Abstract
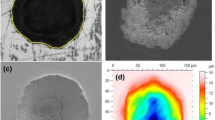
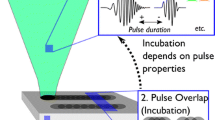
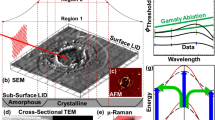
Multi-shot ablation thresholds, \(F_{\text {th}}(N)\) for N number of shots, were investigated for polycrystalline copper and single crystalline silicon using a Near-Infrared femtosecond laser, with wavelength of 800nm and pulse duration of 130fs. Fluences, F, above and below the single-shot threshold \(F_1\) were used in the study. To better understand the incubation effects, the results are compared to two existing incubation models. The first one is the widely used power law and the second one includes the effects of absorption change and critical fluence, \(F_\infty \). No ablation would result for a material even with infinite number of laser shots if \(F < F_\infty \). From the data generated by \(F>F_1\), \(F_{\text {th}}(N)\) were determined. The single-shot ablation threshold, \(F_1\), for polycrystalline copper and single crystalline silicon were determined to be 0.87J/cm\(^2\) and 0.34J/cm\(^2\) respectively. From the data generated by \(F < F_1\), \(F_{\text {th}}(N)\) were also determined and \(F_\infty \) for polycrystalline copper and single crystal silicon were estimated to be 0.18J/cm\(^2\) and 0.21J/cm\(^2\), respectively. For copper, \(F_{\text {th}}(N)\) data from \(F > F_1\) and \(F < F_1\) are consistent with each other, and the power law fit the experimental data reasonably well until the \(F_\infty \) effect sets in when \(N > 1000\). For silicon, we found values of \(F_{\text {th}}(N)\) from \(F < F_1\) are significantly higher than those of \(F > F_1\). This study provides important information for the femtosecond laser nanomilling technique when nanometer depth resolution can be made possible by using multiple pulses with \(F < F_1\).










Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Kirkwood, M. Taschuk, Y. Tsui, R. Fedosejevs, Nanomilling surfaces using near-threshold femtosecond laser pulses. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 59, 126 (2007). (IOP Publishing)
J. Liu, Simple technique for measurements of pulsed gaussian-beam spot sizes. Opt. Lett. 7(5), 196–198 (1982)
J. Bonse, S. Baudach, J. Krüger, W. Kautek, M. Lenzner, Femtosecond laser ablation of silicon-modification thresholds and morphology. Appl. Phys. A 74(1), 19–25 (2002)
A. Garg, A. Kapoor, K. Tripathi, Laser-induced damage studies in gaas. Opt. Laser Technol. 35(1), 21–24 (2003)
C.S. Nathala, A. Ajami, W. Husinsky, B. Farooq, S.I. Kudryashov, A. Daskalova, I. Bliznakova, A. Assion, Ultrashort laser pulse ablation of copper, silicon and gelatin: effect of the pulse duration on the ablation thresholds and the incubation coefficients. Appl. Phys. A 122(2), 1–8 (2016)
P. Mannion, J. Magee, E. Coyne, G. O’connor, T. Glynn, The effect of damage accumulation behaviour on ablation thresholds and damage morphology in ultrafast laser micro-machining of common metals in air. Appl. Surf. Sci. 233(1–4), 275–287 (2004)
A. Rosenfeld, M. Lorenz, R. Stoian, D. Ashkenasi, Ultrashort-laser-pulse damage threshold of transparent materials and the role of incubation. Appl. Phys. A 69(1), 373–376 (1999)
G.F.B.D. Almeida, L.K. Nolasco, G.R. Barbosa, A. Schneider, A. Jaros, I. Manglano Clavero, C. Margenfeld, A. Waag, T. Voss, C.R. Mendonça, Incubation effect during laser micromachining of gan films with femtosecond pulses. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30(18), 16821–16826 (2019)
D. Ashkenasi, M. Lorenz, R. Stoian, A. Rosenfeld, Surface damage threshold and structuring of dielectrics using femtosecond laser pulses: the role of incubation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 150(1–4), 101–106 (1999)
R.N. Oosterbeek, C. Corazza, S. Ashforth, M.C. Simpson, Effects of dopant type and concentration on the femtosecond laser ablation threshold and incubation behaviour of silicon. Appl. Phys. A 122(4), 1–10 (2016)
Y. Jee, M.F. Becker, R.M. Walser, Laser-induced damage on single-crystal metal surfaces. JOSA B 5(3), 648–659 (1988)
B. Neuenschwander, B. Jaeggi, M. Schmid, Dommann, A., Neels, A, Bandi, T., G. Hennig, Factors controlling the incubation in the application of ps laser pulses on copper and iron surfaces. In: Laser Applications in Microelectronic and Optoelectronic Manufacturing (LAMOM) XVIII, vol. 8607, p. 86070 (2013). International Society for Optics and Photonics
G. Raciukaitis, M. Brikas, P. Gecys, M. Gedvilas, Accumulation effects in laser ablation of metals with high-repetition-rate lasers. In: High-Power Laser Ablation VII, vol. 7005, p. 70052 (2008). International Society for Optics and Photonics
J. Krüger, S. Martin, H. Mädebach, L. Urech, T. Lippert, A. Wokaun, W. Kautek, Femto-and nanosecond laser treatment of doped polymethylmethacrylate. Appl. Surf. Sci. 247(1–4), 406–411 (2005)
D. Gómez, I. Goenaga, On the incubation effect on two thermoplastics when irradiated with ultrashort laser pulses: broadening effects when machining microchannels. Appl. Surf. Sci. 253(4), 2230–2236 (2006)
R.N. Oosterbeek, T. Ward, S. Ashforth, O. Bodley, A.E. Rodda, M.C. Simpson, Fast femtosecond laser ablation for efficient cutting of sintered alumina substrates. Opt. Lasers Eng. 84, 105–110 (2016)
F. Di Niso, C. Gaudiuso, T. Sibillano, F.P. Mezzapesa, A. Ancona, P.M. Lugarà, Role of heat accumulation on the incubation effect in multi-shot laser ablation of stainless steel at high repetition rates. Opt. Express 22(10), 12200–12210 (2014)
R. Streubel, S. Barcikowski, B. Gökce, Continuous multigram nanoparticle synthesis by high-power, high-repetition-rate ultrafast laser ablation in liquids. Opt. Lett. 41(7), 1486–1489 (2016)
R. Streubel, G. Bendt, B. Gökce, Pilot-scale synthesis of metal nanoparticles by high-speed pulsed laser ablation in liquids. Nanotechnology 27(20), 205602 (2016)
Z. Sun, M. Lenzner, W. Rudolph, Generic incubation law for laser damage and ablation thresholds. J. Appl. Phys. 117(7), 073102 (2015)
J. Byskov-Nielsen, J.-M. Savolainen, M.S. Christensen, P. Balling, Ultra-short pulse laser ablation of metals: threshold fluence, incubation coefficient and ablation rates. Appl. Phys. A 101(1), 97–101 (2010)
A. Naghilou, O. Armbruster, M. Kitzler, W. Kautek, Merging spot size and pulse number dependence of femtosecond laser ablation thresholds: modeling and demonstration with high impact polystyrene. J. Phys. Chem. C 119(40), 22992–22998 (2015)
C. Gaudiuso, G. Giannuzzi, A. Volpe, P.M. Lugarà, I. Choquet, A. Ancona, Incubation during laser ablation with bursts of femtosecond pulses with picosecond delays. Opt. Express 26(4), 3801–3813 (2018)
H. Mustafa, R. Pohl, T. Bor, B. Pathiraj, D. Matthews, G. Römer, Picosecond-pulsed laser ablation of zinc: crater morphology and comparison of methods to determine ablation threshold. Opt. Express 26(14), 18664–18683 (2018)
S.V. Kirkwood, A. Van Popta, Y. Tsui, R. Fedosejevs, Single and multiple shot near-infrared femtosecond laser pulse ablation thresholds of copper. Appl. Phys. A 81(4), 729–735 (2005)
J. Bonse, A. Rosenfeld, J. Krüger, On the role of surface plasmon polaritons in the formation of laser-induced periodic surface structures upon irradiation of silicon by femtosecond-laser pulses. J. Appl. Phys. 106(10), 104910 (2009)
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge the financial support of the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council. The authors also wish to acknowledge the technical support provided by the Nanofab of University of Alberta for the use of SEM, AFM, optical microscope, and fabrication of copper films.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest/competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, R., McDowell, A., Hegmann, F. et al. A study of incubation effects in femtosecond laser irradiation of silicon and copper. Appl. Phys. A 129, 131 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-06334-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-06334-x