Abstract
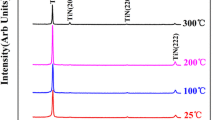
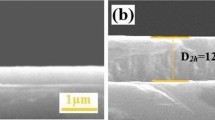
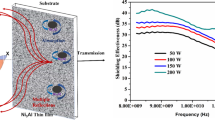
TiNx films with different nitrogen contents were fabricated using direct current reactive magnetron sputtering. Influence of N2 flow rate on the resistivity and electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding effectiveness (SE) of TiNx films was studied. The EMI SE of TiNx films was found to be related with the resistivity. With the rise of N2 flow rate, the resistivity of TiNx films increased, while the EMI SE decreased. When the N2 flow rate was 1 sccm, the EMI SE of TiNx films was over 20 dB with the thickness of 1.47 µm, which was much smaller than the thickness of the presently known EMI-shielding materials. The results indicated that TiNx films could be applied as ultrathin thickness, lightweight, and design flexibility shielding materials.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.T. Hsiao, C.C.M. Ma, H.W. Tien, W.H. Liao, Y.S. Wang, S.M. Li, Y.C. Huang, Using a non-covalent modification to prepare a high electromagnetic interference shielding performance graphene nanosheet/water-borne polyurethane composite. Carbon 60, 57–66 (2013)
P.J. Bora, K.J. Vinoy, P.C. Ramamurthy, G. Kishore, Madras, Electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness of polyaniline-nickel oxide coated cenosphere composite film. Compos. Commun. 4, 37–42 (2017)
K. Sabira, M.P. Jayakrishnan, P. Saheeda, S. Jayalekshmi, On the absorption dominated EMI shielding effects in free standing and flexible films of poly (vinylidene fluoride)/graphene nanocomposite. Eur. Polym. J. 99, 437–444 (2018)
H.J. Oh, V.D. Dao, H.S. Choi, Electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of a thin silver layer deposited onto PET film via atmospheric pressure plasma reduction. Appl. Surf. Sci. 435, 7–15 (2018)
Y. Zhang, Y. Huang, T. Zhang, H. Chang, P. Xiao, H. Chen, Z. Huang, Y. Chen, Broadband and tunable high-performance microwave absorption of an ultralight and highly compressible graphene foam. Adv. Mater. 27, 2049–2053 (2015)
Z. Zeng, H. Jin, M. Chen, W. Li, L. Zhou, Z. Zhang, Lightweight and anisotropic porous MWCNT/WPU composites for ultrahigh performance electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv. Funct. Mater. 26, 303–310 (2016)
Y. Qing, Y. Mu, Y. Zhou, F. Luo, D. Zhu, W. Zhou, Multiwalled carbon nanotubes–BaTiO3/silica composites with high complex permittivity and improved electromagnetic interference shielding at elevated temperature. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 34, 2229–2237 (2014)
S. Frackowiak, J. Ludwiczak, K. Leluk, K. Orzechowski, M. Kozlowski, Foamed poly (lactic acid) composites with carbonaceous fillers for electromagnetic shielding. Mater. Des. 65, 749–756 (2015)
H.B. Zhang, W.G. Zheng, Q. Yan, Z.G. Jiang, Z.Z. Yu, The effect of surface chemistry of graphene on rheological and electrical properties of polymethylmethacrylate composites. Carbon 50, 5117–5125 (2012)
R. Mohan, S. Varma, M. Faisal, S. Jayalekshmi, Polyaniline/graphene hybrid film as an effective broadband electromagnetic shield. RSC Adv. 5, 5917–5923 (2014)
S. Kwon, R. Ma, U. Kim, H.R. Choi, S. Baik, Flexible electromagnetic interference shields made of silver flakes, carbon nanotubes and nitrile butadiene rubber. Carbon 68, 118–124 (2014)
R.R. Mohan, S.J. Varma, J. Sankaran, Impressive electromagnetic shielding effects exhibited by highly ordered, micrometer thick polyaniline films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 108, 7–20466 (2016)
D.D.L. Chung, Electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness of carbon materials. Carbon 39, 279–285 (2001)
C. Xia, H. Ren, S.Q. Shi, H. Zhang, J. Cheng, L. Cai, K. Chen, H.S. Tan, Natural fiber composites with EMI shielding function fabricated using VARTM and Cu film magnetron sputtering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 362, 335–340 (2016)
K. Jagatheesan, A. Ramasamy, A. Das, A. Basu, Electromagnetic shielding behaviour of conductive filler composites and conductive fabrics—a review. Indian J. Fibre Text. 39, 329–342 (2014)
G.S. Kumar, D. Vishnupriya, A. Joshi, S. Datar, T.U. Patro, Electromagnetic interference shielding in 1–18 GHz frequency and electrical property correlations in poly (vinylidene fluoride)-multi-walled carbon nanotube composites. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17, 20347–20360 (2015)
S. Hsiao, C. Ma, W. Liao, Y. Wang, S. Li, Y. Huang, R. Yang, W. Liang, Lightweight and flexible reduced graphene oxide/water-borne polyurethane composites with high electrical conductivity and excellent electromagnetic interference shielding performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 6, 10667–10678 (2014)
J.M. Thomassin, C. Jérôme, T. Pardoen, C. Bailly, I. Huynen, C. Detrembleur, Polymer/carbon based composites as electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 74, 211–232 (2013)
L.L. Wang, B.K. Tay, K.Y. See, Z. Sun, L.K. Tan, D. Lua, Electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness of carbon-based materials prepared by screen printing. Carbon 47, 1905–1910 (2009)
N. Li, Y. Huang, F. Du, X. He, X. Lin, H. Gao, Y. Ma, F. Li, Y. Chen, P.C. Eklund, Electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding of single-walled carbon nanotube epoxy composites. Nano Lett. 6, 1141–1145 (2006)
V. Eswaraiah, V. Sankaranarayanan, S. Ramaprabhu, Inorganic nanotubes reinforced polyvinylidene fluoride composites as low-cost electromagnetic interference shielding materials. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 6, 137 (2011)
V. Eswaraiah, V. Sankaranarayanan, S. Ramaprabhu, Functionalized graphene—PVDF foam composites for EMI shielding, Macromol. Mater. Eng. 296, 894–898 (2011)
N. Joseph, M.T. Sebastian, Electromagnetic interference shielding nature of PVDF-carbonyl iron composites. Mater. Lett. 90, 64–67 (2013)
Q. Wen, W. Zhou, J. Su, Y. Qing, F. Luo, D. Zhu, High performance electromagnetic interference shielding of lamellar MoSi2/glass composite coatings by plasma spraying. J. Alloys Compd. 666, 359–365 (2016)
A.P. Singh, M. Mishra, D.P. Hashim, T.N. Narayanan, M.G. Hahm, P. Kumar, J. Dwivedi, G. Kedawat, A. Gupta, B.P. Singh, Probing the engineered sandwich network of vertically aligned carbon nanotube—reduced graphene oxide composites for high performance electromagnetic interference shielding applications. Carbon 85, 79–88 (2015)
Z. Chen, C. Xu, C. Ma, W. Ren, H.M. Cheng, Lightweight and flexible graphene foam composites for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv. Mater. 25, 1296–1300 (2013)
E. Penilla, J. Wang, Pressure and temperature effects on stoichiometry and microstructure of nitrogen-rich TiN thin films synthesized via reactive magnetron DC-sputtering. J. Nanomater. 2008(5), 145–152 (2014)
W.J. Chou, G.P. Yu, J.H. Huang, Mechanical properties of TiN thin film coatings on 304 stainless steel substrates. Surf. Coat. Technol. 149, 7–13 (2002)
G.L. Zhao, T.B. Zhang, T. Zhang, J.X. Wang, G.R. Han, Electrical and optical properties of titanium nitride coatings prepared by atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 354, 1272–1275 (2008)
F. Vaz, J. Ferreira, E. Ribeiro, L. Rebouta, S. Lanceros-Mendez, J.A. Mendes, E. Alves, P. Goudeau, J.P. Riviere, F. Ribeiro, I. Moutinho, K. Pischow, J. de Rijk, Influence of nitrogen content on the structural, mechanical and electrical properties of TiN thin films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 191, 317–323 (2005)
D.Q. Yu, H.P. Xie, L. Wang, Investigation of interfacial microstructure and wetting property of newly developed Sn–Zn–Cu solders with Cu substrate. J. Alloys Compd. 385, 119–125 (2004)
F.Y. Hung, T.S. Lui, H.C. Liao, A study of nano-sized surface coating on LiMn2O4 materials. Appl. Surf. Sci. 253, 7443–7448 (2007)
N. Arshi, J.Q. Lu, Y.K. Joo, C.G. Lee, J.H. Yoon, F. Ahmed, Influence of nitrogen gas flow rate on the structural, morphological and electrical properties of sputtered TiN films. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 24, 1194–1202 (2013)
H.L. Liang, J. Xu, D.Y. Zhou, X. Sun, S.C. Chu, Y.Z. Bai, Thickness dependent microstructural and electrical properties of TiN thin films prepared by DC reactive magnetron sputtering. Ceram. Int. 42, 2642–2647 (2016)
U.C. Oh, J.H. Je, Effects of strain-energy on the preferred orientation of TiN thin-films. J. Appl. Phys. 74, 1692–1696 (1993)
J.L. Murray, Phase Diagrams of Binary Titanium Alloys (ASM International, Ohio, 1987)
B.E. Warren, X-ray Diffraction. (Addison Wesley Publishing Co., London, 1969)
X. Li, L. Zhang, X. Yin, L. Feng, Q. Li, Effect of chemical vapor infiltration of SiC on the mechanical and electromagnetic properties of SiN–SiC ceramic. Scripta Mater. 63, 657–660 (2010)
F. Shahzad, M. Alhabeb, C.B. Hatter, B. Anasori, H.S. Man, C.M. Koo, Y. Gogotsi, Electromagnetic interference shielding with 2D transition metal carbides (MXenes). Science 353, 1137–1140 (2016)
X. Zhang, X. Zhang, M. Yang, S. Yang, H. Wu, S. Guo, Y. Wang, Ordered multilayer film of (graphene oxide/polymer and boron nitride/polymer) nanocomposites: an ideal EMI shielding material with excellent electrical insulation and high thermal conductivity. Compos. Sci. Technol. 136, 104–110 (2016)
Y.Y. And, M.C. Gupta, K.L.D. And, R.W. Lawrence, Novel carbon nanotube—polystyrene foam composites for electromagnetic interference shielding. Nano Lett. 5(11), 2131–2134 (2005)
S. Maiti, N.K. Shrivastava, S. Suin, B.B. Khatua, Polystyrene/MWCNT/graphite nanoplate nanocomposites: efficient electromagnetic interference shielding material through graphite nanoplate-MWCNT-graphite nanoplate networking. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 5, 4712–4724 (2013)
J. Liang, Y. Wang, Y. Huang, Y. Ma, Z. Liu, J. Cai, C. Zhang, H. Gao, Y. Chen, Electromagnetic interference shielding of graphene/epoxy composites. Carbon 47, 922–925 (2009)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. 3102017ZY050), and State Key Laboratory of Solidification Processing (NWPU), China (Grant No. KP201604).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, L., Luo, F., Qing, Y. et al. Effect of N2 flow rate on electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness of TiNx films. Appl. Phys. A 124, 721 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-2140-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-2140-1