Abstract
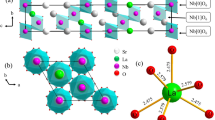
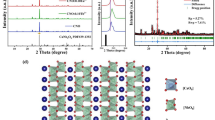
Novel red phosphors Sr7Sb2O12:Eu3+ and Sr7Sb2O12:Eu3+, M+ (M = Li, Na, K) were synthesized via a high temperature solid-state method and their luminescent properties were investigated to figure out the promising application in warm white light-emitting diodes (LED). The phase structure, crystal morphology, luminescence properties, luminescence decay lifetime, thermal stability and chromaticity coordinate of the as-synthesized phosphors were investigated in detail. Sr7Sb2O12:Eu3+ could be efficiently excited by the near-ultraviolet (UV) light and exhibited bright red emission around 612 nm. When co-doped with the charge compensation M+ (M = Li, Na, K) ions, the emission intensity of Eu3+ can be enhanced to some extent. The optimal Eu3+ doping concentration was determined to be about x = 0.2 and concentration quenching mechanism in Sr7Sb2O12:Eu3+ sample was attributed to the electric dipole–dipole interaction. The temperature-dependent spectra of Sr7Sb2O12:Eu3+ implied that this sample shows good thermal-stable properties. The decay lifetime of Sr7Sb2O12:0.2Eu3+ was about 1.44 ms. Combining with the red Sr7Sb2O12:0.20Eu3+, blue BaMgAl10O17:Eu2+, yellow (Ba,Sr)2SiO4:Eu2+ phosphor and a 395 nm near-UV LED chip, a white LED with low correlated color temperature (CCT = 4260 K) and high-color rendering index (Ra = 91.8) was fabricated. The overall work suggested that Sr7Sb2O12:Eu3+ phosphor is a promising red-emitting component applied in warm white LED.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Nyman, M.A. Rodriguez, L.E. Shea-Rohwer et al., Highly versatile rare earth tantalate pyrochlore nanophosphors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 1165211653 (2009)
E.F. Schubert, J.K. Kim, Solid-state light sources getting smart. Science 308, 1274–1278 (2005)
W. Yang, C. Liu, S. Lu, et al., AIE-active smart cyanostyrene luminogens: polymorphism-dependent multicolor mechanochromism, J. Mater, Chem. C, 6(2018)290–298.
C. Feldmann, T. Justel, C.R. Ronda, P.J. Schmidt, Inorganic luminescent materials: 100 years of research and application. Adv. Funct. Mater. 13, 511–516 (2003)
X. Huang, S. Han, W. Huang, X. Liu, Enhancing solar cell efficiency: the search for luminescent materials as spectral converters. Chem. Soc. Rev. 42, 173 (2013)
H. Zhu, C. Lin, W. Luo et al., Highly efficient non- rare-earth red emitting phosphor for warm white light-emitting diode. Nat. Commun. 5, 4312 (2014)
M. Nazarow, Luminescence mechanism of highly efficient YAG and TAG phosphors, Moldavian. J. Phys. Sci. 4, 347–356 (2005)
Z.H. Sun, M.Q. Wang, Z. Yang et al., Enhanced red emission from Eu3+–Bi3+ co-doped Ca2YSbO6 phosphors for white light-emitting diode. J. Alloys Compd. 658, 453–458 (2016)
X. Huang, B. Li, H. Guo, D. Chen, Molybdenum-doping-induced photoluminescence enhancement in Eu3+-activated CaWO4 red-emitting phosphors for white light-emitting diodes. Dyes Pigments 143, 86–89 (2017)
J. Dhanaraj, R. Jagannathan, D.C. Trivedi, Y2O2S:Eu3+ nanocrystals-synthesis and luminescent properties. J. Mater. Chem. 13, 1778–1782 (2003)
R.J. Xie, N. Hirosaki, T. Suehiro et al., A simple, efficient synthetic route to Sr2Si5N8:Eu2+-based red posphors for white light-emitting diodes. Chem. Mater. 18, 5578–5583 (2006)
A. Fu, C. Zhou, Q. Chen, Z. Lu, T. Huang, Preparation and optical properties of a novel double-perovskite phosphor, Ba2GdNbO6:Mn4+, for lighting-emitting diodes. Ceram Int. 43, 6353–6362 (2017)
A. Fu, A. Guan, F. Gao, X. Zhang, L. Zhou, A novel double perovskite La2ZnTiO6:Eu3+ red phosphor for solid-state lighting: synthesis and optimum luminescence. Opt. Laser. Technol. 96, 43–49 (2017)
L. Li, W. Chang, W. Chen et al., double perovskite LiLaMgWO6: Eu3+ novel red-emitting phosphors for solid-state lighting: synthesis, structure and photoluminescent properties. Ceram Int. 43, 2720–2729 (2017)
Y. Guo, B. Kee Moon, S. Heum Park et al., A red-emitting perovskite-type SrLa1-xMgTaO6: xEu3+ for white LED application, J. Lumin. 167(2015)381–385.
E. J. Cussen, T.W. Yip, G.O’Neill, et al., A comparison of the transport properties of lithium-stuffed garnets and the conventional phase LiLn3Te2O12, J. Solid State Chem., 194(2011)470–475.
V. Thangadurai, J. Schwenzel, W. Weppner et al., Tailoring ceramics for specific application: a case study of the development of all-solid-state lithium batteries. Ionics 11, 11–23 (2005)
J. Zhong, D. Chen, W. Zhao et al., garnet-based Li6CaLa2Sb2O12:Eu3+ red phosphors: a potential color-converting materials for warm white light-emitting diodes. J. Mater. Chem. C 3, 4500–4510 (2015)
D. Huang, P. Dang, Y. Wei, et al., A deep-red-emitting, Bi3+/Mn4+-doped CaLi6La2Nb2O12 phosphor: luminescence and energy transfer properties, Mater. Res. Bull., 124(2000).
F. Liu, Y. Fang, N. Zhang et al., Blue light excited Li6CaLa2M2O12: Eu3+ (M= Ta, Sb) red-emitting phosphors: structure and photoluminescence properties. Ceram. Int. 40, 14781–14786 (2014)
Y. Han, S. Wang, H. Liu et al., A novel Al3+ modified Li6CaLa2Sb2O12: Mn4+ far-red-emitting phosphor with garnet structure for plant cultivation. J. Lumin. 221, 117031 (2020)
Z. Yan, X. Yang, S. Xiao, Far-red-emitting Li6SrLa2Sb2O12: Mn4+ phosphor for plant growth LEDs application. Mater. Res. Bull. 133, 111040 (2021)
A. Alemi, A. Renaud, C. R. Seances, Acad. Sci. Ser., C. 287(1978)199.
X. Yao, Y. Zhong, J. Che et al., Optical properties of double-perovskite Sr3TeO6:Sm3+ reddish-orange emitting phosphors for w-LEDs. J. Lumin. 240, 11826 (2021)
F.B. Xiong, F.X. Xu, X.G. Meng et al., Eu3+-activated Ln2TeO6 (Ln=La, Y) as a novel red-emitting phosphor for warm white LEDs. J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron 31, 22945–22956 (2020)
F.B. Xiong, H. Chen, H.F. Lin et al., Novel red emitting LnTaO4: Eu3+ (Ln = La, Y) phosphors for warm white LEDs. Physica B: Conden. Mater. 582, 411981 (2020)
M. Gao, X. Yu, Z. Li et al., synthesis and luminescent properties of Sr2SnO4: Pr3+, M+ (M=Li, Na and K) phosphors with layered perovskite-related structure. J. Lumin. 226, 117423 (2020)
G. Blasse, Energy transfer in oxidic phosphors. Phys. Lett. 28, 444–445 (1968)
L. Ozawa, P.M. Jaffe, The mechanism of the emission color shift with activator concentration in +3 activated phosphors. J. Electrochem. Soc. 118, 1678 (1971)
D.L. Dexter, J.H. Schulman, Theory of concentration quenching in inorganic phosphors. J. Chem. Phys. 22, 1063–1070 (1954)
H. Zhou, Y. Jin, M. Jiang, Q. Wang, X. Jiang, A single-phased tunable emission phosphor MgY2Si3O10:Eu3+, Bi3+ with efficient energy transfer for white LEDs. Dalton Trans. 44, 1102 (2015)
Y.F. Wu, Y.T. Nien, Y.J. Wang et al., Enhancement of photoluminescence and color purity of CaTiO3: Eu phosphor by Li doping. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 95, 1360–1366 (2012)
S.J. Gwak, P. Arunkumar, W.B. Im, a new blue-emitting oxohalide phosphor Sr4OCl6:Eu2+ for thermally stable, efficient white-light-emitting devices under near-UV. J. Phys. Chem. C 188, 2686–2692 (2014)
V. Bachmann, C. Ronda, O. Oeckler, W. Schnick, A. Meijerink, Color point tuning for (Sr, Ca, Ba)Si2O2N2: Eu2+ for white light LEDs. Chem. Mater. 21, 316–323 (2009)
M. Fan, Q. Chen, Y. Wang et al., High efficient Eu3+-activated Ca(La, Gd)MgSbO6 double perovskite phosphors: thermal stability improvement by composition modulating. J. Lumin. 215, 116674 (2019)
Q. Lu, L. Wang, W. Huang et al., Enhanced luminescence properties of doubke perovskite (Ba, Sr)LaMgSbO6: Eu3+ phosphors based on composition modulation. J. Alloys Compd. 717, 156–163 (2017)
C.S. McCamy, Correlated color temperature as an explicit function of chromaticity coordinates. Color Res. Appl. 17, 142–144 (1992)
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by the Fujian Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 2020J01297), and the Science Technology innovation project of Xiamen (Grant No. 3502Z20193056).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, W.B., Xiong, F.B., Yang, Y. et al. A novel red-emitting Sr7Sb2O12:Eu3+, M+ (M = Li, Na, K) phosphor for warm white LED: synthesis, optical properties, and LED fabrication. Appl. Phys. A 128, 584 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-05664-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-05664-0