Abstract
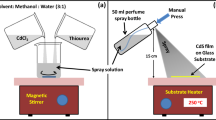
Photo-conducting CdS films were coated on glass at 450 °C using cadmium chloride and thiourea as Cd and S sources, respectively, with different concentrations. The sprayed CdS films are crystallized in the hexagonal structure and orienting along (0 0 2) plane with good adherence. All the films have high optical absorption in the visible region showing optical bandgap values in the range of 2.39–2.43 eV. The variation of precursor alters the surface morphology of the films. The formed grains are uniformly spread over the substrate and highly agglomerated at 0.15 M concentration. Band to band emission and defect-related emission are reported using photoluminescence (PL) measurements. The CdS device shows relatively high photosensitivity of 0.4 A/W, detectivity of 8.46 × 1010 Jones, external quantum efficiency (EQE of 140%) with a rise time about 0.2 s and decay time about 0.3 s. These results propose that the CdS thin films are potential candidates for the visible photo-detector applications prepared using an easy and low-cost fabrication method.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Vrijen, E. Yablonovitch, A spin-coherent semiconductor photo-detector for quantum communication. Phys. E 10(4), 569–575 (2001)
R. Hattori, M. Hironaka, Semiconductor photodetector device, Google Patents, (1991).
P.H. Shen, M.R. Stead, M.A. Taysing-Lara, J. Pamulapati, W.C. Ruff, B.L. Stann, P.N. Uppal, Interdigitated Finger Semiconductor Photodetector for Optoelectronic Mixing, Infrared Detectors and Focal Plane Arrays VI (International Society for Optics and Photonics, Bellingham, 2000), pp. 426–435
M. Tsuji, Ultraspeed low-voltage drive avalanche multiplication type semiconductor photodetector, Google Patents (2002).
Z. Qi, T. Yang, D. Li, H. Li, X. Wang, X. Zhang, F. Li, W. Zheng, P. Fan, X. Zhuang, A. Pan, High-responsivity two-dimensional p-PbI2/n-WS2 vertical heterostructure photodetectors enhanced by photogating effect. Materials Horizons 6, 1474–1480 (2019)
F. Xia, T. Mueller, Y.-M. Lin, A. Valdes-Garcia, P. Avouris, Ultrafast graphene photodetector. Nat. Nanotechnol. 4(12), 839 (2009)
S. Najmaei, M. Dubey, 2d material photo-detector gain and responsivity control and enhancement through induced interface trap doping, Google Patents, (2019).
P. Gant, P. Huang, D.P. de Lara, D. Guo, R. Frisenda, A. Castellanos-Gomez, A strain tunable single-layer MoS2 photodetector. Mater. Today 27, 8–13 (2019)
S. Edwards, T. Oder, Characterization of Ultraviolet ZnO Photodetector (Bulletin of the American Physical Society, Boston, 2019)
M. Long, Y. Wang, P. Wang, X. Zhou, H. Xia, C. Luo, S. Huang, G. Zhang, H. Yan, Z. Fan, X. Wu, X. Chen, W. Lu, W. Hu, Palladium diselenide long-wavelength infrared photodetector with high sensitivity and stability. ACS Nano 13(2), 2511–2519 (2019)
L.H. Zeng, D. Wu, S.H. Lin, C. Xie, H.Y. Yuan, W. Lu, S.P. Lau, Y. Chai, L.B. Luo, Z.J. Li, Controlled synthesis of 2D palladium diselenide for sensitive photodetector applications. Adv. Func. Mater. 29(1), 1806878 (2019)
F. Cao, L. Meng, M. Wang, W. Tian, L. Li, Gradient energy band driven high-performance self-powered perovskite/CdS photodetector. Adv. Mater. 31(12), 1806725 (2019)
D. Wu, Y. Jiang, Y. Zhang, Y. Yu, Z. Zhu, X. Lan, F. Li, C. Wu, L. Wang, L. Luo, Self-powered and fast-speed photodetectors based on CdS: Ga nanoribbon/Au Schottky diodes. J. Mater. Chem. 22(43), 23272–23276 (2012)
M. Shuai, Y. Lingmin, C. Lei, L. Chun, Y. Mingli, F. Xinhui, Resistive-type UV–visible photodetector based on CdS NWs /ZnO nanowalls heterostructure fabricated using in-situ synthesis method. J. Alloy. Compd. 827, 154090 (2020)
K. Deng, L. Li, CdS Nanoscale Photodetectors. Adv. Mater. 26(17), 2619–2635 (2014)
Y. Ye, L. Dai, X. Wen, P. Wu, R. Pen, G. Qin, High-Performance Single CdS Nanobelt Metal-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor-Based Photodetectors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2(10), 2724–2727 (2010)
L. Li, P. Wu, X. Fang, T. Zhai, L. Dai, M. Liao, Y. Koide, H. Wang, Y. Bando, D. Golberg, Single-crystalline CdS nanobelts for excellent field-emitters and ultrahigh quantum-efficiency photodetectors. Adv. Mater. 22(29), 3161–3165 (2010)
L. Li, Z. Lou, G. Shen, Hierarchical CdS Nanowires Based Rigid and Flexible Photodetectors with Ultrahigh Sensitivity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 7(42), 23507–23514 (2015)
M. Mahdi, J. Hassan, S. Ng, Z. Hassan, N.M. Ahmed, Synthesis and characterization of single-crystal CdS nanosheet for high-speed photodetection. Phys. E 44(7–8), 1716–1721 (2012)
J. Jie, W. Zhang, Y. Jiang, X. Meng, Y. Li, S. Lee, Photoconductive characteristics of single-crystal CdS nanoribbons. Nano Lett. 6(9), 1887–1892 (2006)
Z. Lou, L. Li, G. Shen, Ultraviolet/visible photodetectors with ultrafast, high photosensitivity based on 1D ZnS/CdS heterostructures. Nanoscale 8(9), 5219–5225 (2016)
L. Zhu, C. Li, Y. Li, C. Feng, F. Li, D. Zhang, Z. Chen, S. Wen, S. Ruan, Visible-light photodetector with enhanced performance based on a ZnO@ CdS heterostructure. J. Mater. Chem. C 3(10), 2231–2236 (2015)
X.-X. Yu, H. Yin, H.-X. Li, W. Zhang, H. Zhao, C. Li, M.-Q. Zhu, Piezo-phototronic effect modulated self-powered UV/visible/near-infrared photodetectors based on CdS: P3HT microwires. Nano Energy 34, 155–163 (2017)
B. Mereu, G. Sarau, E. Pentia, V. Draghici, M. Lisca, T. Botila, L. Pintilie, Field-effect transistor based on nanometric thin CdS films. Mater. Sci. Eng., B 109(1–3), 260–263 (2004)
R. Ma, L. Dai, G. Qin, Enhancement-mode metal-semiconductor field-effect transistors based on single n-Cd S nanowires. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90(9), 093109 (2007)
Z. Qian, H.-J. Bai, G.-L. Wang, J.-J. Xu, H.-Y. Chen, A photoelectrochemical sensor based on CdS-polyamidoamine nano-composite film for cell capture and detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 25(9), 2045–2050 (2010)
L. Yadava, R. Verma, R. Dwivedi, Sensing properties of CdS-doped tin oxide thick film gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 144(1), 37–42 (2010)
Y.L. Lee, Y.S. Lo, Highly efficient quantum-dot-sensitized solar cell based on co-sensitization of CdS/CdSe. Adv. Func. Mater. 19(4), 604–609 (2009)
S. Bhushan, D. Thakur, Photoconductivity of chemically deposited rare-earth-doped CdS films. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 3(1), 35–40 (1992)
M.A. Mahdi, J.J. Hassan, N.M. Ahmed, S.S. Ng, Z. Hassan, Growth and characterization of CdS single-crystalline micro-rod photodetector. Superlattices Microstruct. 54, 137–145 (2013)
D. Wu, Y. Jiang, S. Li, F. Li, J. Li, X. Lan, Y. Zhang, C. Wu, L. Luo, J. Jie, Construction of high-quality CdS: Ga nanoribbon/silicon heterojunctions and their nano-optoelectronic applications. Nanotechnology 22(40), 405201 (2011)
M. Husham, Z. Hassan, A.M. Selman, N.K. Allam, Microwave-assisted chemical bath deposition of nanocrystalline CdS thin films with superior photodetection characteristics. Sens. Actuators A 230, 9–16 (2015)
M. Waldiya, R. Narasimman, D. Bhagat, D. Vankhade, I. Mukhopadhyay, Nanoparticulate CdS 2D array by chemical bath deposition: Characterization and optoelectronic study. Mater. Chem. Phys. 226, 26–33 (2019)
S. Munde, N. Shinde, P. Khanzode, M. Budrukkar, P. Lahane, J. Dadge, S. Jejurikar, M. Mahabole, R. Khairnar, K. Bogle, Nano-crystalline CdS thick films: a highly sensitive photo-detector. Mater. Res. Express 5(6), 066203 (2018)
M. Shkir, I. Ashraf, S. AlFaify, A.M. El-Toni, M. Ahmed, A. Khan, A noticeable effect of Pr doping on key optoelectrical properties of CdS thin films prepared using spray pyrolysis technique for high-performance photodetector applications. Ceram. Int. 46(4), 4652–4663 (2020)
M. Shkir, I. Ashraf, A. Khan, M.T. Khan, A.M. El-Toni, S. AlFaify, A facile spray pyrolysis fabrication of Sm: CdS thin films for high-performance photodetector applications. Sens. Actuators A 306, 111952 (2020)
M. Shkir, I.M. Ashraf, K.V. Chandekar, I.S. Yahia, A. Khan, H. Algarni, S. AlFaify, A significant enhancement in visible-light photodetection properties of chemical spray pyrolysis fabricated CdS thin films by novel Eu doping concentrations. Sens. Actuators A 301, 111749 (2020)
L. Wenyi, C. Xun, C. Qiulong, Z. Zhibin, Influence of growth process on the structural, optical and electrical properties of CBD-CdS films. Mater. Lett. 59(1), 1–5 (2005)
F. Atay, V. Bilgin, I. Akyuz, S. Kose, The effect of In doping on some physical properties of CdS films. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 6(4), 197–203 (2003)
P.J. Sebastian, p-type CdS thin films formed by in situ Cu doping in the chemical bath. Appl. Phys. Lett. 62(23), 2956–2958 (1993)
R. Bairy, A. Jayarama, G.K. Shivakumar, S.D. Kulkarni, S.R. Maidur, P.S. Patil, Effect of Aluminium doping on photoluminescence and third-order nonlinear optical properties of nanostructured CdS thin films for photonic device applications. Phys. B 555, 145–151 (2019)
L.A. González, I. Carreón-Moncada, M.A. Quevedo-López, Negative differential resistance as effect of Zn doping of chemically processed CdS thin film transistors. Mater. Lett. 192, 161–164 (2017)
M. Paulraj, S. Ramkumar, K.P. Varkey, K.P. Vijayakumar, C. Sudha Kartha, K.G.M. Nair, Characterizations of undoped and Cu doped CdS thin films using photothermal and other techniques. Phys. Status Solidi (a) 202(3), 425–434 (2005)
S. Chander, M.S. Dhaka, Optical and structural constants of CdS thin films grown by electron beam vacuum evaporation for solar cells. Thin Solid Films 638, 179–188 (2017)
M. Shkir, M. Anis, S. Shafik, M.A. Manthrammel, M.A. Sayeed, M.S. Hamdy, S. AlFaify, An effect of Zn content doping on upto-third order nonlinear characteristics of nanostructured CdS thin films fabricated through spray pyrolysis for optoelectronics. Phys. E 118, 113955 (2020)
P. Parameshwari, K.G. Naik, Effect of Cd/S Molar Ratio on the Optical and Electrical Properties of Spray Deposited CdS Thin Films, Physics of Semiconductor Devices (Springer, Berlin, 2014), pp. 347–349
S. Yılmaz, Y. Atasoy, M. Tomakin, E. Bacaksız, Comparative studies of CdS, CdS:Al, CdS: Na and CdS:(Al–Na) thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis. Superlattices Microstruct. 88, 299–307 (2015)
V. Senthamilselvi, K. Saravanakumar, N.J. Begum, R. Anandhi, A. Ravichandran, B. Sakthivel, K. Ravichandran, Photovoltaic properties of nanocrystalline CdS films deposited by SILAR and CBD techniques—a comparative study. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 23(1), 302–308 (2012)
K. Ravichandran, P. Philominathan, Investigations on microstructural and optical properties of CdS films fabricated by a low-cost, simplified spray technique using perfume atomizer for solar cell applications. Sol. Energy 82(11), 1062–1066 (2008)
S. Gosavi, C. Nikam, A. Shelke, A. Patil, S.-W. Ryu, J. Bhat, N. Deshpande, Chemical synthesis of porous web-structured CdS thin films for photosensor applications. Mater. Chem. Phys. 160, 244–250 (2015)
A.A. Ziabari, F. Ghodsi, Effects of the Cd: Zn: S molar ratio and heat treatment on the optical and photoluminescence properties of nanocrystalline CdZnS thin films. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 16(6), 1629–1636 (2013)
K.A. Aly, N. Khalil, Y. Algamal, Q.M. Saleem, Lattice strain estimation for CoAl2O4 nano particles using Williamson-Hall analysis. J. Alloy. Compd. 676, 606–612 (2016)
N. Anitha, M. Anitha, J. Raj Mohamed, S. Valanarasu, L. Amalraj, Influence of tin precursor concentration on physical properties of nebulized spray deposited tin disulfide thin films. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 6(2), 121–131 (2018)
S. AlFaify, L. Haritha, M.A. Manthrammel, V. Ganesh, K.V. Chandekar, S.S. Shaikh, M. Shkir, Fabrication and characterization of Sn:CdS films for optical-nonlinear-limiting applications. Opt. Laser Technol. 126, 106122 (2020)
H. Kumar, S. Kumar, Indium sulfide based metal-semiconductor-metal ultraviolet-visible photodetector. Sens. Actuators A 299, 111643 (2019)
M.S. Mahdi, K. Ibrahim, A. Hmood, N.M. Ahmed, S.A. Azzez, F.I. Mustafa, A highly sensitive flexible SnS thin film photodetector in the ultraviolet to near infrared prepared by chemical bath deposition. RSC Adv. 6(116), 114980–114988 (2016)
M. Husham, Z. Hassan, M. Mahdi, A.M. Selman, N.M. Ahmed, Fabrication and characterization of nanocrystalline CdS thin film-based optical sensor grown via microwave-assisted chemical bath deposition. Superlattices Microstruct. 67, 8–16 (2014)
K. Wilson, M.B. Ahamed, Influence of bath temperature on surface modification and optoelectronic properties of chemical bath deposited CdS thin film nanostructures. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 251, 114444 (2019)
N. Saxena, T. Kalsi, P. Uttam, P. Kumar, Morphological evolution in nanocrystalline CdS thin films from flowers to salt rock like structures. Opt. Mater. 84, 625–630 (2018)
R. Khalfi, D. Talantikite-Touati, A. Tounsi, H. Merzouk, Effect of deposition time on structural and optical properties of ZnSe thin films grown by CBD method. Opt. Mater. 106, 109989 (2020)
T.S. Reddy, M.S. Kumar, Co-evaporated SnS thin films for visible light photodetector applications. RSC Adv. 6(98), 95680–95692 (2016)
M. Nair, P. Nair, Simplified chemical deposition technique for good quality SnS thin films. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 6(2), 132 (1991)
M. Shkir, Z.R. Khan, M. Anis, S.S. Shaikh, S. AlFaify, A comprehensive study of opto-electrical and nonlinear properties of Cu@CdS thin films for optoelectronics. Chin. J. Phys. 63, 51–62 (2020)
M. Husham, Z. Hassan, A.M. Selman, Synthesis and characterization of nanocrystalline CdS thin films for highly photosensitive self-powered photodetector. Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys. 74(1), 10101 (2016)
M. Tan, C. Hu, Y. Lan, J. Khan, H. Deng, X. Yang, P. Wang, X. Yu, J. Lai, H. Song, 2D lead dihalides for high-performance ultraviolet photodetectors and their detection mechanism investigation. Small 13(47), 1702024 (2017)
M. Zhong, L. Huang, H.-X. Deng, X. Wang, B. Li, Z. Wei, J. Li, Flexible photodetectors based on phase dependent PbI 2 single crystals. J. Mater. Chem. C 4(27), 6492–6499 (2016)
Q. An, X. Meng, P. Sun, High-performance fully nanostructured photodetector with single-crystalline CdS Nanotubes as active layer and very long ag nanowires as transparent electrodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 7(41), 22941–22952 (2015)
N.I. Najm, H.K. Hassun, B. KH al-Maiyaly, B.H. Hussein, A.H. Shaban, Highly selective CdS: Ag heterojunction for photodetector applications, in AIP Conference Proceedings, AIP Publishing (2019), p. 020031.
M. Shkir, I.M. Ashraf, S. AlFaify, A.M. El-Toni, M. Ahmed, A. Khan, A noticeable effect of Pr doping on key optoelectrical properties of CdS thin films prepared using spray pyrolysis technique for high-performance photodetector applications. Ceram. Int. 46, 4652–4653 (2019)
M. Shkir, I.M. Ashraf, K.V. Chandekar, I.S. Yahia, A. Khan, H. Algarni, S. AlFaify, A significant enhancement in visible-light photodetection properties of chemical spray pyrolysis fabricated CdS thin films by novel Eu doping concentrations. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 111749, 301 (2019)
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their sincere appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University for funding this research through the Fast-track Research Funding Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Devi, M.D., Juliet, A.V., Hari Prasad, K. et al. An effect of precursor concentrations on the photodetection capabilities of CdS thin films for high-efficiency visible-light photodetector applications. Appl. Phys. A 126, 960 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-04067-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-04067-3