Abstract
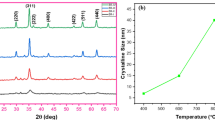
Multiferroic nano-composites with chemical formula (x) Ni0.5Mg0.5Fe2O4 (NMFO) + (1-x) BaTiO3 (BTO); (x = 10, 20, 30 and 40%) were prepared via sol–gel method. XRD patterns confirmed the presence of a single cubic phase of pure NMFO and a single tetragonal phase of BTO. The crystallite size of BTO is found to be larger than that of NMFO. Moreover, the strain of the BTO phase increased, while the porosity decreased with increasing x-content. A high-resolution transmission electron microscope (HRTEM) revealed the formation of a single particle domain in the ferrite (NMFO) phase. Field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM) demonstrated that the grain size increases with increasing x-content. The temperature dependence of D.C electrical resistivity showed a semiconducting behavior of all samples, while the resistivity decreased with increasing x-content. Electrical permittivity (ε') and dielectric loss (tan δ) at low (20–105 Hz) and high (1 MHz–3 GHz) frequencies at room temperature were considered. A resonance phenomenon is observed only in the high-frequency range such that the resonant frequency shifts to a higher frequency with increasing x-content. The ferroelectric hysteresis loops (P-E) revealed that the maximum polarization (Pmax) decreased with increasing x-content. The ferromagnetic hysteresis loops (M-H), carried out using a vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM), confirmed an increase in saturation magnetization (Ms) with increasing x-content. Relative magnetic permeability (µr) as a function of temperature indicated a cooperative phenomenon between ferroelectric and ferromagnetic phases at (380–480) °C.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Ahmed, S.F. Mansour, M. Afifi, Structural, electric and magnetoelectric properties of Ni0.85Cu0.15Fe2O4/BiFe0.7Mn0.3O3 multiferroic nanocomposites. J. Alloy. Compd. 578, 303–308 (2013)
J. Zhai, Z. Xing, S. Dong, J. Li, D. Viehland, An overview: magnetoelectric laminate composites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 91(2), 351–358 (2008)
M.I. Ce-Wen Nan, S.D. Bichurin, D. Viehland, G. Srinivasan, Multiferroic magnetoelectric composites: Historical perspective, status, andfuture directions. J. Appl. Phys. 103, 031101 (2008)
D. Ghanbari, M. Salavati-Niasari, Synthesis of urchin-like CdS-Fe3O4 nanocomposite and its application in flame retardancy of magnetic cellulose acetate. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 24, 284–292 (2015)
M. Salavati-Niasari, Z. Fereshteh, F. Davar, Synthesis of oleylamine capped copper nanocrystals via thermal reductionof a new precursor. Polyhedron 28, 126–130 (2009)
T. Gholami, M. Salavati-Niasari, S. Varshoy, Investigation of the electrochemical hydrogen storage and photocatalytic properties of CoAl2O4pigment: Green synthesis and characterization. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 41(22), 9418–9426 (2016)
S. Mortazavi-Derazkola, M. Salavati-Niasari, O. Amiri, A. Abbasi, Fabrication and characterization of Fe3O4@SiO2@TiO2@Ho nanostructures as a novel and highly efficient photocatalyst for degradation of organic pollution. J. Energy Chem. 26(1), 17–23 (2017)
A. Abbasi, D. Ghanbari, M. Salavati-Niasari, M. Hamadanian, Photo-degradation of methylene blue: photocatalyst and magneticinvestigation of Fe2O3–TiO2 nanoparticles and nanocomposites. J. Mater Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 4800–4809 (2016)
F. Ansari, A. Sobhani, M. Salavati-Niasari, Simple sol-gel synthesis and characterization of new CoTiO3/CoFe2O4 nanocomposite by using liquid glucose, maltose and starch as fuel, capping andreducing agents. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 514, 723–732 (2018)
F. Tavakoli, M. Salavati-Niasari, Alireza badiei, Fatemeh Mohandes, Green synthesis and characterization of graphene nanosheets. Mater. Res. Bull. 63, 51–57 (2015)
M. Yousefi, F. Gholamian, D. Ghanbari, M. Salavati-Niasari, Polymeric nanocomposite materials: Preparation and characterization of star-shaped PbS nanocrystals and their influence on the thermal stability of acrylonitrile–butadiene–styrene (ABS) copolymer. Polyhedron 30, 1055–1060 (2011)
B. Ertuğ, The Overview of the Electrical Properties of Barium Titanate. Am. J. Eng. Res. (AJER). 2(8), 01–07 (2013)
H.S. Singh, Neha Sangwa, Structural and Magnetic Properties of Nickel Ferrite Nanoparticles Synthesized by Ball Milling. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Inven. 6(10), 36–39 (2017)
J. Ronald, Willey, patrick noirclerc, and Guido Busca, preparation and characterization of magnesium chromite and magnesium ferrite aerogels. Chem. Eng. Commun. 123, 1–16 (1993)
Y. Qing, L. Ma, Hu. Xiaochen, Fa. Luo, W. Zhou, NiFe2O4 nanoparticles filled BaTiO3 ceramics for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding applications. Ceram. Int. 44(7), 8706–8709 (2018)
M.M. Vijatović Petrović, R. Grigalaitis, A. Dzunuzovic, J.D. Bobić, B.D. Stojanović, R. Šalaševičius, J. Banys, Positive influence of Sb doping on properties of di phase multiferroics based on barium titanate and nickel ferrite. J. Alloy. Compd. 749, 1043–1053 (2018)
R. Grigalaitis, M.M. Vijatović Petrović, J.D. Bobić, A. Dzunuzovic, R. Sobiestianskas, A. Brilingas, B.D. Stojanović, J. Banys, Dielectric and magnetic properties of BaTiO3 –NiFe2O4 multiferroic composites. Ceram. Int. 40, 6165–6170 (2014)
X. Luo, H. Wang, R. Gao, X. Li, J. Zhang, H. Ban, Effects of molar ratio on dielectric, ferroelectric and magnetic properties of Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4-BaTiO3 composite ceramics. Process. Appl. Ceram. 14(2), 91–101 (2020)
J.-P. Zhou, Li. Lv, Q. Liu, Y.-X. Zhang, P. Liu, Hydrothermal synthesis and properties of NiFe2O4 @ BaTiO3 composites with well-matched interface. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 13, 045001 (2012)
R. Köferstein, T. Walther, D. Hesse, S.G. Ebbinghaus, Fine-grained BaTiO3–MgFe2O4 composites prepared by a Pechini-like process. J. Alloy. Compd. 638, 141–147 (2015)
S.Y. Tan, S.R. Shannigrahi, S.H. Tan, F.E.H. Tay, Synthesis and characterization of composite MgFe2O4 – BaTiO3 multiferroic system. J. Appl. Phys. 103, 094105 (2008)
M. F. A. Zolkepli and Z. Zainuddin, Structure, magnetic and complex impedance analysis of (1-x) BaTiO3 - (x) MgFe2O4 Composite. American Institute of Physics, Conference Proceedings. 1678, 040014 (2015).
Mohamad Fahmi Amin Bin Zolkebli and Zalita Zainuddin, Structural, magnetic and electrical properties of barium titanate and magnesium ferrite composites. Sains Malaysiana. 46(6), 967–973 (2017)
R. Tadi, Y.-I. Kim, D. Sarkar, Cheol Gi Kim, Kwon-SangRyu,Magnetic and electrical properties of bulk BaTiO3 + MgFe2O4 composite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323, 564–568 (2011)
A.M.A. Henaish, M. Mostafa, B.I. Salem, O.M. Hemeda, Improvement of magnetic and dielectric properties of magnetoelectric BST-NCZMF nanocomposite. Phase Trans. 93(5), 470–490 (2020)
L.R. Pradeep Chavan, P.B. Naik, Geeta Chavan Belavi, V.T. Muttannavar, B.K. Bammannavar, R.K. Kotnala, Temperature dependent electric properties and magnetoelectric effects in ferroelectric rich Ni0.8Mg0.2Fe2O4 + BaZr02Ti08O3 magnetoelectric composites. J. Alloy. Compd. 777(10), 1258–1264 (2019)
Md.D. Rahaman, S.K. Saha, T.N. Ahmed, D.K. Saha, A.K.M. Akther Hossain, Magnetoelectric effect of (1–x) Ba05Sr05Zr05Ti05O3 + (x) Ni0.12Mg0.18Cu0.2Zn0.5Fe2O4 composites. J. Magnet. Magnet. Mater. 371, 112–120 (2014)
R. Ashiri, M. Ali Nemati, S. Sasani Ghamsari, M. Aalipour. Sanjabi, A modified method for barium titanate nanoparticles synthesis. Mater. Res. Bull. 46, 2291–2295 (2011)
Abdul Samee Fawzi, A.D. Sheikh, V.L. Mathe, Dielectric, electrical and magnetoelectric characterization of (x) Ni0.8Zn0.2Fe2O4 + (1–x) Pb0.93La0.07(Zr0.60Ti0.40)O3 composites. Mater. Res. Bull. 45, 1000–1007 (2010)
Khalid Mujasam Batoo, M.S. Abd El-sadek, Electrical and magnetic transport properties of Ni–Cu–Mg ferrite nanoparticles prepared by sol–gel method. J. Alloy. Compd 566, 112–119 (2013)
S.A. Lokare, D.R. Patil, B.K. Chougule, Structural, dielectric and magnetoelectric effect in (x) BaTiO3 + (1–x) Ni0.93Co0.02Mn0.05Fe2O4 ME composites. J. Alloy. Compd. 453, 58–63 (2008)
S. Abdul Khader, T. Sankarappa, Dielectric, magnetic and ferroelectric studies in (x) Mn0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 + (1–x) BaTiO3 magnetoelectric nano-composites. Mater. Today 3, 2358–2365 (2016)
Ebtesam E. Ateia, Asmaa A. H. El-Bassuony, Galila Abdellatif, Amira T. Mohamed, The impact of ni substitution on the structural and magnetic properties of Mg Nano-ferrite. Silicon 10, 1687–1696 (2018)
H. Irfan, K. Mohamed Racik, S. Anand, X-ray peak profile analysis of CoAl2O4 nanoparticles by Williamson-Hall and size-strain plot methods. Mod. Electron. Mater. 4(1), 31–40 (2018)
L.S. Ashwini, Y.F. Nadaf and S.S. Bellad, Structural and dc electrical properties of LiMgFe2O4:BaTiO3 ME composites. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Techn. Res. 3(6), (2016).
R.S. Totagi, N.J. Choudhari, S.S. Kakati, C.S. Hiremath, S.B. Koujalagi, R.B. Pujar, Electrical properties of Ni-Mg-Cu nanoferrites synthesized by sucrose precursor technique. Der Pharma Chemica 7(3), 11–15 (2015)
R.C. Kambale, P.A. Shaikh, C.H. Bhosale, K.Y. Rajpure, Y.D. Kolekar, Studies on magnetic, dielectric and magnetoelectric behavior of (x) NiFe1.9Mn0.1O4 and (1- x) BaZr0.08Ti0.92O3 magnetoelectric composites. J. Alloy. Compd. 489, 310-315 (2010).
K. Ramarao, B. Rajesh Babu, B. Kishore Babu, V. Veeraiah, K. Rajasekhar, B. Ranjith Kumar, B. Swarana Latha, Enhancement in magnetic and electrical properties of Ni substituted Mg ferrite. Mater. Sci. Poland. 36(4), 644-654 (2018).
P.B. Belavi, G.N. Chavan, L.R. Naik, V.L. Mathe, R.K. Kotnala, Resistivity and grain size dependent magnetoelectric Effect in (Y) Ni0.85Cd0.1Cu0.05Fe2O4 + (1-Y) BaTiO3 ME composites. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2(12), 298-306(2013).
K.W. Wagner, The distribution of relaxation times in typical dielectrics. Ann. Phys. 40, 817–819 (1973)
C. G Koops, On the dispersion of resistivity and dielectric constant of some semiconductors at audio frequencies. Phys. Rev. 83 (1), (1951).
M. Raghasudha, D. Ravinder, P. Veerasomaiah, Influence of Cr3+ ion on the dielectric properties of nano crystalline Mg-ferrites synthesized by citrate-gel method. Mater. Sci. Appl. 4, 432–438 (2013)
Yang Bai, Yu. Ji Zhou, Bo Li. Sun, Zhenxing Yue, Zhilun Gui, Longtu Li, Effect of electromagnetic environment on the dielectric resonance in the ferroelectric - ferromagnetic composite. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 112907 (2006)
Pei Peng, Ya-Ya Hu, Yong Liu, Shi chen, Jing Shi, Rui Xiong, Yue Zhang, Magnetoelectric effect of CoFe2O4/Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 composite ceramics sintered via spark plasma sintering technology. Ceram. Int. 41(5) part A, 6676-6682 (2015).
N. Shara Sowmya, A. Srinivas, K. Venu Gopal Reddy, J. Paul Praveen, Dibakar Das, S. Dinesh Kumar, V. Subramanian, S. V. Kamat, Magnetoelectric coupling studies on (x) (0.5BZT- 0.5BCT) – (100-x) NiFe2O4 [x = 90-70 wt%] particulate composite. Ceram. Int. 43, 2523-2528 (2017).
Sagar Mane, Pravin Tirmali, Snehal Kadam, Arjun Tarale, Chandrakant Kolekar and Shrinivas Kulkarni, Dielectric, magnetic, and magnetodielectric properties of x [Co0.9Ni0.1Fe2O4] - (1-x) [0.5(Ba0.7Ca0.3)TiO3) - 0.5Ba(Zr0.2Ti0.8)O3] multiferroic composites. J. Chin. Adv. Mater. Soc. 4(4), 269-284 (2016).
G. Nabiyouni, M. Jafari Fesharaki, M. Mozafari, J. Amighian, Characterization and magnetic properties of nickel ferrite nanoparticles prepared by ball milling technique. Chin. Phys. Lett. 27(12), 126401 (2010)
R. Paulsingh, C. Venkataraju, Effect of calcinations on the structural and magnetic properties of magnesium ferrite nanoparticles prepared by sol gelmethod. Chin. J. Phys.. 56(5), 2218–2225 (2018)
B.K. Bammannavar, G.N. Chavan, L.R. Naik, B.K. Chougule, Magnetic properties and magnetoelectric (ME) effect in ferroelectric rich Ni0.2Co0.8 Fe2O4 + PbZr0.8Ti0.2O3 ME composites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 117, 46-50 (2009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
ElGendy, L.I., Ghani, A.A., Darwish, A.S. et al. Synthesis, microstructure analysis, electrical and magnetic properties of Ni0.5Mg0.5Fe2O4 – BaTiO3 Nano-composites. Appl. Phys. A 127, 239 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04384-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04384-1