Abstract
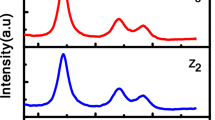
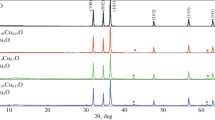
Zinc sulfide (ZnS) is one of the leading semiconductors for optoelectronic device applications. Here, we focused on synthesizing the undoped and transition metal (Cu)-doped ZnS (Zn\(_{1-x}\)Cu\(_{x}\)S) nanoparticles at different copper concentrations (x = 0, 0.03, 0.05, 0.07) using solid-state reaction. The synthesized Zn\(_{1-x}\)Cu\(_{x}\)S nanoparticles were subjected to different characterizations such as XRD, FE-SEM, EDS, UV–visible spectroscopy, PL, and two probe methods to study their structural, morphological, elemental, optical, and electrical properties. The XRD profile revealed that the prepared nanoparticles were in cubic structure with predominant orientation along (1 1 1) plane. The EDAX spectra confirmed the presence of host and dopant elements such as Zn, S, and Cu without any impurity elements. The formation of spherical-shaped clusters was confirmed by FE-SEM images. Using absorption spectra, the band gaps were calculated. Novel luminescence features, i.e., blue, green, and orange-red emission peaks, were observed in the photoluminescence spectra. Electrical properties were studied using two probe method (Keysight B2900 source meter).








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
No datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
L. He et al., One-pot synthesis of color-tunable copper doped zinc sulfide quantum dots for solid-state lighting devices. J. Alloys Compd. 787, 537–542 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.02.150
V. Lahariya, M. Ramrakhiani, Luminescence study on Mn, Ni Co-doped zinc sulfide nanocrystals. Luminescence 35(6), 924–933 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/bio.3802
E. Jubeer, M.A. Manthrammel, M. Shkir, P. Subha, I. Yahia, S. Alfaify, Microwave assisted synthesis of quantum dots like ZnS nanoparticles for optoelectronic applications: An effect of CTAB concentrations. Optik 240, 166812 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2021.166812
D. Sharma, B. Malik, A. Gaur, Two and four photon absorption and nonlinear refraction in undoped, chromium doped and copper doped ZnS quantum dots. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 87, 163–170 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2015.08.011
K. Bindu, E. Anila, Optimized synthesis temperature and doping concentration of copper in zinc sulphide nanoparticles for green emission. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 121, 105317 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2020.105317
M. Jothibas, C. Manoharan, S.J. Jeyakumar, P. Praveen, I.K. Punithavathy, J.P. Richard, Synthesis and enhanced photocatalytic property of Ni doped ZnS nanoparticles. Sol. Energy 159, 434–443 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2017.10.055
C.-J. Chang, Y.-H. Wei, W.-S. Kuo, Free-standing CuS-ZnS decorated carbon nanotube films as immobilized photocatalysts for hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy. 44(58), 30553–30562 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.04.229
A. Segura et al., Sulfidogenic bioreactor-mediated formation of ZnS nanoparticles with antimicrobial and photocatalytic activity. Nanomaterials 13(5), 935 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13050935
T.-F. Yi, Y. Li, Y.-M. Li, S. Luo, Y.-G. Liu, ZnS nanoparticles as the electrode materials for high-performance supercapacitors. Solid State Ion. 343, 115074 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2019.115074
P. Dwivedi, P. Chauhan, R.K. Rawat, Effect of thermal treatment on synthesized Cu doped ZnS nanoparticles. Mater. Today: Proc. 44, 3138–3143 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.02.818
B. Poornaprakash, U. Chalapathi, M. Kumar, S.P. Vattikuti, B. Rajitha, P. Poojitha, S.-H. Park, Tailoring the optical and magnetic properties of ZnS nanoparticles via 3d and 4f elements co-doping. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 121, 105395 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2020.105395
G. Murugadoss, Synthesis and photoluminescence properties of zinc sulfide nanoparticles doped with copper using effective surfactants. Particuology 11(5), 566–573 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.partic.2012.11.003
R. Singh, R.R. Singh, Optical properties of ZnS quantum dots: applications in solar cells and biomedicine. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 13(2), 1–9 (2023). https://doi.org/10.33263/BRIAC132.158
R. Balakarthikeyan, A. Santhanam, S. Vinoth, A.A. Abdeltawab, S.Z. Mohammady, M. Ubaidullah, S.F. Shaikh, M.S. Samdani, M.A. Manthrammel, M. Shkir, Enhancing the optoelectronic properties of low-cost nebulizer spray pyrolysis (NSP) prepared ZnS thin film through praseodymium doping for photodetector applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 289, 116213 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2022.116213
X. Du, H. Zhao, Z. Zhang, Y. Lu, C. Gao, Z. Li, Y. Teng, L. Zhao, K. Świerczek, Core-shell structured ZnS-C nanoparticles with enhanced electrochemical properties for high-performance lithium-ion battery anodes. Electrochim. Acta 225, 129–136 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2016.12.118
W. Zhang, Z. Huang, H. Zhou, S. Li, C. Wang, H. Li, Z. Yan, F. Wang, Y. Kuang, Facile synthesis of ZnS nanoparticles decorated on defective CNTs with excellent performances for lithium-ion batteries anode material. J. Alloys Compd. 816, 152633 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.152633
L. Wang, D. Li, Q. Li, Q. Pan, M. Zhang, L. Zhang, F. Zheng, Y. Huang, H. Wang, Q. Li, Ultrafine ZnS nanoparticles embedded in N-doped carbon as advanced anode materials for lithium ion batteries and sodium ion batteries. J. Alloys Compd. 910, 164783 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.164783
M. Bhushan, R. Jha, R. Bhardwaj, Reduced band gap and diffusion controlled spherical n-type ZnS nanoparticles for absorption of UV-Vis region of solar spectrum. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 135, 109021 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2019.05.018
N. Masmali, Z. Osman, A. Arof, Electrical properties of zinc sulfide and silver sulfide as binary salts in gel polymer electrolytes for quantum Dot-Sensitized solar cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 288, 116168 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2022.116168
R.A.S. Christinal, I. Prakash, A.A. Arunmozhi, S. Chakravarty, A.L. Rajesh, Variation of sulfur concentration on the effective deposition of solution processed ZnS thin films for buffer layer in thin film solar cells. Mater. Today Proc. 68, 356–362 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.05.569
S. Muthukumaran et al., Structural, FTIR and photoluminescence properties of ZnS: Cu thin films by chemical bath deposition method. Mater. Lett. 93, 223–225 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2012.11.091
S.K. Sundaram, S. Subramanian, V. Panneerselvam, S.T. Salammal, Temperature-dependent phase transition of CuZnS thin films and its effects on morphological, optical and electrical properties. Thin Solid Films 733, 138810 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2021.138810
G.K. VS, S.R. Maidur, P.S. Patil, M. Mahesha, Role of copper dopant in two-photon absorption and nonlinear optical properties of sprayed ZnS thin films for optical limiting applications. Phys. Lett. A 398, 127276 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physleta.2021.127276
B. Ayim-Otu, M. Kuncan, Ö. Şahin, S. Horoz, Synthesis and photovoltaic application of ZnS: Cu (3%) nanoparticles. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. 56, 639–643 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-019-00380-0
R. Chauhan, A. Kumar, R.P. Chaudhary, Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue with Cu doped ZnS nanoparticles. J. Lumin. 145, 6–12 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2013.07.005
B. Cullity, Elements of X-ray diffraction, Addison-Wesley publishing company Inc., Massachusetts, USA (1956)
K.C. Kumar, N.M. Rao, S. Kaleemulla, G.V. Rao, Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Sn doped ZnS nano powders prepared by solid state reaction. Phys. B: Condens. Matter 522, 75–80 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2017.07.071
P. Tyagi, A. Vedeshwar, Grain size dependent optical properties of CdI2 films. The European Physical Journal Applied Physics 19(1), 3–13 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1051/epjap:2002043
A. Jesu Jebathew, M. Karunakaran, R. Ade, J.S. Ponraj, V. Ganesh, R.K. Manavalan, Y. Bitla, I. Yahia, H. Algarni, Highly sensitive hexagonal-shaped ZnS-Cu thin films for photo-detector applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 33, 2192–2203 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07426-9
M. Sreedhar, I. Neelakanta Reddy, P. Bera, T. Shyju, C. Anandan, Studies of Cu-doped ZnS thin films prepared by sputtering technique. Surf. Interface Anal. 49(4), 284–290 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/sia.6130
A. Maurya, P. Chauhan, S.K. Mishra, R.K. Srivastava, Structural, optical and charge transport study of rutile TiO\(_{2}\) nanocrystals at two calcination temperatures. J. Alloys Compd. 509(33), 8433–8440 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.05.108
D. Saikia, J. Borah, M. Jangra, A. Puzari, Investigation of photophysical properties of ZnS: Mn\(^{2+}\) nanoparticles. Indian J. Phys. 90(5), 549–555 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-015-0780-y
N. Soltani, A. Dehzangi, A. Kharazmi, E. Saion, W.M.M. Yunus, B.Y. Majlis, M.R. Zare, E. Gharibshahi, N. Khalilzadeh, Structural, optical and electrical properties of ZnS nanoparticles affecting by organic coating. Chalcogenide Lett. 11(2), 79–90 (2014). https://www.researchgate.net/publication/260596677
R. Seoudi, A. Shabaka, W. Eisa, B. Anies, N. Farage, Effect of the prepared temperature on the size of CdS and ZnS nanoparticle. Phys. B: Condens. Matter 405(3), 919–924 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2009.10.015
N. Nripasree, N.K. Deepak, Structural, optical and electrical properties of Sn–N codoped p type ZnO thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis technique for diode applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 211, 121–127 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2016.06.012
H. Labiadh, B. Sellami, A. Khazri, W. Saidani, S. Khemais, Optical properties and toxicity of undoped and Mn-doped ZnS semiconductor nanoparticles synthesized through the aqueous route. Opt. Mater. 64, 179–186 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2016.12.011
A. Mukherjee, P. Mitra, Characterization of Sn doped ZnS thin films synthesized by CBD. Mater. Res. 20, 430–435 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-5373-MR-2016-0628
G. Cody, B. Brooks, B. Abeles, Optical absorption above the optical gap of amorphous silicon hydride. Solar Energy Materials 8(1–3), 231–240 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-1633(82)90065-X
M. Singh, M. Goyal, K. Devlal, Size and shape effects on the band gap of semiconductor compound nanomaterials. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 12(4), 470–475 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/16583655.2018.1473946
W. Peng, G. Cong, S. Qu, Z. Wang, Synthesis and photoluminescence of zns: Cu nanoparticles. Optical Materials 29(2–3), 313–317 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2005.10.003
S. Lee, D. Song, J. Lee, S. Kim, I.Y. Park, M.-S. Won, Enhancement of luminescence efficiency of ZnS: Cu nanocrystals by pH control. Materials Science and Engineering: B 103(3), 241–245 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5107(03)00240-X
N. Prasad, K. Balasubramanian, Optical, phonon and efficient visible and infrared photocatalytic activity of Cu doped ZnS micro crystals. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 173, 687–694 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2016.10.014
A. Datta, S.K. Panda, S. Chaudhuri, Phase transformation and optical properties of Cu-doped ZnS nanorods. J. Solid State Chem. 181(9), 2332–2337 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2008.05.037
K. Jayanthi, S. Chawla, H. Chander, D. Haranath, Structural, optical and photoluminescence properties of ZnS: Cu nanoparticle thin films as a function of dopant concentration and quantum confinement effect. Cryst. Res. Technol. J. Exp. Industr. Crystallogr. 42(10), 976–982 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1002/crat.200710950
D. Van Thai, P. Van Ben, V.Q. Trung, B.H. Van, N.M. Nghia, T.M. Thi, Luminescence enhancement of ZnS: Mn and ZnS: Cu-PVP nanoparticles by laser radiation annealing. Opt. Mater. 135, 113020 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2022.113020
C. Wang, B. Hu, L. Chen, N. Liu, J. Li, Preparation and characterization of ZnS nanostructures. Optik 224, 165673 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.165673
W. Que et al., Photoluminescence and electroluminescence from copper doped zinc sulphide nanocrystals/polymer composite. Appl. Phys. Lett. 73(19), 2727–2729 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.122571
K. Zhang, D. Jing, Q. Chen, L. Guo, Influence of Sr-doping on the photocatalytic activities of CdS-ZnS solid solution photocatalysts. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 35(5), 2048–2057 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2009.12.143
P. Peka, H.-J. Schulz, Empirical one-electron model of optical transitions in Cu-doped ZnS and CdS. Phys. B: Condens. Matter 193(1), 57–65 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1016/0921-4526(94)90052-3
L. Xiao, H. Chen, J. Huang, Visible light-driven photocatalytic H\(_{2}\)-generation activity of CuS/ZnS composite particles. Mater. Res. Bull. 64, 370–374 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2015.01.008
M.H. Suhail, O.G. Abdullah, R.A. Ahmed, S.B. Aziz, Photovoltaic properties of doped zinc sulfide/n-Si heterojunction thin films. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 13, 1472–1483 (2018). https://doi.org/10.20964/2018.02.50
S. Thirumavalavan, K. Mani, S. Sagadevan, Investigation of the structural, optical and electrical properties of copper selenide thin films. Mater. Res. 18, 1000–1007 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1590/1516-1439.039215
J.O. Emegha, E.D. Elete, F.O.-O. Efe, A.C. Adebisi, Optical and electrical properties of semiconducting ZnS thin film prepared by chemical bath deposition technique. Catalysis 4, 1–8 (2019). https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.27024.35841
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ravi Sankar Reddy M contributed to the investigation, data collection, conceptualization, methodology, and manuscript write-up, and S. Kaleemulla contributed to the validation, supervision, and visualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mummadi, R.S.R., Shaik, K. Structural, Optical, and Electrical Properties of Cu-Doped ZnS Nanoparticles Prepared by Solid-State Reaction. Braz J Phys 54, 78 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13538-024-01457-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13538-024-01457-3