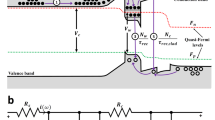
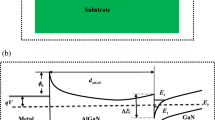
Abstract
Based on the three-dimensional Schrödinger equation and hot-carrier effects, a physical model to clarify how the source–drain voltage affects the energy needed for the emission or absorption of a photon in GaN heterojunctions is proposed. The proposed model predicts that the energy needed for the emission or absorption of a photon in GaN heterojunctions will be linearly reduced by the square of the source–drain voltage and the device temperature. Thus, they will shift the emission or absorption spectrum of emission or absorption. The results of voltage and temperature-dependent spectrum noted in the Raman and photoluminescence experiments support the predicted results by the proposed model. Additionally, temperature-dependent spectral broadening observed in experiments can be described by the proposed model. It suggests that quantum coupling should be considered in GaN devices because of the hot-carrier effects, which denote that the energy of channel electrons can be very high. It is also essential for accurately measuring temperature by Raman measurement.

Source–drain voltage-dependent Raman peak position of GaN HEMTs in on-state. Experimental data come from reference [2]




Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.K. Kaneriya, G. Rastogi, P.K. Basu, R.B. Upadhyay, A.N. Bhattacharya, Microelectron. Eng. 233, 111433 (2020).
K.R. Bagnall, E.A. Moore, S.C. Badescu, L. Zhang, E.N. Wang, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 88, 113111 (2017).
J. Kim, J.A. Freitas, J. Mittereder, R. Fitch, B.S. Kang, S.J. Pearton, F. Ren, Solid-State Electron. 50, 408 (2006)
H. Rao, G. Bosman, Solid-State Electron. 79, 11 (2013)
T. Brazzini, M.A. Casbon, H.R. Sun, M.J. Uren, J. Lees, P.J. Tasker, H. Jung, H. Blanck, M. Kuball, Appl. Phys. Lett. 106, 213502 (2015).
M. Ťapajna, R.J.T. Simms, M. Faqir, M. Kuball, Y. Pei, U.K. Mishra, Presented at the 2010 IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium, 2010 (unpublished).
Q. Hao, H.B. Zhao, Y. Xiao, M.B. Kronenfeld, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 116, 496 (2018)
I. Hwang, J. Kim, S. Chong, H.S. Choi, S.K. Hwang, J. Oh, J.K. Shin, U.I. Chung, IEEE Electron Device Lett. 34, 1494 (2013)
L.-F. Mao, H.-S. Ning, J.-Y. Wang, PLoS ONE 10, e0128438 (2015).
J. Kotani, J. Yaita, A. Yamada, N. Nakamura, K. Watanabe, J. Appl. Phys. 127, 234501 (2020).
L.F. Mao, IEEE Electron Device Lett. 28, 161 (2007)
L.F. Mao, Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 183511 (2007).
L.F. Mao, Appl. Phys. Lett. 91, 123519 (2007).
L.F. Mao, H. Ning, Z.L. Huo, J.Y. Wang, Sci. Rep. 5, 18307 (2015)
L.F. Mao, H. Ning, C. Hu, Z. Lu, G. Wang, Sci. Rep. 6, 24777 (2016)
S.M. Sze, K.K. Ng, Physics of Semiconductor Devices (Wiley, New Jersey, 2006).
A. Rashmi, S. Kranti, R.S. Haldar, Gupta. Solid-State Electron. 46, 621 (2002)
A. Loghmany, P. Valizadeh, J. Phys. D—Appl. Phys. 44, 125102 (2011).
S. Rabbaa, J. Stiens, J. Phys. D—Appl. Phys. 44, 325103 (2011).
A. Pais, Rev. Mod. Phys. 51, 863 (1979)
V.K. Khanna, Extreme-Temperature and Harsh-Environment Electronics.
D.C. Look, D.K. Lorance, J.R. Sizelove, C.E. Stutz, K.R. Evans, D.W. Whitson, J. Appl. Phys. 71, 260 (1992)
M.A. Huque, S.A. Eliza, T. Rahman, H.F. Huq, S.K. Islam, Solid-State Electron. 53, 341 (2009)
K.K. Young, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 36, 399 (1989).
S.H. Lee, Y.S. Yu, S.W. Hwang, D. Ahn, IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 8, 643 (2009)
T. Sawada, Y. Ito, K. Imai, K. Suzuki, H. Tomozawa, S. Sakai, Appl. Surf. Sci. 159–160, 449 (2000)
A.S. Barker, M. Ilegems, Phys. Rev. B 7, 743 (1973)
X.D. Wang, W.D. Hu, X.S. Chen, J.T. Xu, X.Y. Li, W. Lu, Opt. Quant. Electron. 42, 755 (2011)
Y.I. Alivov, E.V. Kalinina, A.E. Cherenkov, D.C. Look, B.M. Ataev, A.K. Omaev, M.V. Chukichev, D.M. Bagnall, Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 4719 (2003)
T.R. Lenka, A.K. Panda, Pramana 79, 151 (2012)
Yu. Tsung-Hsing, K.F. Brennan, J. Appl. Phys. 89, 3827 (2001)
P. Rinke, M. Winkelnkemper, A. Qteish, D. Bimberg, J. Neugebauer, M. Scheffler, Phys. Rev. B 77, 075202 (2008).
S. Schöche, P. Kühne, T. Hofmann, M. Schubert, D. Nilsson, A. Kakanakova-Georgieva, E. Janzén, V. Darakchieva, Appl. Phys. Lett. 103, 212107 (2013).
D.J. As, A. Zado, Q.Y. Wei, T. Li, J.Y. Huang, F.A. Ponce, Japanese J. Appl. Phys. 52, 08JN04 (2013).
Y. Xu, H.-Q. Sun, Y.-N. Xiao, S.-Y. Han, F. Ke, presented at the Advances in Optoelectronics and Micro/nano-optics, 2010 (unpublished).
G. Abstreiter, K. Ploog, Phys. Rev. Lett. 42, 1308 (1979)
A.J. Fischer, W. Shan, J.J. Song, Y.C. Chang, R. Horning, B. Goldenberg, Appl. Phys. Lett. 71, 1981 (1997)
Acknowledgements
The author acknowledges financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 61774014.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mao, LF. Modeling source–drain voltage-dependent energy needed for emission or absorption of a photon in GaN devices. Appl. Phys. A 128, 149 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-05282-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-05282-w