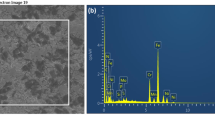
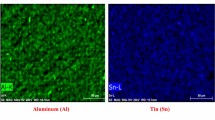
Abstract
The present study explores the effectiveness of powder mixed electrical discharge machining (PM-EDM) by utilizing the unique properties of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) on machining of hard-grade medical alloy (β-type titanium). To investigate the capabilities of the PM-EDM in terms of machinability, biocompatibility, tribological characteristics and surface integrity, the experiments were conducted according to the L18 orthogonal array. The analysis of variance (ANOVA) technique was employed for identifying the significant process parameters affecting metal removal rate (MRR). The ANOVA results revealed that the dielectric medium was the most significant factor that majorly affects the MRR (63.25 mm3/mm) and it was followed by the peak current (Ip), pulse on (pon), pulse off (poff) and electrode material. A 15A peak current at pulse-on/pulse-off time of 100/20 μs by using MWCNTs in the dielectric medium with a tungsten/copper tool electrode is the optimum parametric set. The biocompatibility of machined surfaces was scrutinized by cytotoxicity test which confirmed that the machining with MWCNTs elevated the biological responses of reformed surface and contributed to achieve the cell viability of 94%. The pin-on-disc wear results revealed that MWCNTs machined surface had the least value of wear rate and acted as a low frictional surface. Also, the recast layer produced after MWCNTs machining adhered strongly to the base material and exhibited twofold adhesion strength as compared to the water machined substrate. The formation of oxides and carbides in the presence of MWCNTs entities contributed to the tribological behaviour and biocompatibility of alloy. Thus, the excellent assets of MWCNTs elevate the potential of EDMing by diminishing the bottlenecks like the creation of surface defects in conventional EDM (deionized water medium) at high discharge energies.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Su, C. Luo, Z. Zhang, H. Hermawan, D. Zhu, J. Huang, Y. Liang, G. Li, L. Ren, Bioinspired surface functionalization of metallic biomaterials. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 77, 90–105 (2018)
S. Devgan, S.S. Sidhu, Potential of electrical discharge treatment incorporating MWCNTs to enhance the corrosion performance of the β-titanium alloy. Appl. Phys. A 126(3), 1–16 (2020)
F. Guillemot, Recent advances in the design of titanium alloys for orthopedic applications. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2(6), 741–748 (2005)
S.S. Sidhu, H. Singh, M.A.H. Gepreel, A Review on alloy design, biological response, and strengthening of β-Titanium Alloys as biomaterials. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 121, 111661 (2020)
A. Kumar, S. Maheshwari, C. Sharma, N. Beri, Research developments in additives mixed electrical discharge machining (AEDM): a state of art review. Mater. Manuf. Processes 25(10), 1166–1180 (2010)
A. Mahajan, S.S. Sidhu, T. Ablyaz, EDM surface treatment: an enhanced biocompatible interface, in Biomaterials in Orthopaedics and Bone Regeneration. ed. by S.B. Preetkanwal, S.S. Sarabjeet, B. Marjan, P. Chander (Springer, Singapore, 2019), pp. 33–40
A. Singh, R.K. Ghadai, K. Kalita, P. Chatterjee, D. Pamučar, EDM process parameter optimization for efficient machining of Inconel-718. Facta Univ. Ser. Mech. Eng. 18(3), 473–490 (2020)
Y.H. Guu, H. Hocheng, C.Y. Chou, C.S. Deng, Effect of electrical discharge machining on surface characteristics and machining damage of AISI D2 tool steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 358(1–2), 37–43 (2003)
A. Perumal, A. Azhagurajan, R. Prithivirajan, S.S. Kumar, Experimental investigation and optimization of process parameters in Ti–(6242) alpha–beta alloy using electrical discharge machining. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 31(4), 1787–1800 (2021)
Y.F. Luo, The dependence of interspace discharge transitivity upon the gap debris in precision electrodischarge machining. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 68(2), 121–131 (1997)
A. Mahajan, S.S. Sidhu, S. Devgan, MRR and surface morphological analysis of electrical-discharge-machined Co–Cr alloy. Emerg. Mater. Res. 9(1), 42–46 (2019)
G. Kucukturk, C. Cogun, A new method for machining of electrically nonconductive workpieces using electric discharge machining technique. Mach. Sci. Technol. 14(2), 189–207 (2010)
H. Kumar, Development of mirror like surface characteristics using nano powder mixed electric discharge machining (NPMEDM). Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 76(1–4), 105–113 (2015)
G. Singh, S.S. Sidhu, P.S. Bains, A.S. Bhui 2019 Surface evaluation of ED machined 316L stainless steel in TiO2 nano-powder mixed dielectric medium. Mater. Today Proc. 18, 1297–1303.
G. Singh, T.R. Ablyaz, E.S. Shlykov, K.R. Muratov, A.S. Bhui, S.S. Sidhu, Enhancing corrosion and wear resistance of Ti6Al4V alloy using CNTs mixed electro-discharge process. Micromachines 11(9), 850 (2020)
X. Wang, S. Yi, H. Guo, C. Li, S. Ding, Erosion characteristics of electrical discharge machining using graphene powder in deionized water as dielectric. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 108(1), 357–368 (2020)
V.D. Bui, J.W. Mwangi, A. Schubert, Powder mixed electrical discharge machining for antibacterial coating on titanium implant surfaces. J. Manuf. Process. 44, 261–270 (2019)
T.D. Nguyen, P.H. Nguyen, L.T. Banh, Die steel surface layer quality improvement in titanium μ-powder mixed die sinking electrical discharge machining. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 100(9), 2637–2651 (2019)
M.S. Dresselhaus, G. Dresselhaus, P.C. Eklund, Science of Fullerenes and Carbon Nanotubes: Their Properties and Applications (Elsevier, 1996)
P.J. Harris, Carbon nanotubes and related structures: new materials for the twenty-first century. Am. J. Phys. 72(3), 415 (2004)
L.P. Ichkitidze, S.V. Selishchev, A.Y. Gerasimenko, V.M. Podgaetsky, Mechanical properties of bulk nanocomposite biomaterial. Biomed. Eng. 49(5), 308–311 (2016)
M.A. Hussain, A. Maqbool, F.A. Khalid, N. Bakhsh, A. Hussain, J.U. Rahman, J.K. Park, T.G. Park, L.J. Hyun, M.H. Kim, Mechanical properties of CNT reinforced hybrid functionally graded materials for bioimplants. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 24, s90–s98 (2014)
V. Kavimani, K.S. Prakash, M.A. Pandian, Influence of r-GO addition on enhancement of corrosion and wear behavior of AZ31 MMC. Appl. Phys. A 123(8), 1–11 (2017)
P.S. Bains, G. Singh, A.S. Bhui, S.S. Sidhu, Parametric evaluation of medical grade titanium alloy in MWCNTs mixed dielectric using graphite electrode, in Biomaterials in Orthopaedics and Bone Regeneration. ed. by S.B. Preetkanwal, S.S. Sarabjeet, B. Marjan, P. Chander (Springer, Singapore, 2019), pp. 1–14
M. Gostimirovic, P. Kovac, M. Sekulic, B. Skoric, Influence of discharge energy on machining characteristics in EDM. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 26(1), 173–179 (2012)
V. Yadav, V.K. Jain, P.M. Dixit, Thermal stresses due to electrical discharge machining. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 42(8), 877–888 (2002)
P.V. Ramarao, M.A. Faruqi, Characteristics of the surfaces obtained in electro-discharge machining. Precis. Eng. 4(2), 111–113 (1982)
H.K. Kansal, S. Singh, P. Kumar, Parametric optimization of powder mixed electrical discharge machining by response surface methodology. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 169(3), 427–436 (2005)
A. Mahajan, S. Devgan, S.S. Sidhu, Surface alteration of biomedical alloys by electrical discharge treatment for enhancing the electrochemical corrosion, tribological and biological performances. Surf. Coat. Technol. 405, 126583 (2021)
Y. Xie, H.M. Hawthorne, A model for compressive coating stresses in the scratch adhesion test. Surf. Coat. Technol. 141(1), 15–25 (2001)
K.H. Syed, K. Palaniyandi, Performance of electrical discharge machining using aluminium powder suspended distilled water. Turk. J. Eng. Environ. Sci. 36(3), 195–207 (2012)
H. Rafii-Tabar, Computational modelling of thermo-mechanical and transport properties of carbon nanotubes. Phys. Rep. 390(4–5), 235–452 (2004)
S.M. Uddin, T. Mahmud, C. Wolf, C. Glanz, I. Kolaric, C. Volkmer, H. Höller, U. Wienecke, S. Roth, H.J. Fecht, Effect of size and shape of metal particles to improve hardness and electrical properties of carbon nanotube reinforced copper and copper alloy composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 70(16), 2253–2257 (2010)
P. Janmanee, A. Muttamara, Surface modification of tungsten carbide by electrical discharge coating (EDC) using a titanium powder suspension. Appl. Surf. Sci. 258(19), 7255–7265 (2012)
H. Marashi, A.A. Sarhan, M. Hamdi, Employing Ti nano-powder dielectric to enhance surface characteristics in electrical discharge machining of AISI D2 steel. Appl. Surf. Sci. 357, 892–907 (2015)
A. Mahajan, G. Singh, S. Devgan, S.S. Sidhu, EDM performance characteristics and electrochemical corrosion analysis of Co–Cr alloy and duplex stainless steel: a comparative study. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part E J. Process Mech. Eng. 235(4), 812–823 (2020)
T. Muthuramalingam, B. Mohan, Influence of discharge current pulse on machinability in electrical discharge machining. Mater. Manuf. Processes 28(4), 375–380 (2013)
R.S. Ruoff, D. Qian, W.K. Liu, Mechanical properties of carbon nanotubes: theoretical predictions and experimental measurements. C R Phys. 4(9), 993–1008 (2003)
M.M. Sari, M.Y. Noordin, E. Brusa, Role of multi-wall carbon nanotubes on the main parameters of the electrical discharge machining (EDM) process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 68(5), 1095–1102 (2013)
J.A. Rodríguez-González, C. Rubio-González, M. Jiménez-Mora, L. Ramos-Galicia, C. Velasco-Santos, Influence of the hybrid combination of multiwalled carbon nanotubes and graphene oxide on interlaminar mechanical properties of carbon fiber/epoxy laminates. Appl. Compos. Mater. 25(5), 1115–1131 (2018)
E. Mooney, P. Dockery, U. Greiser, M. Murphy, V. Barron, Carbon nanotubes and mesenchymal stem cells: biocompatibility, proliferation and differentiation. Nano Lett. 8(8), 2137–2143 (2008)
A. Mahajan, S.S. Sidhu, S. Devgan, Examination of hemocompatibility and corrosion resistance of electrical discharge-treated duplex stainless steel (DSS-2205) for biomedical applications. Appl. Phys. A 126(9), 1–11 (2020)
M. Atarian, H.R. Salehi, M. Atarian, A. Shokuhfar, Effect of oxide and carbide nanoparticles on tribological properties of phenolic-based nanocomposites. Iran. Polym. J. 21(5), 297–305 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Devgan, S., Mahajan, A. & Sidhu, S.S. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes in powder mixed electrical discharge machining: an experimental study, state of the art and feasibility prospect. Appl. Phys. A 127, 806 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04934-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04934-7