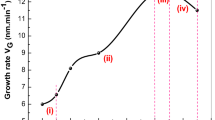
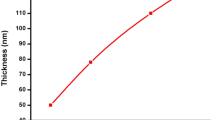
Abstract
Synthesizing thin films on various substrates and serving as electrodes for photosensor is challenging task. In this work, influence of pH on structural and optical properties of cadmium sulfide (CdS) thin film investigated using a chemical bath deposition method on a glass substrate. The fabricated CdS film was characterized by using an X-ray diffraction pattern and field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM). From the structural analysis study, it shows that CdS thin film has a hexagonal phase structure. FE-SEM analysis study revealed uniform and homogenous deposition on the glass. Moreover, at pH = 10, the smallest crystal size obtained ~3 nm. From optical properties, analysis shows that CdS has a 3.12 eV–3.13 eV bandgap. The electrical parameters for films show substantial growth in current after light illumination. Also, the photosensitivity found that their sensitivity to light increases with reduction in the pH value.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.S. Ferekides et al., CdTe thin film solar cells: device and technology issues. Sol. Energy 77(6), 823–830 (2004)
G. Sasikala, P. Thilakan, C. Subramanian, Modification in the chemical bath deposition apparatus, growth and characterization of CdS semiconducting thin films for photovoltaic applications. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 62, 275–293 (2000)
C. Thanachayanont, K. Inpor, S. Sahasithiwat, V. Meeyoo, MEH-PPV/CdS nanorod polymer solar cells. Korean Phys. Soc. 52, 1540–1544 (2008)
C.S. Ferekides, D. Marinskiy, V. Viswanathan, B. Tetali, V. Palekis, P. Sevaraj, D.L. Morel, High effciency CSS CdTe solar cells. Thin Solid Films 361, 520–526 (2000)
H.R. Moutinho et al., Deposition and properties of CBD and CSS CdS thin films for solar cell application. Thin Solid Films 436(2), 175–180 (2003)
X. Wu, et al., High-efficiency polycrystalline CdTe thin-film solar cells with an oxygenated amorphous cds (a-CdS:O) window layer. 531–534 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1109/PVSC.2002.1190619
M. Devi et al., An effect of precursor concentrations on the photodetection capabilities of CdS thin films for high-efficiency visible-light photodetector applications. Appl. Phys. A (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-04067-3
M. Shkir et al., A significant enhancement in visible-light photodetection properties of chemical spray pyrolysis fabricated CdS thin films by novel Eu doping concentrations. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 301, 111749 (2020)
J. Zhao et al., Efficient CdSe/CdS quantum dot light-emitting diodes using a thermally polymerized hole transport layer. Nano Lett. 6(3), 463–467 (2006)
U. Pal et al., Optical characterization of vacuum evaporated cadmium sulfide films. Thin Solid Films 305(1–2), 345–350 (1997)
S.A. Mahmoud, A.A. Ibrahim, A.S. Riad, Physical properties of thermal coating CdS thin films using amodified evaporation source. Thin Solid Films. 372, 144–148 (2000)
M.F. Rahman et al., A novel synthesis and characterization of transparent CdS thin films for CdTe/CdS solar cells. Appl. Phys. A 126(2), 145 (2020)
A.S.Z. Lahewil et al., Structural and optical investigations of cadmium sulfide nanostructures for optoelectronic applications. Sol. Energy 86(11), 3234–3240 (2012)
K. Veerathangam, M.S. Pandian, P. Ramasamy, Size-dependent photovoltaic performance of cadmium sulfide (CdS) quantum dots for solar cell applications. J. Alloy. Compd. 735, 202–208 (2018)
R.R. Chamberlin, J.S. Skarman, Chemical spray deposition process for inorganic films. J. Electrochem. Soc. 113, 86–89 (1966)
M. Shkir et al., A remarkable effect of Pr doping on key optoelectrical properties of CdS thin films prepared using spray pyrolysis technique for high-performance photodetector applications. Ceram. Int. 46, 4652 (2020)
M. Shkir et al., A facile spray pyrolysis fabrication of Sm:CdS thin films for high-performance photodetector applications. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 306, 111952 (2020)
M. Shkir et al., An effect of Zn content doping on opto-third order nonlinear characteristics of nanostructured CdS thin films fabricated through spray pyrolysis for optoelectronics. Phys. E Low-dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 118, 113955 (2020)
M. Shkir, S. Alfaify, Tailoring the structural, morphological, optical and dielectric properties of lead iodide through Nd3+ doping. Sci. Rep. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-16086-x
J. Chu et al., An in-situ chemical reaction deposition of nanosized wurtzite CdS thin films. Thin Solid Films 520(6), 1826–1831 (2012)
J. Li, Preparation and properties of CdS thin films deposited by chemical bath deposition. Ceram. Int. 41, S376–S380 (2015)
Z.M. Kakhaki et al., Effects of buffer salt concentration on the dominated deposition mechanism and optical characteristics of chemically deposited cadmium sulfide thin films. Surf. Rev. Lett. 23(03), 1650014 (2016)
S. Yılmaz et al., Surface modification of CBD-grown CdS thin films for hybrid solar cell applications. Optik 185, 256–263 (2019)
S.U. Shaikh et al., Effects of air annealing on CdS quantum dots thin film grown at room temperature by CBD technique intended for photosensor applications. Mater. Res. Bull. 47(11), 3440–3444 (2012)
J. Barman, J.P. Borah, K. Sarma, Effect of pH variation on size and structure of CdS nanocrystalline thin films. Chalcogenide Lett. 5, 265–271 (2008)
A. Kariper et al., Effect of pH on the physical properties of CdS thin films deposited by CBD. Chalcogenide Lett. 9, 27–40 (2012)
R. Ochoa-Landín et al., Observations on the influence of pH control on the properties of chemically deposited CdS films in an ammonia-free system. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 70, 1034 (2009)
B. Altiokka, A.K. Yildirim, Electrodeposition of CdS thin films at various pH values. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 72(6), 687–691 (2018)
Q.Q. Liu et al., Morphological and stoichiometric study of chemical bath deposited CdS films by varying ammonia concentration. Phys. B 405(20), 4360–4365 (2010)
D.A. Tonpe et al., Development of organic/inorganic PANI/ZnO 1D nanostructured hybrid thin film solar cell by soft chemical route. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30(17), 16056–16064 (2019)
V.V. Kutwade et al., Enhanced photosensing by Mg-doped ZnO hexagonal rods via a feasible chemical route. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32(5), 6475–6486 (2021)
M. Barote, A. Yadav, E. Masumdar, Effect of deposition parameters on growth and characterization of chemically deposited Cd1-xPbxS thin films. Chalcogenide Lett. 8(2), 129–138 (2011)
R. Ramírez-Bon et al., Structural transition of chemically deposited CdS films on thermal annealing. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 9(45), 10051–10058 (1997)
T. Ben Nasr et al., Effect of pH on the properties of ZnS thin films grown by chemical bath deposition. Thin Solid Films 500(1), 4–8 (2006)
H. Ahmed, A. Khazeal, and F. Atallah, Effect pH on structural and optical properties of nanostructure CdS films prepared by chemical bath deposition technique. J. Unive. Anbar Pure Sci. 7(1) (2013)
K. Subba Ramaiah et al., Structural and optical investigations on CdS thin films grown by chemical bath technique. Mater. Chem. Phys. 68(1), 22–30 (2001)
Y.-M. Mo et al., Synthesis of fluorescent CdS quantum dots of tunable light emission with a new in situ produced capping agent. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 51(17), 5995–6000 (2012)
H. Zhang, B. Chen, J.F. Banfield, Particle size and pH effects on nanoparticle dissolution. J. Phys. Chem. C 114(35), 14876–14884 (2010)
A. Romdhane et al., Effect of pH and ionic strength on the electrical charge and particle size distribution of starch nanocrystal suspensions. Starch - Stärke 67(3–4), 319–327 (2015)
B. Wei et al., Effect of pHs on dispersity of maize starch nanocrystals in aqueous medium. Food Hydrocoll. 36, 369–373 (2014)
R. Banerjee, R. Jayakrishnan, P. Ayyub, Effect of the size-induced structural transformation on the band gap in CdS nanoparticles. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 12, 10647 (2000)
I.M.S. Mohammed et al., Effect of Cd/S ratio on growth and physical properties of CdS thin films for photosensor application. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31(13), 9989–9996 (2020)
M. Singh, M. Goyal, K. Devlal, Size and shape effects on the band gap of semiconductor compound nanomaterials. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 12(4), 470–475 (2018)
K.C. Wilson, M.B. Ahamed, Influence of bath temperature on surface modification and optoelectronic properties of chemical bath deposited CdS thin film nanostructures. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 251, 114444 (2019)
B. Barman, K.V. Bangera, G.K. Shivakumar, Effect of substrate temperature on the suitability of thermally deposited cadmium sulfide thin films as window layer in photovoltaic cells. Superlattices Microstruct. 123, 374–381 (2018)
Acknowledgements
The authors are highly thankful and would like to acknowledge the Department of Physics, Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Marathwada University Aurangabad for providing necessary laboratory facilities. The authors also like to acknowledge the UGC SAP and DST FIST program for providing financial support to our laboratory.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammed, I.M.S., Gubari, G.M.M., Sonawane, M.E. et al. Influence of pH on the physical properties of CdS thin film and its photosensor application. Appl. Phys. A 127, 597 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04743-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04743-y