Abstract
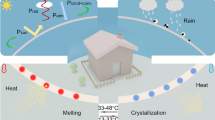
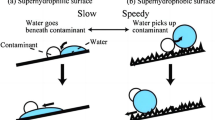
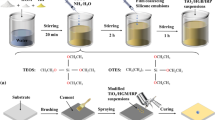
Passive daytime radiation cooling (PDRC) materials have attracted more and more attention due to their low energy consumption, no pollution and energy saving potential. However, current PDRC materials face many challenges in practical applications, such as expensive raw materials, complex manufacturing processes, and performance degradation due to surface contamination by dust. Herein, we prepared a poly-4-methyl-1-pentene/polyvinylidene fluoride (TPX/PVDF) superhydrophobic PDRC coating by a simple scraping method. By optimizing the amount of TPX in the scraping solution, the surface contact angle (CA) of the coating can reach 153.5° and the sliding angle (SA) is 8.9°, showing good self-cleaning properties. At the same time, the solar reflectance (Rs) can reach 91.6%, and the infrared emissivity (EIR) is larger than 0.97. Under direct sunlight in hot summer months, the coating sample can achieve a radiative cooling effect of 7.5 °C below the ambient temperature on average. Additionally, the TPX/PVDF coating was used as the roof and exterior paint of a miniature house (MH), and the cooling performance of the TPX/PVDF coating under direct sunlight was studied. The result indicated that the mean interior temperature of the MH covered with TPX/PVDF coating is 13.5 °C lower than that of the unmodified MH. Importantly, once the radiative cooling ability of the TPX/PVDF coating degraded due to surface dirt accumulating, it can recover automatically via its self-cleaning function. The TPX/PVDF based superhydrophobic and radiative cooling coating has a broad application prospect in the field of building energy conservation.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used in the present work is available in the manuscript.
Abbreviations
- TPX:
-
Poly-4-methyl-1-pentene
- PVDF:
-
Polyvinylidene fluoride
- PDRC:
-
Passive daytime radiation cooling
- SPDRC:
-
Superhydrophobic and passive daytime radiation cooling
- ATW:
-
Atmosphere transparent window
- CA:
-
Contact angle
- SA:
-
Sliding angle
- DMAC:
-
Dimethylacetamide
- R S :
-
Solar reflectance
- E IR :
-
Infrared thermal emissivity
- CCP:
-
Commercial cooling paint
- TPC:
-
TPX/PVDF coating
- MH:
-
Miniature house
- AC:
-
Artificial contamination
References
DOE, Building Energy Data Book, Department of Energy, US (2011)
X. Lu, P. Xu, H. Wang, T. Yang, J. Hou, Cooling potential and applications prospects of passive radiative cooling in buildings: the current state-of-the-art. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 65, 1079–1097 (2016)
R. Family, M.P. Mengüç, Materials for radiative cooling: a review. Procedia Environ. Sci. 38, 752–759 (2017)
K. Panchabikesan, K. Vellaisamy, V. Ramalingam, Passive cooling potential in buildings under various climatic conditions in India. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 78, 1236–1252 (2017)
J.H. Chen, L. Lu, Development of radiative cooling and its integration with buildings: a comprehensive review. Sol. Energy 212, 125–151 (2020)
X.Q. Li, W.R. Xie, C.X. Sui, P.C. Hsu, Multispectral thermal management designs for net-zero energy buildings. ACS Mater. Lett. 2, 1624–1643 (2020)
A.M. Omer, Energy, environment and sustainable development. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 12, 2265–2300 (2008)
Y.F. Wu, H.X. Zhao, H.L. Sun, M.F. Duan, B.R. Lin, S.D. Wu, A review of the application of radiative sky cooling in buildings: challenges and optimization. Energy Convers. Manag. 265, 115768 (2022)
U. Eicker, A. Dalibard, Photovoltaic-thermal collectors for night radiative cooling of buildings. Sol. Energy 85, 1322–1335 (2011)
M. Hanif, T.M.I. Mahliaa, A. Zare, T.J. Saksahdan, H.S.C. Metselaar, Potential energy savings by radiative cooling system for a building in tropical climate. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 32, 642–650 (2014)
Y. Cui, Y. Wang, L. Zhu, Performance analysis on a building-integrated solar heating and cooling panel. Renew. Energy 74, 627–632 (2015)
A.P. Raman, M.A. Anoma, L.X. Zhu, E. Rephaeli, S.H. Fan, Passive radiative cooling below ambient air temperature under direct sunlight. Nature 515, 540–544 (2014)
Y. Zhai, Y.G. Ma, S.N. David, D.L. Zhao, R.N. Lou, G. Tan, R.G. Yang, X.B. Yin, Scalable-manufactured randomized glass-polymer hybrid-metamaterial for daytime radiative cooling. Science 355, 1062–1066 (2017)
T. Li, Y. Zhai, S.M. He, W.T. Gan, Z.Y. Wei, M. Heidarinejad, D. Dalgo, R.Y. Mi, X.P. Zhao, J.W. Song, J.Q. Dai, C.J. Chen, A. Aili, A. Vellore, A.S. Martini, R.G. Yang, J. Srebric, X.B. Yin, L.B. Hu, A radiative cooling structural material. Science 364, 760–763 (2019)
P. Yang, C. Chen, Z. Zhang, A dual-layer structure with record-high solar reflectance for daytime radiative cooling. Sol. Energy 169, 316–324 (2018)
K.-T. Lin, J. Han, Ke. Li, C. Guo, H. Lin, B. Jia, Radiative cooling: fundamental physics, atmospheric influences, materials and structural engineering, applications and beyond. Nano Energy 80, 105517 (2021)
C.G. Granqvist, A. Hjortsberg, T.S. Eriksson, Radiative cooling to low temperatures with selectivity IR emitting surfaces. Thin Solid Films 90, 187–190 (1982)
J.W. Liu, J. Zhang, H.J. Tang, Z.H. Zhou, D.B. Zhang, L. Ye, D.L. Zhao, Recent advances in the development of radiative sky cooling inspired from solar thermal harvesting. Nano Energy 81, 105611 (2021)
X.Q. Li, X.Z. Min, J.L. Li, N. Xu, P.C. Zhu, B. Zhu, S.N. Zhu, J. Zhu, Storage and recycling of interfacial solar steam enthalpy. Joule 2, 2477–2484 (2018)
K.X. Lin, L.K. Chao, H.H. Lee, R. Xin, S. Liu, T.C. Ho, B.L. Huang, K.M. Yu, C.Y. Tso, Potential building energy savings by passive strategies combining daytime radiative coolers and thermochromic smart windows. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 28, 101517 (2021)
X. Xue, M. Qiu, Y.W. Li, Q.M. Zhang, S.Q. Li, Z. Yang, C. Feng, W.D. Zhang, J.G. Dai, D.Y. Lei, W. Jin, L.J. Xu, T. Zhang, J. Qin, H.Q. Wang, S.H. Fan, Creating an eco-friendly building coating with smart subambient radiative cooling. Adv. Mater. 32, 1906751 (2020)
T. Xia, H. Wang, High reflective polyethylene glycol terephthalate package 1ayer for passive daytime radiative cooling in photo voltaic cells. Solar Energ. 237, 313–319 (2022)
Z. Wang, D. Kortge, J. Zhu, Z.G. Zhou, H. Torsina, C.Y. Lee, P. Bermel, Lightweight, passive radiative cooling to enhance concentrating photovoltaics. Joule 4, 2702–2717 (2020)
S.N. Zeng, S.J. Pian, M.Y. Su, Z.N. Wang, M.Q. Wu, X.H. Liu, M.Y. Chen, Y.Z. Xiang, J.W. Wu, M.N. Zhang, Q.Q. Cen, Y.W. Tang, X.H. Zhou, Z.H. Huang, R. Wang, A. Tunuhe, X.Y. Sun, Z.G. Xia, M.W. Tian, M. Chen, X. Ma, L. Yang, J. Zhou, H.M. Zhou, Q. Yang, X. Li, Y.G. Ma, G.M. Tao, Hierarchical-morphology metafabric for scalable passive daytime radiative cooling. Science 373, 692–696 (2021)
X.S. Zhang, W.F. Yang, Z.W. Shao, Y.G. Li, Y. Su, Q.H. Zhang, C.Y. Hou, H.Z. Wang, A moisture-wicking passive radiative cooling hierarchical metafabric. ACS Nano 16, 2188 (2022)
L. Zhou, H.M. Song, J.W. Liang, M. Singer, M. Zhou, E. Stegenburgs, N. Zhang, C. Xu, T. Ng, Z.F. Yu, B. Ooi, Q.Q. Gan, A polydimethylsiloxane-coated metal structure for all-day radiative cooling. Nat. Sustain. 2, 718 (2019)
X. Wang, X.H. Liu, Z.Y. Li, H.W. Zhang, Z.W. Yang, H. Zhou, T.X. Fan, Scalable flexible hybrid membranes with photonic structures for daytime radiative cooling. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30, 1907562 (2019)
S.D.H. Rezaei, Z.G. Dong, J.Y.E. Chan, J. Trisno, R.J.H. Ng, Q.F. Ruan, C.W. Qiu, N.A. Mortensen, J.K.W. Yang, Nanophotonic structural colors. ACS Photonics 8, 18–33 (2021)
E. Rephaeli, A. Raman, S. Fan, Ultrabroadband photonic structures to achieve high-performance daytime radiative cooling. Nano Lett. 13, 1457–1461 (2013)
A.R. Gentle, G.B. Smith, Radiative heat pumping from the earth using surface phonon resonant nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 10, 373–379 (2010)
X.Z. Ao, M.K. Hu, B. Zhao, N. Chen, G. Pei, C.W. Zou, Preliminary experimental study of a specular and a diffuse surface for daytime radiative cooling. Sol. Energ. Mater. Sol. C. 191, 290–296 (2019)
Y.W. Liu, A.Q. Bai, Z.G. Fang, Y.R. Ni, C.H. Lu, Z.Z. Xu, A pragmatic bilayer selective emitter for efficient radiative cooling under direct sunlight. Materials 12, 1208 (2019)
Y.P. Tian, H. Shao, X.J. Liu, F.Q. Chen, Y.S. Li, C.Y. Tang, Y. Zheng, Superhydrophobic and recyclable cellulose-fiber-based composites for high-efficiency passive radiative cooling. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 13, 22521–22530 (2021)
A. Aili, Z.Y. Wei, Y.Z. Chen, D.L. Zhao, R.G. Yang, X.B. Yin, Selection of polymers with functional groups for daytime radiative cooling. Mater. Today Phys. 10, 100127 (2019)
S.J. Nie, X.Y. Tan, X.Y. Li, K. Wei, T. Xiao, L.H. Jiang, J.L. Geng, Y. Liu, W.W. Hu, X.B. Chen, Facile and environmentally-friendly fabrication of robust composite film with superhydrophobicity and radiative cooling property. Comp. Sci. Tech. 230, 109750 (2022)
C.H. Xue, R.X. Wei, X.J. Guo, B.Y. Liu, M.M. Du, M.C. Huang, H.G. Li, S.T. Jia, Fabrication of superhydrophobic P(VDF-HFP)/SiO2 composite film for stable radiative cooling. Comp. Sci. Tech. 220, 109279 (2022)
H.D. Wang, C.H. Xue, X.J. Guo, B.Y. Liu, Z.Y. Ji, M.C. Huang, S.T. Jia, Superhydrophobic porous film for daytime radiative cooling. Appl. Mater. Today 24, 101100 (2021)
G.L. Chen, Y.M. Wang, J. Qiu, J.Y. Cao, Y.C. Zou, S.Q. Wang, J.H. Ouyang, D.C. Jia, Y. Zhou, A visibly transparent radiative cooling film with self-cleaning function produced by solution processing. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 90, 76–84 (2021)
F.S. Gill, D. Uniyal, B. Prasad, S. Saluja, A. Mishra, R.K. Bachheti, S. Juyal, Investigation of increased electrical conductivity by rGO in rGO/PVDF/PMMA/PTFE nanocomposites. J. Mol. Struct. 1267, 133541 (2022)
N. María, Y. Patil, G. Polymeropoulos, A. Peshkov, V. Rodionov, J. Maiz, N. Hadjichristidis, A.J. Müller, (PVDF)2(PEO)2 miktoarm star copolymers: Synthesis and isothermal crystallization leading to exclusive β-phase formation. Eur. Polym. J. 179, 111506 (2022)
L.N. Sim, S.R. Majid, A.K. Arof, FTIR studies of PEMA/PVdF-HFP blend polymer electrolyte system incorporated with LiCF3SO3 salt. Vib. Spectrosc. 58, 57–66 (2012)
R. Jayaraman, P. Vickraman, N.M.V. Subramanian, A.S. Justin, A.C impedance, XRD, DSC, FTIR studies on PbTiO3 dispersoid pristine PVdF-co-HFP and PEMA blended PVdF-co-HFP microcomposite electrolytes. J Non-Cryst Solids 435, 27–32 (2016)
M. Choi, J.Y. Seo, S.W. Yoon, Y.S. Nam, J.C. Lee, B.J. Lee, All-day radiative cooling using a grating-patterned PDMS film emitter. Appl. Therm. Eng. 214, 118771 (2022)
J. Liu, C.F. Xu, X.Z. Ao, K.G. Lu, B. Zhao, G. Pei, A dual-layer polymer-based film for all-day sub-ambient radiative sky cooling. Energy 254, 124350 (2022)
Z.F. Huang, X.L. Ruan, Nanoparticle embedded double-layer coating for daytime radiative cooling. Int. J. Heat Mass Tran. 104, 890–896 (2017)
H. Bao, C.N. Yan, B.X. Wang, X. Fang, C.Y. Zhao, X.L. Ruan, Double-layer nanoparticle-based coatings for efficient terrestrial radiative cooling. Sol. Energ. Mater. Sol. C. 168, 78–84 (2017)
J. Mandal, Y.K. Fu, A.C. Overvig, M.X. Jia, K.R. Sun, N.N. Shi, H. Zhou, X.H. Xiao, N.F. Yu, Y. Yang, Hierarchically porous polymer coatings for highly efficient passive daytime radiative cooling. Science 362, 315–319 (2018)
X.Y. Li, J. Peoples, Z.F. Huang, Z.X. Zhao, J. Qiu, X.L. Ruan, Full daytime sub-ambient radiative cooling in commercial-like paints with high figure of merit. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 1, 100221 (2020)
X.Y. Li, J. Peoples, P. Yao, X.L. Ruan, Ultrawhite BaSO4 paints and films for remarkable daytime subambient radiative cooling. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 13, 21733–21739 (2021)
S. Zhang, W.L. Jing, Z. Chen, C.Y. Zhang, D.X. Wu, Y.F. Gao, H.T. Zhu, Full daytime sub-ambient radiative cooling film with high efficiency and low cost. Renew Energ. 194, 850–857 (2022)
M.V. Bagepalli, J.D. Yarrington, A.J. Schrader, Z.M. Zhang, D. Ranjan, P.G. Loutzenhiser, Measurement of flow properties coupled to experimental and numerical analyses of dense, granular flows for solar thermal energy storage. Sol. Energy 207, 77–90 (2020)
J. Huang, M.Z. Li, D.S. Fan, Core-shell particles for devising high-performance full-day radiative cooling paint. Appl. Mater. Today 25, 101209 (2021)
Funding
This work was financial supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China (No. 21KJB430002), Program for International S&T Cooperation Projects of Changzhou City (No. CZ20210028).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The manuscript was written through contributions of all authors. All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (MP4 6377 KB)
Supplementary file2 (MP4 6264 KB)
Supplementary file3 (AVI 5463 KB)
Supplementary file4 (AVI 6111 KB)
Supplementary file5 (AVI 16039 KB)
Supplementary file6 (MOV 32929 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, F., Wang, F., Lei, S. et al. Superhydrophobic poly-4-methyl-1-pentene/polyvinylidene fluoride coating with excellent passive daytime radiation cooling performance. Appl. Phys. A 129, 266 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-06560-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-06560-x