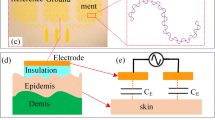
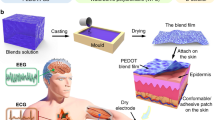
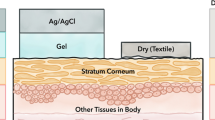
Abstract
Current soft surface electrodes have attracted more and more attention owing to their potential applications in the fields of biological signal monitoring, wearable human–machine interface and internet of things. The paper presents that soft dry electrode based on PDMS-CB conductive polymer is designed and fabricated to continuous, long-term, stable electrocardiogram (ECG) signal recordings which is conformal contact with the soft skin surface. The wearable electronic platform based on the soft dry electrode is built up to collect the ECG data. Integration of the soft dry electrodes with wearable electronic platform would improve the wearability and adaptability of the soft electrode in biological healthy monitoring which represents the future application in ubiquitous healthcare. Experiments have demonstrated that ECG data from the soft electrodes are recorded with PQRST wave which are similar to ECG data from Ag/AgCl gel electrodes. Meanwhile, robustness and stability of ECG signal are validated by the soft dry electrodes with different body actions.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.H. Yeo, Y.S. Kim, J. Lee, A. Ameen, L. Shi, M. Li et al., Multifunctional epidermal electronics printed directly onto the skin. Adv. Mater. 25, 2773–2778 (2013)
W. Dong, X. Cheng, T. Xiong, X. Wang, Stretchable bio-potential electrode with self-similar serpentine structure for continuous, long-term, stable ECG recordings. Biomed. Microdevice 21, 6 (2019)
Y.K. Lim, K.K. Kim, K.S. Park, The ECG measurement in the bathtub using the insulated electrodes, in 26th Annual International Conference of the IEEE, San Francisco, CA, pp. 2383–2385 (2004)
F. Andreotti, F. Grasser, H. Malberg, S. Zaunseder, Non-invasive fetal ECG signal quality assessment for multichannel heart rate estimation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 64, 2793–2802 (2017)
A.A. Arefin, Propagate the ECG signal and understand the major heart diseases. J. Biomed. Inform. 2, 3 (2017)
J. Coll-Font, B. Erem, D.H. Brooks, A potential-based inverse spectral method to non-invasively localize discordant distributions of alternans on the heart from the ECG. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 65, 1554–1563 (2017)
M. Fernandez, R. Pallas-Areny, Ag-AgCl electrode noise in high-resolution ECG measurements. Biomed. Instrum. Technol. Assoc. Adv. Med. Instrum. 34, 125–130 (1999)
T. Cheng, Y. Zhang, W.Y. Lai, W. Huang, Stretchable thin-film electrodes for flexible electronics with high deformability and stretchability. Adv. Mater. 27, 3349–3376 (2015)
J.W. Jeong, M.K. Kim, H. Cheng, W.H. Yeo, X. Huang, Y. Liu et al., Capacitive epidermal electronics for electrically safe, long-term electrophysiological measurements. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 3, 642–648 (2014)
Y. Wang, Y. Qiu, S.K. Ameri, H. Jang, Z. Dai, Y. Huang et al., Low-cost, μm-thick, tape-free electronic tattoo sensors with minimized motion and sweat artifacts. npj Flex. Electron. 2, 6 (2018)
W. Dong, Y. Wang, Y. Zhou, Y. Bai, Z. Ju, J. Guo et al., Soft human–machine interfaces: design, sensing and stimulation. Int. J. Intell. Robot. Appl. 23, 313–338 (2018)
B.J. Polk, A. Stelzenmuller, G. Mijares, W. MacCrehan, M. Gaitan, Ag/AgCl microelectrodes with improved stability for microfluidics. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 114, 239–247 (2006)
L.-F. Wang, J.-Q. Liu, B. Yang, C.-S. Yang, PDMS-based low cost flexible dry electrode for long-term EEG measurement. IEEE Sens. J. 12, 2898–2904 (2012)
H.J. Baek, J.L. Hong, G.L. Yong, K.S. Park, Conductive polymer foam surface improves the performance of a capacitive EEG electrode. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 59, 3422–3431 (2012)
J.J. Norton, D.S. Lee, J.W. Lee, W. Lee, O. Kwon, P. Won et al., Soft, curved electrode systems capable of integration on the auricle as a persistent brain–computer interface. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 112, 3920–3925 (2015)
M. Ochoa, P. Wei, A.J. Wolley, K.J. Otto, B. Ziaie, A hybrid PDMS-Parylene subdural multi-electrode array. Biomed. Microdevice 15, 437–443 (2013)
A. Lopez, P.C. Richardson, Capacitive electrocardiographic and bioelectric electrodes. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 16, 99 (1969)
C.T. Freeman, Electrode array-based electrical stimulation using ILC with restricted input subspace. Control Eng. Pract. 23, 32–43 (2014)
Q. Zhong, J. Zhong, X. Cheng, X. Yao, B. Wang, W. Li et al., Paper-based active tactile sensor array. Adv. Mater. 27, 7130–7136 (2015)
H.-C. Jung, J.-H. Moon, D.-H. Baek, J.-H. Lee, Y.-Y. Choi, J.-S. Hong et al., CNT/PDMS composite flexible dry electrodesfor long-term ECG monitoring. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 59, 1472–1479 (2012)
M.A. Yokus, J.S. Jur, Fabric-based wearable dry electrodes for body surface biopotential recording. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 63, 423 (2016)
H.-L. Peng, J.-Q. Liu, H.-C. Tian, B. Xu, Y.-Z. Dong, B. Yang et al., Flexible dry electrode based on carbon nanotube/polymer hybrid micropillars for biopotential recording. Sens. Actuators A 235, 48–56 (2015)
K.I. Jang, H.U. Chung, S. Xu, C.H. Lee, H. Luan, J. Jeong et al., Soft network composite materials with deterministic and bio-inspired designs. Nat. Commun. 6, 6566 (2015)
D.-H. Kim, N. Lu, R. Ma, Y.-S. Kim, R.-H. Kim, S. Wang et al., Epidermal electronics. Science 333, 838–843 (2011)
Y. Sun, X.B. Yu, Capacitive biopotential measurement for electrophysiological signal acquisition: a review. IEEE Sens. J. 16, 2832–2853 (2016)
W. Dong, L. Xiao, C. Zhu, D. Ye, S. Wang, Y. Huang et al., Theoretical and experimental study of 2D conformability of stretchable electronics laminated onto skin. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 60, 1415 (2017)
N. Gandhi, C. Khe, D. Chung, Y.M. Chi, G. Cauwenberghs, Properties of dry and non-contact electrodes for wearable physiological sensors. International Conference on Body Sensor Networks, BSN 2011, Dallas, Texas, USA, pp.107–112 (2011)
T. Matsuda, M. Makikawa, ECG monitoring of a car driver using capacitively-coupled electrodes, in 2008 30th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Vancouver, BC, pp. 1315–1318 (2008)
F. Yin, D. Ye, C. Zhu, L. Qiu, Y. Huang, Stretchable, highly durable ternary nanocomposite strain sensor for structural health monitoring of flexible aircraft. Sensors 17, 2677 (2017)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge supports from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Young Scientists Fund (51705376), Youth Project of Jiangxi Education Department (GJJ180360). The authors would like to thank Key Laboratory of Advanced Control & Optimization of Jiangxi Province for providing the measurement instruments for electrical performance test of the soft PDMS-CB dry electrodes.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, X., Bao, C., Wang, X. et al. Soft surface electrode based on PDMS-CB conductive polymer for electrocardiogram recordings. Appl. Phys. A 125, 876 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-3124-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-3124-5