Abstract
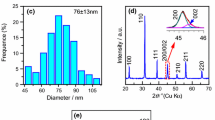
This paper describes synthesis of the functional BaTiO3 (BT) nanostructures by composite-hydroxide-mediated (CHM) approach. The effect of processing temperature on the nucleation and the optical, structural properties is investigated. The nanostructures prepared at various temperatures (180, 220 and 250 °C) are thermally stable and nucleate in different morphologies, which shows a temperature-dependent mechanism of the CHM approach. The nanostructures are cubic in nature with an average particle size in the range of 97–250 nm. The local crystal structure investigated by Raman spectroscopy reveals a certain degree of tetragonality on atomic scale in the local phase structure. The micrographs of scanning electron microscopy (SEM) indicate formation of the nanocuboids at 180 and 220 °C with larger particle size. At 250 °C, the product shows ball-like spherical morphology. Energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) confirms the existence of Ba, Ti and O elements in the product, which indicates a chemically pure product. Further signature on the formation, purity and chemical bonding is obtained from FT-IR spectroscopy. Based on these experimental results, size, morphology manipulation and possible growth mechanisms are proposed with CHM at low temperature and without surfactant.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.E. Lines, A.M. Glass, Principles and Applications of Ferroelectrics and Related Materials (Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1977)
S.-T. Huang, W.W. Lee, J.-L. Chang, W.-S. Huang, S.-Y. Chou, C.-C. Chen, J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 45(4), 1927–1936 (2014)
J. Miao, C. Hu, H. Liu, Y. Xiong, Mater. Lett. 62, 235–238 (2008)
W.W. Lee, C.-S. Lu, C.-W. Chuang, Y.-J. Chen, J.-Y. Fu, C.-W. Siao, C.-C. Chen, RSC Adv. 5, 23450–23463 (2015)
Y.-R. Jiang, S.-Y. Chou, J.-L. Chang, S.-T. Huang, H.-P. Lin, C.-C. Chen, RSC Adv. 5, 30851–30860 (2015)
X.H. Zhu, J.M. Zhu, S.H. Zhou, Z.G. Liu, N.B. Ming, D. Hesse, Solid State Phenom. 106, 41–46 (2005)
U. Manzoor, D.K. Kim, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 23, 655–658 (2007)
W.W. Lee, W.-H. Chung, W.-S. Huang, W.-C. Lin, W.-Y. Lin, Y.-R. Jiang, C.-C. Chen, J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 44(4), 660–669 (2013)
J.-H. Park, D.H. Yoo, B.K. Moon, G.-J. Jung, J. Korean Phys. Soc. 49, S680–S683 (2006)
T.M. Khan, T. Shahid, M. Zakria, R.I. Shakoor, J Electron Mater Lett 11, 366–373 (2015)
T.M. Khan, M. Zakria, R.I. Shakoor, M. Ahmad, M. Raffi, Advanced Materials Lett 6, 592–599 (2015)
C. Hu, Y. Xi, H. Liu, Z.L. Wang, J. Mater. Chem. 19, 858–868 (2009)
J. Miao, C. Hu, H. Liu, Y. Xiong, Mater. Lett. 62, 235–238 (2008)
R.L. Brutchey, D.E. Morse, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 45, 6564–6566 (2006)
M.R.A. Bhuiyan, M.M. Alam, M.A. Momin, M.J. Uddin, M. Islam, Int. J. Mater. Mech. Eng. 1, 21–24 (2012)
Y. Mao, S. Mao, Z.-G. Ye, Z. Xie, L. Zheng, Mater. Chem. Phys. 124, 1232–1238 (2010)
M.B. Smith, K. Page, T. Siegrist, P.L. Redmond, E.C. Walter, R. Seshadri, L.E. Brus, M.L. Steigerwald, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 6955–6963 (2008)
M. El Marssi, F. Le Marrec, I.A. Lukyanchuk, M.G. Karkut, J. Appl. Phys. 94, 3307–3312 (2003)
G. Busca, G. Ramis, J.M. Gallardo Amores, V. Sanchez Escribano, P. Piaggio, J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 90, 3181–3190 (1994)
M.L. Moreira, G.P. Mambrini, D.P. Volanti, E.R. Leite, M.O. Orlandi, P.S. Pizani, V.R. Mastelaro, E. Longo, J.A. Varela, Chem. Mater. 20, 5381–5387 (2008)
E.A. Stefanescu, X. Tan, Z. Lin, N. Bowler, M.R. Kessler, Polymer 52, 2016–2024 (2011)
X. Wei, G. Xu, Z. Ren, G. Shen, G. Han, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 91, 3774–3780 (2008)
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge Health Physics Division (PINSTECH) for providing the required infrastructure and facilities for this research work. We are also thankful to Dr. M. Nasir khan (PINSTECH) for performing XRD analysis. The chemicals and furnace were also provided by the PINSTECH Health Physics Division.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, T.M., Zakria, M., Shakoor, R.I. et al. Composite-hydroxide-mediated approach an effective synthesis route for BaTiO3 functional nanomaterials. Appl. Phys. A 122, 274 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-9766-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-9766-7