Abstract
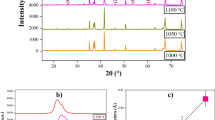
Samples of CoFe1.5Ni0.5O4 were synthesized using the solid-state reaction method. As depicted from XRD plots, peak intensities increases as the sintering temperature goes from 1200 to 1300 °C signifying that the crystallinity has improved. Both the samples possess a spinel structure with space group Fd-3 m. The Rietveld refinement of the samples was done using Full-Prof software to calculate the cationic distribution and other structural parameters. The cation distribution for CoFe1.5Ni0.5O4 sintered at 1200 and 1300 °C were found to be (Co0.25Fe0.75) [Co0.75Fe1.23Ni0.03]O4 and (Co0.25Fe0.75) [Co0.76Fe1.21Ni0.03]O4 respectively. Also the value of lattice constants for the sample sintered at 1300 °C was found to be 8.355 Å which is greater than the lattice constant (8.342 Å) of the sample sintered at 1200 °C. The temperature-dependent dielectric characteristics of the samples were investigated in this work. This study revealed that as the sintering temperature rises, έ and tan δ decrease. Magnetic properties such as coercivity, remanence and saturation magnetizations were reported to decrease as the sintering temperature increased. The respective values of coercivity (Hc), remanence (Mr) and saturation magnetization (Ms) were 87.06 and 71.85 Oe, 9.61 and 7.98 and 63.90 and 56.90 emu/g for the samples sintered at 1200 and 1300 °C. Using low dielectric constant materials, low heat dissipation and parasitic capacitance are obtained, allowing these materials to be utilized in faster switching speeds in devices.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Q. Zhao, Z. Yan, C. Chen, J. Chen, Spinels: controlled preparation, oxygen reduction/evolution reaction application, and beyond. Chem. Rev. 117, 10121–10211 (2017)
A. Šutka, K.A. Gross, Spinel ferrite oxide semiconductor gas sensors. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 222, 95–105 (2016)
T. Tatarchuk, M. Bououdina, J. J. Vijaya, L. J. Kennedy, Spinel ferrite nanoparticles: synthesis, crystal structure, properties, and perspective applications. In Proc. international conference on nanotechnology and nanomaterials (Springer Nature, Switzerland, 2016), p.305–325.
S. Dou, Review and prospects of Mn-based spinel compounds as cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Ionics 21, 3001–3030 (2015)
S.D. Bhame, P.A. Joy, J. Appl. Phys. 100, 113911 (2006)
K. Kamala Bharathi, C.V. Ramana, J. Mater. Res. 26, 584–591 (2011)
B. Zhou, Y.-W. Zhang, C.-S. Liao, C.-H. Yan, L.-Y. Chen, S.-Y. Wang, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 280, 327–333 (2004)
S. Wells, C.V. Ramana, Ceram. Int. 39, 9549–9556 (2013)
A. Rafferty, T. Prescott, D. Brabazon, Sintering behavior of cobalt ferrite ceramic. Ceram. Int. 34, 15–21 (2008)
R.C. Che, C.Y. Zhi, C.Y. Liang, X.G. Zhou, Fabrication and microwave absorpotion of carbon nanotubes/CoFe2O4 spinel nanocomposite. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 033105-1–033105-3 (2006)
H. Yüngevis, E. Ozel, Effect of milling process on the properties of CoFe2O4. Ceram. Int. 39, 5503–5511 (2013)
M. Sugimoto, The past, present and future of ferrites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 82, 269–280 (1999)
K. Kamala Bharathi, G. Markendeyulu, C.V. Ramana, Structural, magnetic, electrical and magnetoelectric properties of Sm- and Hosubstituted nickel ferrites. J. Phys. Chem. C. 115, 554–560 (2011)
K. Kamala Bharathi, M. Noor-A-Alam, R.S. Vemuri, C.V. Ramana, Correlation between microstructure, electrical and optical properties of nanocrystalline NiFe1.925Dy0.075O4 thin films. RSC Adv. 2, 941–948 (2012)
K. Kamala Bharathi, G. Markendeyulu, C.V. Ramana, Enhanced dielectric property of Ni ferrite by Sm and Ho substitution. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 13, G98–G102 (2010)
Z. Gu, X. Xiang, G. Fan, F. Li, Facile synthesis and characterization of cobalt ferrite nanocrystal via a simple reduction–oxidation route. J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 18459–18466 (2008)
U. Kurtan, R. Topkaya, A. Baykal, M.S. Toprak, Temperature dependent magnetic properties of CoFe2O4/CTAB nanocomposite synthesized by sol–gel auto-combustion method. Ceram. Int. 39, 6551–6558 (2013)
R. Peelamedu, C. Grimes, D. Agrawal, R. Roy, P. Yadoji, Ultralow dielectric constant nickel–zinc ferrites using microwave sintering. J. Mater. Res. 18, 2292–2295 (2003)
S. Phanichphant, Cellulose-precursor synthesis of nanocrystalline Co0. 5Cu0. 5Fe2O4 spinel ferrites. Mater. Res. Bull. 47, 473–477 (2012)
G.J. Long, F. Grandjean, Mossbauer spectroscopy applied to inorganic chemistry, vol. 3 (Springer Science & Business Media, Heidelberg, 2013)
A. Belous et al., High-Q microwave dielectric materials based on the spinel Mg2TiO4. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 89, 3441–3445 (2006)
T.J. Coutts, X. Wu, W.P. Mulligan, J.M. Webb, High-performance, transparent conducting oxides based on cadmium stannate. J. Electron. Mater. 25, 935–943 (1996)
N. Ueda et al., New oxide phase with wide band gap and high electroconductivity, MgIn2O4. Appl. Phys. Lett. 61, 1954–1955 (1992)
M. Labeau, V. Reboux, D. Dhahri, J.C. Joubert, New mixed oxides as thin film transparent electrodes: spinel phase CdIn2O4. Thin Sol. Films 136, 257–262 (1986)
A.J. Nozik, Optical and electrical properties of Cd2 Sn O4: a defect semiconductor. Phys. Rev. B 6, 453 (1972)
A.R. Molla et al., Microstructure, mechanical, thermal, EPR and optical properties of MgAl2O4: Cr3. spinel glass-ceramic nanocomposites. J. Alloy. Compd. 583, 498–509 (2014)
M. AsifKhan et al., Cleaved cavity optically pumped InGaN-GaN laser grown on spinel substrates. Appl. Phys. Lett. 69, 2418–2420 (1996)
M.S. Whittingham, Lithium batteries and cathode materials. Chem. Rev. 104, 4271–4302 (2004)
C. Wei et al., Valence change ability and geometrical occupation of substitution cations determine the pseudocapacitance of spinel ferrite XFe2O4 (X= Mn Co, Ni, Fe). Chem. Mater. 28, 4129–4133 (2016)
Y. Slimani et al., Calcination efect on the magneto-optical properties of vanadium substituted NiFe2O4 nanoferrites. J. Mater. Sci. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01243-x
Y. Slimani et al., Investigation of structural and physical properties of Eu3+ ions substituted Ni0.4Cu0.2Zn0.4Fe2O4 spinel ferrite nanoparticles prepared via sonochemical approach. Result. Phys. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2020.103061
A.A. Munirah et al., Effect of Nb3+ substitution on the structural, magnetic, and optical properties of Co0.5Ni0.5Fe2O4 nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 9, 430 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9030430
M.A. Almessiere, Impact of La3+ and Y3+ ion substitutions on structural, magnetic and microwave properties of Ni0.3Cu0.3Zn0.4Fe2O4 nanospinel ferrites synthesized via sonochemical route. RSC Adv. 9, 30671 (2019)
S. Jauhar, J. Kaur, A. Goyal, S. Singhal, Tuning the properties of cobalt ferrite: a road towards diverse applications. R. Soc. Chem. Adv. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA21224G
N.B. Velhal, N.D. Patil, A.R. Shelke, N.G. Deshpande, V.R. Puri, Structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of nickel substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles: effect of nickel concentration. AIP Adv. 5, 097166 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4931908
G.R. Gajula, L.R. Buddiga, K.N. Chidambara Kumar, N. Vattikunta, M. Dasari, Effect of Gd and Nb on dielectric and magnetic transition temperature of BaTiO3- Li0.5Fe2.5O4 composites. Phys. B 560, 1–5 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2019.02.035
G.R. Gajula, L.R. Buddiga, K.N. Chidambara Kumar, N. Vattikunta, M. Dasari, Dielectric, magnetic and magneto-electric studies of lithium ferrite synthesized by solid state technique for wave propagation application. J. Sci. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsamd.2018.04.007
G.R. Gajula et al., Structural, ferroelectric, dielectric, impedance and magnetic properties of Gd and Nb doped barium titanate-lithium ferrite solid solutions. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 494, 165822 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.165822
G.P. Nethala et al., Influence of Cr on structural, spectroscopic and magnetic properties of CoFe2O4 grown by the wet chemical method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 238, 121903 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.121903
G.R. Gajula, K.N. Chidambara Kumar, L.R. Buddiga, G.P. Nethala, Dielectric and impedance properties of Li0.5Fe2.5O4 doped BaTiO3 composite ceramics. Result. Phys. 11, 899–904 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2018.10.057
Y. Slimani et al., Role of WO3 nanoparticles in electrical and dielectric properties of BaTiO3–SrTiO3 ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03317-7
M.H.A. Mhareb, Y. Slimani, Y.S. Alajerami, M.I. Sayyed, E. Lacomme, M.A. Almessiere, Structural and radiation shielding properties of BaTiO3 ceramic with different concentrations of Bismuth and Ytterbium. Ceram. Int. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.08.055
Y. Slimani et al., Study on the addition of SiO2 nanowires to BaTiO3: Structure, morphology, electrical and dielectric properties. J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 156, 110183 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2021.110183
Y. Slimani, S.E. Shirsath, E. Hannachi, M.A. Almessiere, M.M. Aouna, N.E. Aldossary et al., (BaTiO3)1–x + (Co0.5Ni0.5Nb0.06Fe1.94O4)x nanocomposites: structure, morphology, magnetic and dielectric properties. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 104, 1–11 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1111/jace.17931
Y. Slimani et al., Excess conductivity study in nano-CoFe2O4-added YBa2Cu3O7−d and Y3Ba5Cu8O18±x superconductors. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-015-3144-0
E. Hannachi, M.A. Almessiere, Y. Slimani, A. Baykal, F. Ben Azzouz, AC susceptibility investigation of YBCO superconductor added by carbon nanotubes. J. Alloy. Compd. 812, 152150 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.152150
Y. Slimani, E. Hannachi, A. Ekicibil, M.A. Almessiere, F. Ben Azzouz, Investigation of the impact of nano-sized wires and particles TiO2 on Y-123 superconductor performance. J. Alloy. Compd. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.12.062
A. Hamrita et al., Superconducting properties of polycrystalline YBa2Cu3O7—d prepared by sintering of ball-milled precursor powder. Ceram. Int. 40, 1461–1470 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.07.030
K. Venkata Siva, S. Sudersan, A. Arockiarajan, Bipolar magnetostriction in CoFe2O4: effect of sintering, measurement temperature and prestress. J. Appl. Phys. 128, 103904 (2020)
S. Ramay, M. Saleem, S. Atiq, S.A. Siddiqi, S. Naseem, M.S. Anwar, Influence of temperature on structural and magnetic properties of Co0:5Mn0:5Fe2O4 ferrites. Bull. Mater. Sci. 34, 1415–1419 (2011)
C.R. Stein, M.T.S. Bezerra, G.H.A. Holanda et al., Structural and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation at increasing temperatures. AIP Adv. 8, 056303 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5006321
F. Acosta-Humánez, O. Almanza, C. Vargas-Hernández, Effect of sintering temperature on the structure and mean crystallite size of Zn1-xCoxO x = 0.01–0.05 samples. Superficiesy Vacío 27(2), 43–48 (2014)
M. Al-Maashani, A. Gismelseed, K. Khalaf, A.A. Yousif, A. Al-Rawas, H. Widatallah, M. Elzain, Structural and Mössbauer study of nanoparticles CoFe2O4 prepared by sol-gel auto-combustion and subsequent sintering. Hyperfine Interact. 239, 439 (2018)
C. Caizer, M. Stefanescu, Magnetic characterization of nanocrystalline Ni–Zn ferrite powder prepared by the glyoxylate precursor method. J. Phys. D 35, 3035 (2002)
P. Anjana, R.S. Arun Raj, R. Jose, P.M. Manisha Kumari, D. Sarun, K.L. Sajan, Joy, Highly enhanced dielectric permittivity in CoFe2O4 by the Gd substitution in the octahedral sites. J. Alloy. Compd. 854, 155758 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.155758
G.A. Lone, M. Ikram, Investigating the structural and dielectric properties of CoFe2−xNixO4 spinel ferrite. J. Alloy. Compd. 908, 164589 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.164589
R. Das, S. Sarkar, Determination of intrinsic strain in poly(vinylpyrrolidone)-capped silver nano-hexapod using X-ray diffraction technique. Curr. Sci. 109(4), 775–778 (2015)
D. Nath, F. Singh, R. Das, X-ray diffraction analysis by Williamson-Hall Halder-Wagner and size-strain plot methods of CdSe nanoparticles—a comparative study. Mater. Chem. Phys. 239, 122021 (2020)
K.V. Chandekar, K. Mohan Kant, Size-strain analysis and elastic properties of CoFe2O4 nanoplatelets by hydrothermal method. J. Mol. Struct. 0022–2860(17), 31315–31317 (2018)
M. Birkholz, Thin film analysis by X-ray scattering (Wiley-VCH Verlag, Weinheim, 2006)
D. Balzar, H. Ledbetter, Voigt-function modeling in fourier analysis of size- and strain-broadened X-ray diffraction peaks. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 26(1), 97–103 (1993)
V.D. Mote, Y. Purushotham, B.N. Dole, Williamson-Hall analysis in estimation of lattice strain in nanometer-sized ZnO particles. J. Theor. Appl. Phys. 6, 6–14 (2012)
P. Arora Jha, A.K. Jha, Influence of processing conditions on the grain growth and electrical properties of barium zirconate titanate ferroelectric ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 513, 580–585 (2012)
R. Nongjai, K. Shakeel Khan, H.A. Asokan, I. Khan, Magnetic and electrical properties of in doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 112, 084321 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4759436
U. Kumar, K. Ankur, D. Yadav, S. Upadhyay, Synthesis and characterization of Ruddlesden-Popper system (Ba1xSrx)2SnO4. Mater. Charact. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2020.110198110198
K. Sakthipandi, K. Kannagi, A. Hossain, Effect of lanthanum doping on the structural, electrical, and magnetic properties of Mn0.5Cu0.5LaxFe2-xO4 nanoferrites. Ceram. Int. 46, 19634–19638 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.04.255
L.L. Hench, J.K. West, Principles of electronic ceramics (John Wiley, New York, 1990)
N. Nazir, M. Ikram, Structural, dielectric, and conductivity studies of strontium-doped Gd2NiMnO6 perovskite. J. Mater. Sci. 31, 23002–23011 (2020)
S.A. Islam, F.A. Andrabi, F. Mohmed, K. Sultan, M. Ikram, K. Asokan, Ba doping induced modifications in the structural, morphological and dielectric properties of double perovskite La2NiMnO6 ceramics. J. Solid-State Chem. 290, 121597 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2020.121597
M.D. Rather, R. Samad, B. Want, J. Electron. Mater. 47, 2143 (2018)
W. Chiu, S. Radiman, R. Abd-Shukor, M. Abdullah, P. Khiew, Tunable coercivity of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles via thermal annealing treatment. J. Alloys Compd. 459, 291–297 (2008)
U. Kurtan, R. Topkaya, A. Baykal, M. Toprak, Temperature dependent magnetic properties of CoFe2O4/CTAB nanocomposite synthesized by sol–gel auto-combustion technique. Ceram. Int. 39, 6551–6558 (2013)
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the central research facility centre (CRFC) National Institute of Technology Srinagar for providing the XRD facility. The Ministry of India (MoE) is also acknowledged for financial support. SEM/EDX and Dielectric measurements were taken from IUAC, New Delhi under the supervision of Dr K. Asokan, Mr R.C.Meena and Dr Saif. The authors are also highly thankful to Dr Basharat want (Professor, Dept. of Physics, Kashmir University) for the VSM facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lone, G.A., Ikram, M. Effect of sintering temperature on structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of CoFe1.5Ni0.5O4 prepared by solid-state reaction method. Appl. Phys. A 128, 1013 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-06159-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-06159-8