Abstract
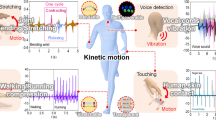
In this paper, we report the fabrication of a high-sensitivity strain sensor fabricated using graphene platelets (GnPs) and multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) for monitoring joint-bending movement. The optimized ultrasonic time and the ball mill-mixing process make the GnPs disperse evenly in the MWCNTs. The strain sensor made up of the GnP/MWCNT mixture (30 wt% GnPs loading) is fabricated by a spray-method and its conductivity is up to 104 S/m. The as-prepared GnP/MWCNT sensor exhibits relatively high tensile strength of 5.4 MPa, sensing range of 7.5%, gauge factor of 181.36, linearity of 99.545%, and great bending reproducibility over 5000 cycles. These remarkable features endow our sensing devices to monitor joint bending in human health monitoring, e.g., elbow, finger and wrist bending. The results demonstrate that our flexible GnP/MWCNT sensor shows promising applications prospects in smart wearable device monitoring human health.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.D. Kersey, T.A. Berkoff, W.W. Morey, Multiplexed fiber Bragg grating strain-sensor system with a fiber Fabry-Perot wavelength filter. Opt. Lett. 18(16), 1370–1372 (1993)
X. Chen, X. Han, Q.D. Shen, PVDF-based ferroelectric polymers in modern flexible electronics. Adv. Electron. Mater. 3(5), 1600460 (2017)
W. Yuan, J. Yang, K. Yang et al., High-performance and multifunctional skinlike strain sensors based on graphene/springlike mesh network. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 10(23), 19906–19913 (2018)
H. Wu, Q. Liu, W. Du et al., Transparent polymeric strain sensors for monitoring vital signs and beyond. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 10(4), 3895–3901 (2018)
Q. Liu, J. Chen, Y. Li et al., High-performance strain sensors with fish-scale-like graphene-sensing layers for full-range detection of human motions. ACS Nano 10(8), 7901–7906 (2016)
S. Gong, D.T.H. Lai, B. Su et al., Highly stretchy black gold E-Skin nanopatches as highly sensitive wearable biomedical sensors. Adv. Electron. Mater. 1(4), 1400063 (2015)
A.A. Barlian, W.T. Park, J.R. Mallon et al., Semiconductor piezoresistance for microsystems. Proc. IEEE 97(3), 513–552 (2009)
Y. Wang, L. Wang, T. Yang et al., Wearable and highly sensitive graphene strain sensors for human motion monitoring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 24(29), 4666–4670 (2014)
Y. Wang, R. Yang, Z. Shi et al., Super-elastic graphene ripples for flexible strain sensors. ACS Nano 5(5), 3645–3650 (2011)
C. Cochrane, V. Koncar, M. Lewandowski et al., Design and development of a flexible strain sensor for textile structures based on a conductive polymer composite. Sensors 7(4), 473–492 (2007)
M. Zhang, C. Wang, H. Wang et al., Carbonized cotton fabric for high-performance wearable strain sensors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 27(2), 1604795 (2017)
L. Cai, L. Song, P. Luan et al., Super-stretchable, transparent carbon nanotube-based capacitive strain sensors for human motion detection. Sci. Rep. 3, 3048 (2013)
T. Yamada, Y. Hayamizu, Y. Yamamoto et al., A stretchable carbon nanotube strain sensor for human-motion detection. Nat. Nanotechnol. 6(5), 296 (2011)
S.K. Krishnan, E. Singh, P. Singh et al., A review on graphene-based nanocomposites for electrochemical and fluorescent biosensors. RSC Adv. 9(16), 8778–8881 (2019)
T. Yamada, Y. Hayamizu, Y. Yamamoto et al., A stretchable carbon nanotube strain sensor for human-motion detection. Nat. Nanotechnol. 6(5), 296 (2011)
E. Singh, M. Meyyappan, H.S. Nalwa, Flexible graphene-based wearable gas and chemical sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 9(40), 34544–34586 (2017)
H. Montazerian, A. Rashidi, A. Dalili et al., Graphene-coated spandex sensors embedded into silicone sheath for composites health monitoring and wearable applications. Small 2019, 1804991 (2019)
S.H. Bae, Y. Lee, B.K. Sharma et al., Graphene-based transparent strain sensor. Carbon 51, 236–242 (2013)
D. Akinwande, N. Petrone, J. Hone, Two-dimensional flexible nanoelectronics. Nat. Commun. 5, 5678 (2014)
M.V. Kamalakar, C. Groenveld, A. Dankert et al., Long distance spin communication in chemical vapour deposited graphene. Nat. Commun. 6, 6766 (2015)
I.G. Serrano, J. Panda, F. Denoel et al., Two-dimensional flexible high diffusive spin circuits. Nano Lett. 19(2), 666–673 (2019)
X. Yu, H. Cheng, M. Zhang et al., Graphene-based smart materials. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2(9), 17046 (2017)
H. Xu, Y.F. Lu, J.X. Xiang et al., A multifunctional wearable sensor based on a graphene/inverse opal cellulose film for simultaneous, in situ monitoring of human motion and sweat. Nanoscale 10(4), 2090–2098 (2018)
S. Lu, C. Zhao, L. Zhang et al., Real time monitoring of the curing degree and the manufacturing process of fiber reinforced composites with a carbon nanotube buckypaper sensor. RSC Adv. 8(39), 22078–22085 (2018)
X. Chen, L. Shen, C.A. Yuan et al., Molecular model for the charge carrier density dependence of conductivity of polyaniline as chemical sensing materials. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 177, 856–861 (2013)
L.C. Tang, Y.J. Wan, D. Yan et al., The effect of graphene dispersion on the mechanical properties of graphene/epoxy composites. Carbon 60, 16–27 (2013)
S.M.A. Darbandi, M. Nouri, J. Mokhtari, Electrospun nanostructures based on polyurethane/MWCNTs for strain sensing applications. Fibers Polym. 13(9), 1126–1131 (2012)
X. Wang, J. Sparkman, J. Gou, Strain sensing of printed carbon nanotube sensors on polyurethane substrate with spray deposition modeling. Compos. Commun. 3, 1–6 (2017)
L. Vertuccio, V. Vittoria, L. Guadagno et al., Strain and damage monitoring in carbon-nanotube-based composite under cyclic strain. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 71, 9–16 (2015)
Y.L. Zheng, X.R. Ding, C.C.Y. Poon et al., Unobtrusive sensing and wearable devices for health informatics. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 61(5), 1538–1554 (2014)
Z. Wang, Y. Huang, J. Sun et al., Polyurethane/cotton/carbon nanotubes core-spun yarn as high reliability stretchable strain sensor for human motion detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 8(37), 24837–24843 (2016)
H. Zhao, Y. Zhang, P.D. Bradford et al., Carbon nanotube yarn strain sensors. Nanotechnology 21(30), 305502 (2010)
T. Yan, Z. Wang, Y.Q. Wang et al., Carbon/graphene composite nanofiber yarns for highly sensitive strain sensors. Mater. Des. 143, 214–223 (2018)
H. Liu, J. Gao, W. Huang et al., Electrically conductive strain sensing polyurethane nanocomposites with synergistic carbon nanotubes and graphene bifillers. Nanoscale 8(26), 12977–12989 (2016)
D.I. Bower, Temperature dependence of gauge factor and magnetoresistance of some platinum–tungsten strain gauges. J. Phys. E: Sci. Instrum. 5(9), 846 (1972)
S. Sayed, M. Gamil, F. El-Bab et al., LASER reduced graphene on flexible substrate for strain sensing applications: temperature effect on gauge factor. Key Eng. Mater. Trans. Tech. Publ. 644, 115–119 (2015)
Z. Sun, H. Chang, Graphene and graphene-like two-dimensional materials in photodetection: mechanisms and methodology. ACS Nano 8(5), 4133–4156 (2014)
Acknowledgements
The financial contributions are gratefully acknowledged. This work was financially supported by National Nature Science Fund (11602150, U1733123), Aeronautical Science Foundation (2017ZE54029), Shenyang science project (18-013-0-23), Natural science foundation of Liaoning Province (20170540695, 20180550751), Scientific Research Fund for Public Welfare of Liaoning province (20170014), Scientific Research Project of Liaoning Provincial Education Department (L201725), China Aerospace Science and Technology Group Innovation Fund (17580404) and Liaoning Province Distinguished Professor Program. The financial contributions are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, S., Ma, J., Ma, K. et al. Highly sensitive graphene platelets and multi-walled carbon nanotube-based flexible strain sensor for monitoring human joint bending. Appl. Phys. A 125, 471 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2765-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2765-8