Abstract
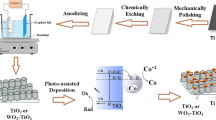
Water splitting using photoelectrochemical technology is an excellent way to generate clean hydrogen, for which TiO2 is regarded as the most promising photoanode because of its unique properties. The large band gap and high recombination rate of charge carriers, however, limit its solar-to-hydrogen conversion efficiency. Herein, we fabricated the reduced TiO2 nanotubes by electrochemical anodization technique followed by hydrazine treatment to create oxygen vacancies (or Ti3+ sites) in the sample. The samples were then characterized by XRD and FESEM for structural and morphological analysis, validating the formation of Titania nanotube arrays (TNTA). Absorbance spectra of hydrazine-treated samples showed the absorption edge at about 447 nm, which corresponds to a band gap of 2.67 eV. This reduction in the band gap may be due to the introduction of Ti3+ states beneath the conduction band, as confirmed by XPS spectra. Photoluminescence spectra depicted the presence of oxygen vacancies in the hydrazine-treated sample. The hydrazine treatment, as a result of the introduction of Ti3+ states, enhanced the photocurrent density of the sample without affecting its photostability.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
References
H. Eidsvåg, S. Bentouba, P. Vajeeston, S. Yohi, D. Velauthapillai, TiO2 as a photocatalyst for water splitting—an experimental and theoretical review. Molecules 26, 1–30 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061687
P. Sharma, M.L. Kolhe, Review of sustainable solar hydrogen production using photon fuel on artificial leaf. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 42, 22704–22712 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.07.115
Y.H. Chiu, T.H. Lai, C.Y. Chen, P.Y. Hsieh, K. Ozasa, M. Niinomi, K. Okada, T.F.M. Chang, N. Matsushita, M. Sone, Y.J. Hsu, Fully depleted Ti-Nb-Ta-Zr-O nanotubes: interfacial charge dynamics and solar hydrogen production. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 10, 22997–23008 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b00727
J. Bansal, R. Tabassum, S.K. Swami, S. Bishnoi, P. Vashishtha, G. Gupta, S.N. Sharma, A.K. Hafiz, Performance analysis of anomalous photocatalytic activity of Cr-doped TiO2 nanoparticles [Cr(x)TiO2(1–x)]. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 126, 1–10 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-03536-z
J. Bansal, A.K. Hafiz, S.N. Sharma, Photoreduction of dye with noble metal gold permeated with metal oxide titania. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 20, 3896–3901 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2020.17501
P. Acevedo-Peña, I. González, Relation between morphology and photoelectrochemical performance of TiO2 nanotubes arrays grown in ethylene glycol/water. Proc. Chem. 12, 34–40 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proche.2014.12.038
P. Deák, J. Kullgren, B. Aradi, T. Frauenheim, L. Kavan, Water splitting and the band edge positions of TiO2. Electrochim. Acta. 199, 27–34 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2016.03.122
M. Zare, S. Solaymani, A. Shafiekhani, S. Kulesza, Ş Ţǎlu, M. Bramowicz, Evolution of rough-surface geometry and crystalline structures of aligned TiO2 nanotubes for photoelectrochemical water splitting. Sci. Rep. 8, 1–11 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-29247-3
R.A. Zargar, R.A. Zargar, N. Boora, M.M. Hassan, M.M. Hassan, A. Khan, A.K. Hafiz, Screen printed TiO2 film: a candidate for photovoltaic applications. Mater. Res. Express. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab9ceb
V.S. Katta, M. Velpandian, V.R. Chappidi, M.S. Ahmed, A. Kumar, S. Asthana, P. Meduri, S.S.K. Raavi, Er3+ doped titania photoanode for enhanced performance of photo-electrochemical water splitting devices. Mater. Lett. 302, 130297 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2021.130297
A. Mir, K. Iqbal, S. Rubab, M.A. Shah, Effect of concentration of Fe-dopant on the photoelectrochemical properties of Titania nanotube arrays. Ceram. Int. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.09.037
M. Motola, L. Hromadko, J. Prikryl, H. Sopha, M. Krbal, J.M. Macak, Intrinsic properties of high-aspect ratio single- and double-wall anodic TiO2 nanotube layers annealed at different temperatures. Electrochim. Acta. 352, 136479 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2020.136479
Katta, V.S., Das, A., Dileep K., R., Cilaveni, G., Pulipaka, S., Veerappan, G., Ramasamy, E., Meduri, P., Asthana, S., Melepurath, D., Raavi, S.S.K.: Vacancies induced enhancement in neodymium doped titania photoanodes based sensitized solar cells and photo-electrochemical cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells. 220, 110843 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2020.110843
J. Bansal, S.K. Swami, R. Tabassum, S.N. Sharma, A.K. Hafiz, Encapsulation of Cu-doped TiO2 nanocomposites with the understanding of weak photocatalytic properties for sunscreen applications. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 43, 364–374 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2020.1841653
S. Zhou, S. Liu, K. Su, K. Jia, Facile synthesis of Ti3+ self-doped and sulfur-doped TiO2 nanotube arrays with enhanced visible-light photoelectrochemical performance. J. Alloys Compd. 804, 10–17 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.06.294
F. Zuo, L. Wang, T. Wu, Z. Zhang, D. Borchardt, P. Feng, Self-doped Ti3+ enhanced photocatalyst for hydrogen production under visible light. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 11856–11857 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja103843d
K. Komaguchi, T. Maruoka, H. Nakano, I. Imae, Y. Ooyama, Y. Harima, Electron-transfer reaction of oxygen species on TiO2 nanoparticles induced by Sub-band-gap illumination. J. Phys. Chem. C. 114, 1240–1245 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp909678e
Y. Xu, R. Ahmed, D. Klein, S. Cap, K. Freedy, S. McDonnell, G. Zangari, Improving photo-oxidation activity of water by introducing Ti3+ in self-ordered TiO2 nanotube arrays treated with Ar/NH3. J. Power Sources. 414, 242–249 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2018.12.083
J. Song, M. Zheng, X. Yuan, Q. Li, F. Wang, L. Ma, Y. You, S. Liu, P. Liu, D. Jiang, L. Ma, W. Shen, Electrochemically induced Ti3+ self-doping of TiO2 nanotube arrays for improved photoelectrochemical water splitting. J. Mater. Sci. 52, 6976–6986 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-0930-z
Y. Fu, A. Mo, A review on the electrochemically self-organized titania nanotube arrays: synthesis, modifications, and biomedical applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-018-2597-z
K. Arifin, R.M. Yunus, L.J. Minggu, M.B. Kassim, Improvement of TiO2 nanotubes for photoelectrochemical water splitting: review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 46, 4998–5024 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.11.063
Z. Su, W. Zhou, Formation, morphology control and applications of anodic TiO2 nanotube arrays. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 8955–8970 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1039/c0jm04587j
Q. Kang, J. Cao, Y. Zhang, L. Liu, H. Xu, J. Ye, Reduced TiO2 nanotube arrays for photoelectrochemical water splitting. J. Mater. Chem. A. 1, 5766–5774 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ta10689f
M.A. Boda, M.A. Shah, Fabrication mechanism of compact TiO2 nanotubes and their photo-electrochemical ability. Mater. Res. Express. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aa7cd2
A. Mir, M.A. Shah, Cyclic voltammetry response of TiO2 nanostructures prepared via fast and facile microwave irradiation. Bull. Mater. Sci. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-022-02703-7
K.S. Ali, R. Karunanithi, M. Prashanth, S. Sivasakaran, B. Subramanian, H.S. Jailani, Structure and mechanical properties of in-situ synthesized α-Ti/TiO2/TiC hybrid composites through mechanical milling and spark plasma sintering. Ceram. Int. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.12.342
J.F. Mir, S. Rubab, M.A. Shah, Hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanosheets with enhanced photo-electrochemical ability fabricated via single step anodization. Chem. Phys. Lett. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cplett.2020.137584
S.W. Park, J.T. Jang, J. Cheon, H.H. Lee, D.R. Lee, Y. Lee, Shape-dependent compressibility of TiO2 anatase nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C. 112, 9627–9631 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp801555a
J. Bansal, S.K. Swami, A. Singh, T. Sarao, V. Dutta, A.K. Hafiz, S.N. Sharma, Apparatus-dependent sol-gel synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 42, 432–439 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2019.1699427
V.N. Kuznetsov, N.I. Glazkova, R.V. Mikhaylov, N. Serpone, Additional specific channel of photoactivation of solid semiconductors. A revisit of the thermo-/photo-stimulated bleaching of photoinduced Ti3+ color centers in visible-light-active photochromic rutile titania. J. Phys. Chem. C. 122, 13294–13303 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b08998
Sekiya, T., Yagisawa, T., Kamiya, N., Mulmi, D. Das, Kurita, S., Murakami, Y., Kodaira, T.: Defects in anatase TiO2 single crystal controlled by heat treatments. J. Phys. Soc. Japan. 73, 703–710 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1143/JPSJ.73.703
A. Mateen Tantray, M.A. Shah, Photo electrochemical ability of dense and aligned ZnO nanowire arrays fabricated through electrochemical anodization. Chem. Phys. Lett. 747, 137346 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cplett.2020.137346
V.N. Kuznetsov, N. Serpone, On the origin of the spectral bands in the visible absorption spectra of visible-light-active TiO2 specimens analysis and assignments. J. Phys. Chem. C. 113, 15110–15123 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp901034t
C. Kim, S. Kim, J. Lee, J. Kim, J. Yoon, Capacitive and oxidant generating properties of black-colored TiO2 nanotube array fabricated by electrochemical self-doping. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 7, 7486–7491 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b00123
W. Liao, J. Yang, H. Zhou, M. Murugananthan, Y. Zhang, Electrochemically self-doped TiO2 nanotube arrays for efficient visible light photoelectrocatalytic degradation of contaminants. Electrochim. Acta. 136, 310–317 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2014.05.091
W.W. Gärtner, Depletion-layer photoeffects in semiconductors. Phys. Rev. 116, 84–87 (1959). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.116.84
Y. Yang, J. Liao, Y. Li, X. Cao, N. Li, C. Wang, S. Lin, Electrochemically self-doped hierarchical TiO2 nanotube arrays for enhanced visible-light photoelectrochemical performance: an experimental and computational study. RSC Adv. 6, 46871–46878 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra05805a
H. Choi, D. Shin, B.C. Yeo, T. Song, S.S. Han, N. Park, S. Kim, Simultaneously controllable doping sites and the activity of a W-N codoped TiO2 photocatalyst. ACS Catal. 6, 2745–2753 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.6b00104
J. Li, C. Liu, Y. Ye, J. Zhu, S. Wang, J. Guo, T.K. Sham, Tracking the local effect of fluorine self-doping in anodic TiO2 nanotubes. J. Phys. Chem. C. 120, 4623–4628 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b11445
X. Deng, H. Zhang, R. Guo, Q. Ma, Y. Cui, X. Cheng, M. Xie, Q. Cheng, Effect of Ti3+ on enhancing photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical properties of TiO2 nanorods/nanosheets photoelectrode. Sep. Purif. Technol. 192, 329–339 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2017.10.029
J. Huo, Y. Hu, H. Jiang, C. Li, In situ surface hydrogenation synthesis of Ti3+ self-doped TiO2 with enhanced visible light photoactivity. Nanoscale 6, 9078–9084 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4nr00972j
H. Cui, W. Zhao, C. Yang, H. Yin, T. Lin, Y. Shan, Y. Xie, H. Gu, F. Huang, Black TiO2 nanotube arrays for high-efficiency photoelectrochemical water-splitting. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2, 8612–8616 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ta00176a
G. Wang, H. Wang, Y. Ling, Y. Tang, X. Yang, R.C. Fitzmorris, C. Wang, J.Z. Zhang, Y. Li, Hydrogen-treated TiO2 nanowire arrays for photoelectrochemical water splitting. Nano Lett. 11, 3026–3033 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl201766h
H. Li, J. Chen, Z. Xia, J. Xing, Microwave-assisted preparation of self-doped TiO2 nanotube arrays for enhanced photoelectrochemical water splitting. J. Mater. Chem. A. 3, 699–705 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ta05021e
S.A. Bakar, C. Ribeiro, Low temperature synthesis of N-doped TiO2 with rice-like morphology through peroxo assisted hydrothermal route: materials characterization and photocatalytic properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 377, 121–133 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.03.137
Z. Zhang, M.N. Hedhili, H. Zhu, P. Wang, Electrochemical reduction induced self-doping of Ti3+ for efficient water splitting performance on TiO2 based photoelectrodes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 15, 15637–15644 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cp52759j
Q. Li, M. Zheng, B. Zhang, C. Zhu, F. Wang, J. Song, M. Zhong, L. Ma, W. Shen, InP nanopore arrays for photoelectrochemical hydrogen generation. Nanotechnology (2016). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/27/7/075704
A.I. Kontos, V. Likodimos, T. Stergiopoulos, D.S. Tsoukleris, P. Falaras, I. Rabias, G. Papavassiliou, D. Kim, J. Kunze, P. Schmuki, Self-organized anodic TiO2 nanotube arrays functionalized by iron oxide nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 21, 662–672 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/cm802495p
M. Shang, H. Hu, G. Lu, Y. Bi, Synergistic effects of SrTiO3 nanocubes and Ti3+ dual-doping for highly improved photoelectrochemical performance of TiO2 nanotube arrays under visible light. J. Mater. Chem. A. 4, 5849–5853 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ta00033a
A. Wolcott, W.A. Smith, T.R. Kuykendall, Y. Zhao, J.Z. Zhang, Photoelectrochemical water splitting using dense and aligned TiO2 nanorod arrays. Small 5, 104–111 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.200800902
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support of the Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi for the establishment of LMN Laboratory through the Nano-Mission project. The authors are also indebted to NIT Srinagar for fellowship and valuable discussions of Mohsin, Jaffar, and Mateen besides also thanking Mr. Nayeem for investing his precious time in performing various characterizations of samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mir, A., Shah, M.A. Fabrication of highly stable Titania photoanode with enhanced photocurrent density. Appl. Phys. A 128, 1105 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-06198-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-06198-1