of CdS with a preference for orientation along the (1 0 1) plane. The maximum crystallite size was observed for the Al–La co-doped CdS film compared to other prepared thin films. The granular structure was distributed uniformly for all the films according to FESEM data. To determine the optical characteristics with Al, La, and Al–La co-doping, transmittance was examined and found that the Al–La co-doped CdS thin film exhibit lower transparency due to enhanced light scattering. The energy band-gap value slightly decreased from 1.58 to 1.56 eV for the undoped and co-doped CdS films. The doping causes an enhancement of the emission peaks for doped and co-doped CdS films at ambient temperature, and the gas-sensing performance of both pristine and doped CdS thin films was examined for ammonia (NH3) gas. Doped CdS films were shown to be significantly more sensitive and a higher gas response (1390) to NH3 than pristine CdS thin film. The present study also showed that the co-doping of Al and La with CdS exhibited a faster response and recovery time of (42/21 s) during NH3 gas detection.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data supporting this study's findings are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
P. Dhamodharan, J. Chen, C. Manoharan, Fabrication of In doped ZnO thin films by spray pyrolysis as photoanode in DSSCs. Surf. Interfaces 23, 100965 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2021.100965
A.A. Aboud, A. Mukherjee, N. Revaprasadu, A.N. Mohamed, The effect of Cu-doping on CdS thin films deposited by the spray pyrolysis technique. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 8, 2021–2030 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2018.10.017
A. Fernández-Pérez, C. Navarrete, P. Valenzuela, W. Gacitúa, E. Mosquera, H. Fernández, Characterization of chemically-deposited aluminum-doped CdS thin films with post-deposition thermal annealing. Thin Solid Films 623, 127–134 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2016.12.036
S.T. Navale, A.T. Mane, M.A. Chougule, N.M. Shinde, J. Kim, V.B. Patil, Highly selective and sensitive CdS thin film sensors for detection of NO2 gas. RSC Adv. 4, 44547–44554 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra06531j
K.C. Wilson, M. Basheer Ahamed, Influence of bath temperature on surface modification and optoelectronic properties of chemical bath deposited CdS thin film nanostructures. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid State Mater. Adv. Technol. 251, 114444 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2019.114444
N. Nobari, M. Behboudnia, R. Maleki, Systematics in morphological, structural and optoelectrical properties of nanocrystalline CdS thin films grown by electrodeposition method. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid State Mater. Adv. Technol. 224, 181–189 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2017.08.002
J.I. Contreras-Rascón, J. Diáz-Reyes, A. Flores-Pacheco, L.E. Serrano-De La Rosa, P. Del Ángel Vicente, R. Lozada Morales, M.E. Álvarez Ramos, P. López Salazar, Enhanced photoluminescence effects in nanostructured cubic CdS matrix doped with Cu2+ obtained by chemical Bath deposition. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9, 364–372 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2019.10.065
F.J. Willars-Rodríguez, I.R. Chávez-Urbiola, R. Ramírez-Bon, P. Vorobiev, Y.V. Vorobiev, Effects of aluminum doping in CdS thin films prepared by CBD and the performance on Schottky diodes TCO/CdS:Al/C. J. Alloys Compd. 817, 152740 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.152740
M. Al-Hashem, S. Akbar, P. Morris, Role of oxygen vacancies in nanostructured metal-oxide gas sensors: a review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 301, 126845 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.126845
M.A. Manthrammel, M. Shkir, M. Anis, S.S. Shaikh, H.E. Ali, S. AlFaify, Facile spray pyrolysis fabrication of Al:CdS thin films and their key linear and third order nonlinear optical analysis for optoelectronic applications. Opt. Mater. (Amst) 100, 109696 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2020.109696
R. Bairy, A. Jayarama, G.K. Shivakumar, S.D. Kulkarni, S.R. Maidur, P.S. Patil, Effect of Aluminium doping on photoluminescence and third-order nonlinear optical properties of nanostructured CdS thin films for photonic device applications. Phys. B Condens. Matter 555, 145–151 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2018.11.054
H. Khallaf, G. Chai, O. Lupan, L. Chow, S. Park, A. Schulte, Investigation of aluminium and indium in situ doping of chemical bath deposited CdS thin films. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. (2008). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/41/18/185304
S.J. Ikhmayies, R.N. Ahmad-Bitar, Effects of processing on the electrical and structural properties of spray deposited CdS: In thin films. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 404, 2419–2424 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2009.04.052
H. Khallaf, G. Chai, O. Lupan, L. Chow, S. Park, A. Schulte, Characterization of gallium-doped CdS thin films grown by chemical bath deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 255, 4129–4134 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2008.10.115
L. Saravanan, R. Jayavel, S. Aldeyab, J. Zaidi, K. Ariga, A. Vinu, Synthesis and morphological control of europium doped cadmium sulphide nanocrystals. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 11, 7783–7788 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2011.4728
L. Saravanan, A. Pandurangan, R. Jayavel, Synthesis and luminescence enhancement of Cerium doped CdS nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 66, 343–345 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2011.09.006
Y. Hanifehpour, N. Hamnabard, S. Joo, Sonochemical synthesis, characterization and sonocatalytic performance of terbium-doped CdS nanoparticles. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater.Organomet. Polym. Mater. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-016-0352-4
M.A. Manthrammel, V. Ganesh, M. Shkir, I.S. Yahia, S. Alfaify, Facile synthesis of La-doped CdS nanoparticles by microwave assisted co-precipitation technique for optoelectronic application. Mater. Res. Express. 6, 25022 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aaed9c
Y. Qin, F. Fang, Z. Xie, H. Lin, K. Zhang, X. Yu, K. Chang, La, Al-Co doped SrTiO3 as a photocatalyst in overall water splitting: significant surface engineering effects on defect engineering. ACS Catal.Catal. 11, 11429–11439 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.1c02874
X. Zhu, L. Pei, R. Zhu, Y. Jiao, R. Tang, W. Feng, Preparation and characterization of Sn/La co-doped TiO2 nanomaterials and their phase transformation and photocatalytic activity. Sci. Rep. 8, 1–14 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-30050-3
R.A. Gunasekaran, P.L. Steger, On the effect of Cd doping and Cd-La codoping in YBa2Cu3O7–δ. Mater. Lett. 28, 251–257 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-577X(96)00032-8
R. Sharma, G. Dhyani, S. Ojha, U.C. Srivastava, O.P. Sinha, Study on gas sensing properties of CdS and PVP capped CdS nanoparticles. Mater. Today Proc. 49, 3310–3314 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.01.080
R.Y. Petrus, H.A. Ilchuk, A.I. Kashuba, I.V. Semkiv, E.O. Zmiiovska, Optical-energy properties of CdS thin films obtained by the method of high-frequency magnetron sputtering. Opt. Spectrosc. 126, 220–225 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0030400X19030160
S.A.-J. Jassim, A.A.R.A. Zumaila, G.A.A. Al Waly, Influence of substrate temperature on the structural, optical and electrical properties of CdS thin films deposited by thermal evaporation. Results Phys. 3, 173–178 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2013.08.003
M.F. Rahman, J. Hossain, A.B.M. Ismail, Structural, surface morphological and optical properties and their correlation with the thickness of spin coated superior quality CdS thin film synthesized using a novel chemical route. SN Appl. Sci. 2, 1956 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-03836-2
S.A. Vanalakar, V.L. Patil, S.M. Patil, S.P. Deshmukh, P.S. Patil, J.H. Kim, Chemical and gas sensing property tuning of cadmium sulfide thin films. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 282, 115787 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2022.115787
K. Veerathangam, M. Senthil Pandian, P. Ramasamy, Photovoltaic performance of Pb-doped CdS quantum dots for solar cell application. Mater. Lett. 220, 74–77 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2018.03.007
H. Khallaf, I.O. Oladeji, L. Chow, Optimization of chemical bath deposited CdS thin films using nitrilotriacetic acid as a complexing agent. Thin Solid Films 516, 5967–5973 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2007.10.079
F. Yang, X. Tian, K. Zhang, X. Zhang, L. Liu, The morphology-property effect and synergetic catalytic effect of CdS as electrocatalysts for dye-sensitized solar cells. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 7, P311–P316 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0111806jss
S. Yilmaz, Y. Atasoy, M. Tomakin, E. Bacaksiz, Comparative studies of CdS, CdS:Al, CdS:Na and CdS:(Al-Na) thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis. Superlatt. Microstruct. 88, 299–307 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2015.09.021
M.G. Faraj, M.Z. Pakhuruddin, P. Taboada, Structural and optical properties of cadmium sulfide thin films on flexible polymer substrates by chemical spray pyrolysis technique. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 6628–6634 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-6353-4
D.I. Halge, V.N. Narwade, P.M. Khanzode, S. Begum, I. Banerjee, J.W. Dadge, J. Kovac, A.S. Rana, K.A. Bogle, Development of highly sensitive and ultra-fast visible-light photodetector using nano-CdS thin film. Appl. Phys. A 127, 446 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04611-9
S. Saravanakumar, K.S. Usha, G. Vijaya-Prasath, Ammonia gas sensing performance of Co/Ni co-doped CdS thin films by chemical bath deposition. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 34, 1–14 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09396-y
D. Herrera-Molina, J.E. Diosa, A. Fernández-Pérez, E. Mosquera-Vargas, Influence of aluminum doping on structural, morphological, vibrational, and optical properties of CdS thin films obtained by chemical bath deposition. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 273, 115451 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2021.115451
A.H. Rubel, J. Podder, Structural and electrical transport properties of CdS and Al-doped CdS thin films deposited by spray pyrolysis. J. Sci. Res. 4, 11 (2011). https://doi.org/10.3329/jsr.v4i1.8548
N. Rouabah, B. Boudine, R. Nazir, M. Zaabat, M. Sebais, O. Halimi, M.T. Soltani, A. Chala, Structural, optical and photocatalytic properties of PVC/CdS nanocomposites prepared by soft chemistry method. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 31, 1102–1110 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01752-x
R. Murugesan, S. Sivakumar, K. Karthik, P. Anandan, M. Haris, Effect of Mg/Co on the properties of CdS thin films deposited by spray pyrolysis technique. Curr. Appl. Phys. 19, 1136–1144 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2019.07.008
P.C. Dey, R. Das, Photoluminescence quenching in ligand free CdS nanocrystals due to silver doping along with two high energy surface states emission. J. Lumin. 183, 368–376 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2016.11.071
S.R. Dhage, H.A. Colorado, H.T. Hahn, Photoluminescence properties of thermally stable highly crystalline CdS nanoparticles. Mater. Res. 16, 504–507 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-14392013005000020
T. Fu, Sensing behavior of CdS nanoparticles to SO2, H2S and NH3 at room temperature. Mater. Res. Bull. 48, 1784–1790 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2013.01.037
P. Yadav, A.K. Sharma, S.K. Yadav, A.K. Vishwakarma, L. Yadava, Sensing response of toluene gas and structural properties of CdS-SnO2 thick films sensor. Mater. Today Proc. 38, 2792–2796 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.08.735
A.K. Vishwakarma, A.K. Sharma, N.K. Yadav, L. Yadava, Development of CdS-doped TiO2 nanocomposite as acetone gas sensor. Vacuum 191, 110363 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2021.110363
M. Prabhu, V.S. Manikandan, N. Soundararajan, K. Ramachandran, Ethanol gas sensing by Zn-doped CdS/CdTe nanoparticles. AIP Conf. Proc. 1731, 1–4 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4947795
S.M.H. Al-Jawad, S.N. Rafic, M.M. Muhsen, Preparation and characterization of polyaniline-cadmium sulfide nanocomposite for gas sensor application. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 31, 1–15 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0217984917502347
Q. Zhang, S. Ma, R. Zhang, K. Zhu, Y. Tie, S. Pei, Optimization NH3 sensing performance manifested by gas sensor based on Pr-SnS2/ZnS hierarchical nanoflowers. J. Alloys Compd. 807, 151650 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.151650
Y. Xiong, W. Xu, D. Ding, W. Lu, L. Zhu, Z. Zhu, Y. Wang, Q. Xue, Ultra-sensitive NH3 sensor based on flower-shaped SnS2 nanostructures with sub-ppm detection ability. J. Hazard. Mater. 341, 159–167 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.07.060
A. Akbar, M. Das, D. Sarkar, Room temperature ammonia sensing by CdS nanoparticle decorated polyaniline (PANI) nanorods. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 310, 112071 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2020.112071
Acknowledgements
The author extends their appreciation to the research center for advance materials science (RCAMS), King Khalid University for funding this work under Grant No. RCAMS/KKU/026-23.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors contributed equally to the article. KHP: investigation, writing, and formal analysis. SV: review, writing original article, and source. VG: investigation, original writing analysis, and characterization. RA: writing and formal analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies involving animals performed by any authors. Also, this article does not contain any studies involving human participants performed by any authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hari Prasad, K., Vinoth, S., Ganesh, V. et al. Fabrication of Al and La co-doped CdS thin film for ammonia gas-sensing application through low-cost nebulizer spray pyrolysis technique. Appl. Phys. A 130, 204 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-024-07355-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-024-07355-4