Abstract
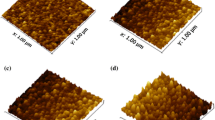
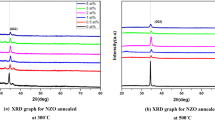
In this study pure and Mg, Ga, Al-doped ZnO thin films were prepared using sol–gel and spin-coating methods. The effect of dopant ion substitution on structural, morphological, optical and low temperature electrical properties of thin films were investigated using X-ray diffraction (XRD), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), UV–Visible spectroscopy, spectro fluorophotometer and two probe resistivity measurement method, respectively. The XRD result confirmed the wurtzite structure of prepared thin films without the presence of any characteristic impurity peak of Mg, Ga and Al. The average crystallite size of ZnO thin film was found to be 22.17 nm which was found to decrease to 21.13 nm, 16.06 nm and 16.03 nm when Mg2+, Ga3+ and Al3+ ions substitutes Zn2+ ions, respectively. The photoluminescence study had confirmed the presence of defect states in the prepared thin films. Furthermore, the low temperature dependent electrical study had shown that Ga-doping decreased the electrical resistivity and confirmed the presence of thermally activated and hopping type conduction mechanism up to 100 K. Thus, the ability of Ga-doping to facilitate the conduction process down up to 100 K, low activation energy of 0.23 eV and high optical transmittance in Ga and Ga-Mg doped-ZnO thin films makes it a suitable transparent and conductive material for optoelectronic devices.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on reasonable request.
References
A.K. Zak, W.A. Majid, M.R. Mahmoudian, M. Darroudi, R. Yousefi, Starch-stabilized synthesis of ZnO nanopowders at low temperature and optical properties study. Adv. Powder Technol. 24(3), 618–624 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2012.11.008
R. Kara, L. Mentar, A. Azizi, Synthesis and characterization of Mg-doped ZnO thin-films electrochemically grown on FTO substrates for optoelectronic applications. RSC Adv. 10(66), 40467–40479 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA06541B
A. Shah, P. Torres, R. Tscharner, N. Wyrsch, H. Keppner, Photovoltaic technology: the case for thin-film solar cells. Science 285(5428), 692–698 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.285.5428.692
S. Singh, P. Thiyagarajan, K.M. Kant, D. Anita, S. Thirupathiah, N. Rama, M.R. Rao, Structure, microstructure and physical properties of ZnO based materials in various forms: bulk, thin film and nano. J. Phys. D 40(20), 6312 (2007)
W. Shockley, H.J. Queisser, Detailed balance limit of efficiency of p-n junction solar cells. J. Appl. Phys. 32(3), 510–519 (1961). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1736034
X.H. Shi, K.J. Xu, Properties of fluorine-doped tin oxide films prepared by an improved sol-gel process. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 58, 1–7 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2016.09.038
Z.Z. Li, Z.Z. Chen, W. Huang, S.H. Chang, X.M. Ma, The transparence comparison of Ga-and Al-doped ZnO thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257(20), 8486–8489 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.04.138
A. Stadler, Transparent conducting oxides—an up-to-date overview. Mater. 5(4), 661–683 (2012). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma5040661
P.P. Edwards, A. Porch, M.O. Jones, D.V. Morgan, R.M. Perks, Basic materials physics of transparent conducting oxides. Dalton Trans. 19, 2995–3002 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1039/B408864F
P. Mondal, D. Das, Further improvements in conducting and transparent properties of ZnO: Ga films with perpetual c-axis orientation: materials optimization and application in silicon solar cells. Appl. Surf. Sci. 411, 315–320 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.03.171
N. Srinatha, P. Raghu, H.M. Mahesh, B. Angadi, Spin-coated Al-doped ZnO thin films for optical applications: Structural, micro-structural, optical and luminescence studies. J. Alloys Compd. 722, 888–895 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.06.182
K. Ellmer, Past achievements and future challenges in the development of optically transparent electrodes. Nat. Photon. 6(12), 809–817 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2012.282
A.N. Mallika, A.R. Reddy, K.S. Babu, C. Sujatha, K.V. Reddy, Structural and photoluminescence properties of Mg substituted ZnO nanoparticles. Opt. Mater. 36(5), 879–884 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2013.12.015
M. Kaddes, K. Omri, N. Kouaydi, M. Zemzemi, Structural, electrical and optical properties of ZnO nanoparticle: combined experimental and theoretical study. Appl. Phys. A 124, 1–7 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-1921-x
F.H. Wang, H.P. Chang, C.C. Tseng, C.C. Huang, H.W. Liu, Influence of hydrogen plasma treatment on Al-doped ZnO thin films for amorphous silicon thin film solar cells. Curr. Appl. Phys. 11(1), S12–S16 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2010.11.109
D.T. Phan, A.A.M. Farag, F. Yakuphanoglu, G.S. Chung, Optical and photoluminescence properties of Ga doped ZnO nanostructures by sol-gel method. J. Electroceram. 29, 12–22 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-012-9731-6
Z.R. Khan, M.S. Khan, M. Zulfequar, M.S. Khan, Optical and structural properties of ZnO thin films fabricated by sol-gel method. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2(5), 340–345 (2011)
Y. Natsume, H. Sakata, Zinc oxide films prepared by sol-gel spin-coating. Thin Solid Films 372(1–2), 30–36 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-6090(00)01056-7
S. Bandyopadhyay, G.K. Paul, R. Roy, S.K. Sen, S. Sen, Study of structural and electrical properties of grain-boundary modified ZnO films prepared by sol–gel technique. Mater. Chem. Phys. 74(1), 83–91 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0254-0584(01)00402-3
Y.Z. Yoo, T. Fukumura, Z. Jin, K. Hasegawa, M. Kawasaki, P. Ahmet, H. Koinuma, ZnO–CoO solid solution thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 90(8), 4246–4250 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1402142
O.D. Jayakumar, I.K. Gopalakrishnan, S.K. Kulshreshtha, The structural and magnetization studies of Co-doped ZnO co-doped with Cu: synthesized by co-precipitation method. J. Mater. Chem. 15(34), 3514–3518 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1039/B507201H
R. Kumar, N. Khare, Temperature dependence of conduction mechanism of ZnO and Co-doped ZnO thin films. Thin Solid Films 516(6), 1302–1307 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2007.06.121
D. Fang, K. Lin, T. Xue, C. Cui, X. Chen, P. Yao, H. Li, Influence of Al doping on structural and optical properties of Mg–Al co-doped ZnO thin films prepared by sol–gel method. J. Alloys Compd. 589, 346–352 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.11.061
P.R. Kumar, C.S. Kartha, K.P. Vijayakumar, F. Singh, D.K. Avasthi, Effect of fluorine doping on structural, electrical and optical properties of ZnO thin films. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 117(3), 307–312 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2004.12.040
S.S. Shinde, P.S. Shinde, Y.W. Oh, D. Haranath, C.H. Bhosale, K.Y. Rajpure, Structural, optoelectronic, luminescence and thermal properties of Ga-doped zinc oxide thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 258(24), 9969–9976 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.06.058
F. Baig, M.W. Ashraf, A. Asif, M. Imran, A comparative analysis for effects of solvents on optical properties of Mg doped ZnO thin films for optoelectronic applications. Optik 208, 164534 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.164534
D. Bokov, A.T. Jalil, S. Chupradit, W. Suksatan, M.J. Ansari, I.H. Shewael, E. Kianfar, Nanomaterial by sol-gel method: synthesis and application. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1–21 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/5102014
O. Garcia-Martinez, R.M. Rojas, E. Vila, J.M. De Vidales, Microstructural characterization of nanocrystals of ZnO and CuO obtained from basic salts. Solid State Ion 63, 442–449 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-2738(93)90142-P
R. Sagheer, M. Khalil, V. Abbas, Z.N. Kayani, U. Tariq, F. Ashraf, Effect of Mg doping on structural, morphological, optical and thermal properties of ZnO nanoparticles. Optik 200, 163428 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2019.163428
S. Fabbiyola, L.J. Kennedy, A.A. Dakhel, M. Bououdina, J.J. Vijaya, T. Ratnaji, Structural, microstructural, optical and magnetic properties of Mn-doped ZnO nanostructures. J. Mol. Struct. 1109, 89–96 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2015.12.071
S. Ayaz, P. Mishra, S. Sen, Structure correlated optoelectronic and electrochemical properties of Al/Li modified ZnO. J. Appl. Phys. 126(2), 024302 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5099894
N. Kumar, S. Azad, S. Chand, Fabrication and electrical characterization of solution processed Ni/MgO/p-Si/Al MIS diodes. Appl. Phys. A 128(3), 1–10 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-05378-3
Y. Caglar, M. Caglar, S. Ilican, Microstructural, optical and electrical studies on sol gel derived ZnO and ZnO: Al films. Curr. Appl. Phys. 12(3), 963–968 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2011.12.017
J.H. Lee, B.O. Park, Transparent conducting ZnO: Al, In and Sn thin films deposited by the sol–gel method. Thin Solid Films 426(1–2), 94–99 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-6090(03)00014-2
J.S. Jang, J. Kim, U. Ghorpade, H.H. Shin, M.G. Gang, S.D. Park, J.H. Kim, Comparison study of ZnO-based quaternary TCO materials for photovoltaic application. J. Alloys Compd. 793, 499–504 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.04.042
S. Azad, N. Kumar, S. Chand, Effect of Mg2+ ions substitution on phase formation, structural, morphological, and optical properties of Zn0.1−xMgxO structure. J. Mater. Sci. 33, 861–871 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07356-6
J. Hu, R.G. Gordon, Textured aluminum-doped zinc oxide thin films from atmospheric pressure chemical-vapor deposition. J. Appl. Phys. 71(2), 880–890 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.351309
A. López-Suárez, D. Acosta, C. Magaña, F. Hernández, Optical, structural and electrical properties of ZnO thin films doped with Mn. J. Mater. Sci. 31, 7389–7397 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02830-8
T.H. Kim, J.J. Park, S.H. Nam, H.S. Park, N.R. Cheong, J.K. Song, S.M. Park, Fabrication of Mg-doped ZnO thin films by laser ablation of Zn: Mg target. Appl. Surf. Sci. 255(10), 5264–5266 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2008.07.105
B.S. Patial, S. Chand, N. Thakur, On high-field conduction and I-V measurements in quaternary Se–Te–In–Pb nano-chalcogenide thin films. J. Mater. Sci. 31(4), 2741–2756 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02814-8
S. Vipul, P.D. Amit, Effect of doping concentration on optical and electrical properties of intrinsic n-type ZnO (i-ZnO) and (Cu, Na and K) doped p-type ZnO thin films grown by chemical bath deposition method. Nanosyst. Phys. Chem. Math. 11(4), 391–400 (2020). https://doi.org/10.17586/2220-8054-2020-11-4-391-400
N. Kılınç, L. Arda, S. Öztürk, Z.Z. Öztürk, Structure and electrical properties of Mg-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Cryst. Res. Technol. 45(5), 529–538 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1002/crat.200900662
R. Dingle, Luminescent transitions associated with divalent copper impurities and the green emission from semiconducting zinc oxide. Phys. Rev. Lett. 23(11), 579 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.23.579
J.Y. Cho, I.K. Kim, I.O. Jung, J.H. Moon, J.H. Kim, Effects of Mg doping concentration on the band gap of ZnO/Mg x Zn 1–x O multilayer thin films prepared using pulsed laser deposition method. J. Electroceram. 23(2–4), 442 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-008-9485-3
Y. Ammaih, A. Lfakir, B. Hartiti, A. Ridah, P. Thevenin, M. Siadat, Structural, optical and electrical properties of ZnO: Al thin films for optoelectronic applications. Opt. Quantum Electron. 46(1), 229–234 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-013-9757-2
K.S. An, W. Cho, B.K. Lee, S.S. Lee, C.G. Kim, Atomic layer deposition of undoped and Al-doped ZnO thin films using the Zn alkoxide precursor methyl zinc isopropoxide. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 8(9), 4856–4859 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2008.IC47
M.C. Jun, S.U. Park, J.H. Koh, Comparative studies of Al-doped ZnO and Ga-doped ZnO transparent conducting oxide thin films. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 7(1), 1–6 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1186/1556-276X-7-639
Acknowledgements
The author would like to thank NIT Hamirpur for providing research fellowship funded by MHRD, Government of India.
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Seema: methodology, experimental work, data analysis, writing-original draft and investigation. SC: supervision, conceptualization, writing-review and editing, validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. There is no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Azad, S., Chand, S. Synthesis and characterization of doped-ZnO thin films over wide temperature range for applications as a transparent conducting material. Appl. Phys. A 129, 686 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-06973-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-06973-8