Abstract
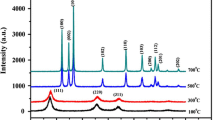
We have grown ZnS (zinc sulfide) nanoparticles (NPs) by hydrothermal and microwave (MW) heating method and a comparative study on the physical properties was carried out. Zinc acetate dihydrate (ZAD) and thioacetamide (TA) were used as Zn and S precursors, respectively. X-ray diffraction (XRD) and selected area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern revealed the cubic structure for ZnS and nanocrystalline nature of the samples. The careful observation of the XRD patterns of the samples grown by hydrothermal and microwave heating method indicate that microwave-synthesized ZnS (ZnS–MW) samples were strained compared to those grown by conventional hydrothermal methods. Uniform sized smaller nanoparticles were formed during microwave irradiation in a much shorter time. UV–Vis absorption spectra indicated quantum confinement effect. The emission peaks in photoluminescence spectra indicate the presence of various point defects in the samples. In the microwave synthesized sample, nucleation and growth process of the ZnS crystallites are very quick, leading to the formation of defects. The dielectric studies of both types of the samples show a typical behavior of polycrystalline semiconducting material. Under the applied A.C. fields, the conduction phenomena provide sufficient evidence for the electronic hopping between localized sites. Lower values of activation energy obtained for both dipolar relaxation and DC conductivity in the case of microwave synthesized sample indicate the applicability of such materials in various switching applications.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.P. Alivisatos, Semiconductor clusters, nanocrystals, and quantum dots. Science 271, 933 (1996)
X. Fang, T. Zhai, U.K. Gautam, L. Li, L. Wu, Y. Bando, D. Golberg, ZnS nanostructures: from synthesis to applications. Prog. Mater Sci. 56, 175 (2011)
D.W. Synnott, M.K. Seery, S.J. Hinder, G. Michlits, S.C. Pillai, Anti-bacterial activity of indoor-light activated photocatalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 130–131, 106 (2013)
J. Souriau, Y. Dong, J. Penczek, H.G. Paris, C.J. Summers, Cathodoluminescent properties of coated SrGa 2 S4: Eu2+ and ZnS:Ag, Cl phosphors for field emission display applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 76, 165 (2000)
I.O. Oladeji, L. Chow, Synthesis and processing of CdS/ZnS multilayer films for solar cell application. Thin Solid Films 474, 77 (2005)
M. Koneswaran, R. Narayanaswamy, l-Cysteine-capped ZnS quantum dots based fluorescence sensor for Cu2+ ion. Sensors Actuators, B Chem. 139, 104 (2009)
Z. Li, J. Wang, X. Xu, X. Ye, The evolution of optical properties during hydrothermal coarsening of ZnS nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 62, 3862 (2008)
C. Ramamoorthy, V. Rajendran, Formation of solid and hollow sphere ZnS nanoparticles by hydrothermal process and their structural, optical and photocatalytic activity. Appl. Phys. A 124, 500 (2018)
N.I. Kovtyukhova, E.V. Buzaneva, C.C. Waraksa, T.E. Mallouk, Ultrathin nanoparticle ZnS and ZnS: Mn films : surface sol–gel synthesis, morphology, photophysical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 70, 411 (2000)
J. Yuan, K. Kajiyoshi, K. Yanagisawa, Fabrication of silica nanocoatings on ZnS–type phosphors via a sol–gel route using cetyltrimethylammonium chloride dispersant. Mater. Lett. 60, 1284 (2006)
J.F. Xu, W. Ji, J.Y. Lin, S.H. Tang, Y.W. Du, Preparation of ZnS nanoparticles by ultrasonic radiation method. Appl. Phys. A 641, 639 (1998)
R.S. Sudar, D. Pukazhselvan, C.K. Mahadevan, Studies on the synthesis of cubic ZnS quantum dots, capping and optical–electrical characteristics. J. Alloys Compd. 517, 139 (2012)
U. Baishya, D. Sarkar, ZnS nanocomposite formation: effect of ZnS source concentration ratio. Indian J. Pure Appl. Phys. 49, 186 (2011)
K.J. Rao, B. Vaidhyanathan, M. Ganguli, P.A. Ramakrishnan, Synthesis of inorganic solids using microwaves. Chem. Mater. 11, 882 (1999)
S. Naween Dahal, J. Garcıa, S.M. Zhou, Humphrey, Beneficial effects of microwave-assisted heating versus conventional heating in noble metal nanoparticle synthesis. ACS Nano 6, 9433 (2012)
J. Zhu, M. Zhou, J. Xu, X. Liao, Preparation of CdS and ZnS nanoparticles using microwave irradiation. Mater. Lett. 47, 25 (2001)
Y. Zhao, J.M. Hong, J.J. Zhu, Microwave-assisted self-assembled ZnS nanoballs. J. Cryst. Growth 270, 438 (2004)
Q. Ma, Y. Wang, J. Kong, H. Jia, Tunable synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic properties of various ZnS nanostructures. Ceram. Int. 42, 2854 (2016)
B.D. Cullity, Elements of X-ray diffraction, 2nd edn. (Addison Wiley Publishing Company, Newyork, 1972), p. 110
S. Lee, D. Song, D. Kim, J. Lee, S. Kim, I.Y. Park, Y.D. Choi, Effects of synthesis temperature on particle size/shape and photoluminescence characteristics of ZnS:Cu nanocrystals. Mater. Lett. 58, 342 (2004)
A.L. Rogach, A. Kornowski, M. Gao, A. Eychmüller, H. Weller, Synthesis and characterization of a size series of extremely small thiol-stabilized CdSe nanocrystals. J Phys Chem B 103, 3065 (1999)
J. Tauc, Menth, states in Gap. J Non-crystalline Solids 8, 569 (1972)
L. E. Brus, electron–electron and electron-hole interactions in small semiconductor crystallites: the size dependence of the lowest excited electronic state. J Chem. Phys 80, 4403 (1984)
S. Mondal, S. Sudhu, S. Bhattacharya, S.K. Saha, Strain-induced tunable band gap and morphology-dependent photocurrent in RGO–CdS nanostructures. J. Phys. Chem. C 119, 27749 (2015)
D. Denzler, M. Olschewski, K. Sattler, Luminescence studies of localized gap states in colloidal ZnS nanocrystals. J. Appl. Phys. 84, 2841 (1998)
A.K. Kole, P. Kumbhakar, Effect of manganese doping on the photoluminescence characteristics of chemically synthesized zinc sulfide nanoparticles. Appl. nano sci 2, 15 (2012)
J.F. Suyver, S.F. Wuister, J.J. Kelly, A. Meijerink, Synthesis and photoluminescence of nanocrystalline ZnS: Mn2+. Nano Lett. 1, 429 (2001)
J. Bohnemann, R. Libanori, M.L. Moreira, E. Longo, High-efficient microwave synthesis and characterisation of SrSnO3. Chem. Eng. J. 155, 905 (2009)
M. Sookhakian, Y.M. Amin, W.J. Basirun, M.T. Tajabadi, N.Kamarulzaman Synthesis, structural and optical properties of type-II ZnO–ZnS core–shell nanostructure. J. Lumin. 145, 244 (2014)
B. Poornaprakash, U. Chalapathi, S.V.P. Vattikuti, Optical, and magnetic properties of Fe, Co, and Ni doped ZnS nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A 123, 275 (2017)
N. Karar, Photoluminescence from doped ZnS nanostructures. Solid State Commun. 142, 261 (2007)
X. Liu, Z. Li, C. Zhao, W. Zhao, J. Yang, Y. Wang, F. Li, Facile synthesis of core–shell CuO/Ag nanowires with enhanced photocatalytic and enhancement in photocurrent. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 419, 9 (2014)
K.C. Anoop Chandran, George, Defect induced modifications in the optical, dielectric, and transport properties of hydrothermally prepared ZnS nanoparticles and nanorods. J. Nanopart. Res. 16, 2238 (2014)
R. Gerhardt, Impedance and dielectric spectroscopy revisited—distinguishing localised relaxations from long range conductivity. J. Phys.Chem.Solids 55, 1491 (1994)
J.C. Maxwell, A Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism (Oxford University Press, New York, 1973)
T. Shekharam, V.L. Rao, G. Yellaiah, T.M. Kumar, M. Nagabhushanam, AC conductivity, dielectric and impedance studies of Cd0.8xPbxZn0.2S mixed semiconductor compounds. J. Alloys Compd. 617, 952 (2014)
A.S. Roy, S. Gupta, S. Sindhu, A. Parveen, P.C. Ramamurthy, Dielectric properties of novel PVA/ZnO hybrid nanocomposite films. Compos. Part B Eng. 47, 314 (2013)
A.K. Jonscher, A new understanding of the dielectric relaxation of solids. J. Mater. Sci. 16, 2037 (1981)
A. Artemenko, S. Payan, A. Rousseau, D. Levasseur, E. Arveux, G. Guegan, M. Maglione, Low temperature dielectric relaxation and charged defects in ferroelectric thin films Low temperature dielectric relaxation and charged defects in ferroelectric thin films. AIP Adv. 3, 0 42111 (2013)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank UGC-DAE Consortium for Scientific Research, Mumbai Centre for dielectric measurements, DST-SAIF centre at Karnatak University-Dharwad for photoluminescence measurements, Manipal Academy of Higher Education- Manipal for other characterisations and Bhandarkars’ Arts and Science college, Kundapura for sample preparation facilities. One of the authors, Lalitha Devi B thanks the University Grants Commission, Government of India, for teacher fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Devi, B.L., Rao, K.M., Kekuda, D. et al. Evolution of defects and their effect on photoluminescence and conducting properties of green-synthesized ZnS nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A 124, 767 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-2196-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-2196-y