Abstract
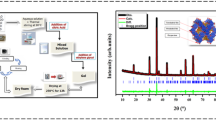
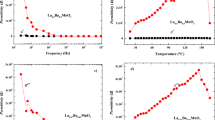
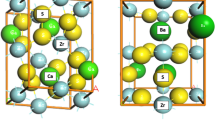
BiHoZnCeO6, the double pervoskite was synthesized using a cost-effective solid-state reaction method. The structural evaluation of the double pervoskite, when carried out by using the X-ray diffraction pattern suggested an orthorhombic crystal geometry with non- centrosymmetry space group Pca21. The microstructural investigation on the above material is carried out with the help of a scanning electron micrograph. These SEM micrographs showed that the grains of varying sizes (0.5–2 μm) are uniformly distributed. The study of dielectric characteristics as a function of temperature and frequency revealed some interesting characteristics of the material. One such observation is the identification of ferroelectric transition temperature at 435 °C. The strong anomaly at 435 °C and the ferroelectric behavior of the material is further validated by the study of spontaneous polarization (the hysteresis loop). In the present communication, the detailed microstructural, dielectric (dielectric constant, tangent loss, and electric polarization), thermal and electrical (impedance, electrical modulus, conductivity) studies on bismuth holmium zinc ceranate is presented along with the existence of ferroelectricity.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Valasek, Piezo-electric and allied phenomena in rochelle salt. Phys. Rev. 17, 475–481 (1921). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.17.475
M. Fiebig, Revival of the magnetoelectric effect. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 38, R123–R152 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/38/8/r01
E.V. Colla, E.Y. Koroleva, N.M. Okuneva, S.B. Vakhrushev, Long-time relaxation of the dielectric response in lead magnoniobate. Phys. Rev. Lett. 74, 1681–1684 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.74.1681
W. Prellier, M.P. Singh, P. Murugavel, The single-phase multiferroic oxides: from bulk to thin film. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 17, R803–R832 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/17/30/r01
A. Levstik, Z. Kutnjak, C. Filipič, R. Pirc, Glassy freezing in relaxor ferroelectric lead magnesium niobate. Phys. Rev. B 57, 11204–11211 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.57.11204
D. Viehland, S.J. Jang, L.E. Cross, M. Wuttig, Deviation from Curie-Weiss behavior in relaxor ferroelectrics. Phys. Rev. B 46, 8003–8006 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.46.8003
S.K.C. Chitra, Structural, dielectric and ferroelectric properties of dysprosium doped (Ba0.7Ca 0.3)(Ti0.92 Sn0.08)O3 lead free ceramics. Ferroelectrics 518, 1–10 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/00150193.2017.1360115
L. Chu, W. Ahmad, W. Liu et al., Lead-free halide double perovskite materials: a new superstar toward green and stable optoelectronic applications. Nano-Micro Lett. 11, 16 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-019-0244-6
G.H. Ryu, A. Hussain, M.H. Lee et al., Lead-free high performance Bi(Zn0.5Ti0.5)O3-modified BiFeO3-BaTiO3 piezoceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 38, 4414–4421 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2018.05.032
K. Parida, S.K. Dehury, R.N.P. Choudhary, Structural, electrical and magneto-electric characteristics of double perovskite: BiCaFeCeO6. Chin. J. Phys. 59, 231–241 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjph.2019.03.009
S.E. Nunes, C.-H. Wang, K. So et al., Bismuth zinc vanadate, BiZn2VO6: New crystal structure type and electronic structure. J. Solid State Chem. 222, 12–17 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2014.10.036
P.G.R. Achary, S.K. Dehury, R.N.P. Choudhary, Structural, electrical and dielectric properties of double perovskites: BiHoZnZrO6 and BiHoCuTiO6. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-8667-2
V. Senthil, T. Badapanda, A. Chithambararaj et al., Impedance spectroscopy and photocatalysis water splitting for hydrogen production with cerium modified SrBi2Ta2O9 ferroelectrics. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 41, 22856–22865 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.08.139
V. Senthil, T. Badapanda, A. Chandrabose, S. Panigrahi, Dielectric and ferroelectric behavior of cerium modified SrBi2Ta2O9 ceramic. Mater. Lett. 159, 138–141 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2015.06.093
N.M. Khusayfan, Ferroelectric properties of Ce doped hydroxyapatite nanoceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 685, 350–354 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.05.273
S. Liu, L. Zhang, J. Wang et al., Rapid stability of ferroelectric polarization in the Ca, Ce hybrid doped BaTiO3 ceramics. Sci. Rep. 6, 38354 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep38354
M.A. Peña, J.L.G. Fierro, Chemical structures and performance of perovskite oxides. Chem. Rev. 101, 1981–2018 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1021/cr980129f
V. Stournari, S.F.P. ten Donkelaar, J. Malzbender et al., Creep behavior of perovskite-type oxides Ba0.5Sr0.5(Co0.8Fe0.2)1−xZrxO3−δ. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 35, 1841–1846 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2015.01.005
X. Liu, R. Hong, C. Tian, Tolerance factor and the stability discussion of ABO 3-type ilmenite. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron 20, 323 (2009)
K.A. Razak, W.C. Song, C.Y. Ng, Properties of Ce-doped Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3 synthesized using the soft combustion method. Proced. Chem. 19, 816–821 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proche.2016.03.107
J.D. Bobić, B.D. StojanoviĆ, C.O. Paiva-Santos et al., Structure and properties of barium bismuth titanate prepared by mechanochemical synthesis. Ferroelectrics 368, 145–153 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1080/00150190802368305
A. Abbassi, H. Zaari, C. Azahaf et al., Spontaneous polarization and magnetic investigation of BiXO3 (X=Co, Mn, Fe, V, Zn): first-principle study. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 29, 487–491 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-015-3315-z
H. Liu, X. Yang, A brief review on perovskite multiferroics. Ferroelectrics 507, 69–85 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/00150193.2017.1283171
Y. Markandeya, Y.S. Reddy, S. Bale et al., Characterization and thermal expansion of Sr2FexMo2−xO6 double perovskites. Bull. Mater. Sci. 38, 1603–1608 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-015-0972-2
S. Khetre, A. Chopade, C. Khilare et al., Electrical and dielectric properties of nanocrystalline LaCrO3. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-013-1411-z
D.R. Patil, S.A. Lokare, R.S. Devan et al., Dielectric properties and magnetoelectric effect of (x)NiFe2O4+(1–x)Ba0.8Sr0.2TiO3 composites. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 68, 1522–1526 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2007.03.029
W. Wan, J. Luo, C. Huang et al., Calcium copper titanate/polyurethane composite films with high dielectric constant, low dielectric loss and super flexibility. Ceram. Int. 44, 5086–5092 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.12.108
C. Rayssi, S. El Kossi, J. Dhahri, K. Khirouni, Frequency and temperature-dependence of dielectric permittivity and electric modulus studies of the solid solution Ca0.85Er0.1Ti1−xCo4x/3O3 (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.1). RSC Adv. 8, 17139–17150 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA00794B
W.Q. Cao, L. Yang, M.M. Ismail, P. Feng, Dielectric and ferroelectric properties of Ba0.8Sr0.2Ti1−5x/4NbxO3 ceramics. Ceram. Int. 37, 1587 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2011.01.031
D. Guyomar, G. Sebald, B. Guiffard, L. Seveyrat, Ferroelectric electrocaloric conversion in 0.75(PbMg1/3Nb2/3O3)-0.25(PbTiO3) ceramics. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 39, 4491–4496 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/39/20/029
K. Yao, S. Chen, M. Rahimabady et al., Nonlinear dielectric thin films for high-power electric storage with energy density comparable with electrochemical supercapacitors. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 58, 1968–1974 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/TUFFC.2011.2039
D.-W. Fu, H.-L. Cai, Y. Liu et al., Diisopropylammonium bromide is a high-temperature molecular ferroelectric crystal. Science 339, 425–428 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1229675
P. Gupta, P.K. Mahapatra, R.N.P. Choudhary, TbFeO3 ceramic: an exciting colossal dielectric with ferroelectric properties. Phys. Status Solidi Basic Res. 1900236, 1–14 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/pssb.201900236
A. Mukherjee, M. Banerjee, S. Basu et al., Enhanced magnetic and electrical properties of y and Mn co-doped BiFeO3 nanoparticles. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 448, 199–203 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2014.03.082
S. Nagar, K.V. Rao, L. Belova et al., Room temperature ferromagnetism and lack of ferroelectricity in thin films of “Biferroic?” YbCrO3. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 1183, 163–168 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1557/proc-1161-i07-04
A.K. Jonscher, Dielectric relaxation in solids. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 32, R57 (1999)
S. Hajra, M. Sahu, V. Purohit, R.N.P. Choudhary, Dielectric, conductivity and ferroelectric properties of lead-free electronic ceramic:0.6Bi(Fe0.98Ga0.02)O3–0.4BaTiO3. Heliyon 5, e01654 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.HELIYON.2019.E01654
J. Ross Macdonald, Note on the parameterization of the constant-phase admittance element. Solid State Ionics 13, 147–149 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-2738(84)90049-3
R. Ranjan, R. Kumar, N. Kumar et al., Impedance and electric modulus analysis of Sm-modified Pb(Zr0.55Ti0.45)1–x/4O3 ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 6388–6394 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.03.003
S. Terny, P.E. di Prátula, J. de Frutos, M.A. Frechero, Dielectric relaxation of vanadium–molybdenum tellurite glasses modified by alkaline-earth oxides. J. Non Cryst. Solids 444, 49–54 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2016.04.041
M. Usman, K. Rasool, S.S. Batool et al., Humidity effect on transport properties of titanium dioxide nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 30, 748–752 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2013.12.002
S. Sasaki, C.T. Prewitt, J.D. Bass, W.A. Schulze, Orthorhombic perovskite CaTiO${\sb 3}$ and CdTiO${\sb 3}$: structure and space group. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C 43, 1668–1674 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1107/S0108270187090620
K. Parida, R.N.P. Choudhary, Structural, electrical, optical and magneto-electric characteristics of chemically synthesized {CaCu}3Ti4O12 dielectric ceramics. Mater. Res. Express 4, 76302 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aa76cd
M.A.E.-F. Gabal, Y.M. Al Angari, A.Y. Obaid, Structural characterization and activation energy of NiTiO3 nanopowders prepared by the co-precipitation and impregnation with calcinations. Comptes Rendus Chim 16, 704–711 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crci.2013.01.009
A. Belboukhari, E. Choukri, Y. Gagou et al., Investigation on relaxation and conduction mechanism in Pb0.75K0.5Nb2O6 new ferroelectric ceramic. Superlattices Microstruct. 71, 7–22 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2014.03.031
Acknowledgements
The present work is funded by the UGC-DAE-CSR, Mumbai (CRS-M-297).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Padhy, M., Dehury, S.K., Choudhary, R. et al. Structural, dielectric, thermal and electrical characteristics of lead-free double perovskite: BiHoZnCeO6. Appl. Phys. A 126, 655 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-03852-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-03852-4