Abstract
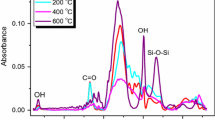
In addition to inducing second-order nonlinear properties, significant structural and compositional alteration can be imparted to glass surfaces during the process of thermal poling. In this work, we focus on how thermal poling affects a structurally complex, nominally alkali-free boroaluminosilicate display glass composition. We provide evidence for electrolysis of the glass network, characterized by the migration of both cations (Ba2+, Na+) and anions (O−, F−) towards opposing electrode interfaces. This process results in oxidation of the positively biased electrode and forms a network-former rich, modifier-depleted glass surface layer adjacent to the anodic interface. The modified glass layer thickness is qualitatively correlated to the oxidation resistance of the electrode material, while extrinsic ions such as H+/H3O+ at not found in the depletion layer to compensate for the migration of modifier cations out of the region. Rather, FTIR spectroscopy suggests a local restructuring of the B2O3–Al2O3–SiO2 network species to accommodate the charge imbalance created by the exodus of network-modifying cations, specifically the conversion of tetrahedral B(4) to trigonal B(3) as Ba or Na ions are removed from B-related sites in the parent network. The resultant poling-induced depletion layer exhibits enhanced hydrolytic resistance under acidic conditions, and the IR spectra are substantially unlike those produced by acid leaching the same glass.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Dussauze et al., Thermal poling of optical glasses: mechanisms and second-order optical properties. Int. J. Appl. Glass Sci. 3(4), 309–320 (2012)
S. Fleming, H. An, Progress in creating second-order optical nonlinearity in silicate glasses and waveguides through thermal poling. Front Optoelectron. China 3(1), 84–91 (2010)
M. Dussauze et al., Polarization mechanisms and structural rearrangements in thermally poled sodium-alumino phosphate glasses. J. Appl. Phys. 107(4), 043505 (2010). 1-043505/6
M. Dussauze et al., How does thermal poling affect the structure of soda-lime glass? J. Phys. Chem. C 114(29), 12754–12759 (2010)
D. Moncke et al., Thermal poling induced structural changes in sodium borosilicate glasses. Phys. Chem. Glasses Eur. J. Glass Sci. Technol. Part B 50(3), 229–235 (2009)
M. Dussauze et al., Structural rearrangements and second-order optical response in the space charge layer of thermally poled sodium niobium borophosphate glasses. J. Phys. Chem. C 111(39), 14560–14566 (2007)
D.E. Carlson, K.W. Hang, G.F. Stockdale, Ion depletion of glass at a blocking anode: II, properties of ion-depleted glasses. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 57(7), 295–300 (1974)
D.E. Carlson, Ion depletion of glass at a blocking anode: I, theory and experimental results for alkali silicate glasses. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 57(7), 291–294 (1974)
E.C. Ziemath, V.D. Araujo, J.C.A. Escanhoela, Compositional and structural changes at the anodic surface of thermally poled soda-lime float glass. J. Appl. Phys. 104(5), 054912–054917 (2008)
K.P. Gadkaree et al., Single-crystal silicon films on glass. J. Mater. Res. 22(9), 2363–2367 (2007)
K.B. Albaugh, Irreversibility of anodic bonding. Mater. Lett. 4(11–12), 465–469 (1986)
D.E. Carlson, K.W. Hang, G.F. Stockdale, Electrode “polarization” in alkali-containing glasses. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 55(7), 337–341 (1972)
T. Cremoux et al., Trapped molecular and ionic species in poled borosilicate glasses: toward a rationalized description of thermal poling in glasses. J. Phys. Chem. C. 118(7), 3716–3723 (2014)
Baucke, F.G.K. and J.A. Duffy, Electrolysis of a sodium borate glass: a new mechanism of oxide ion transport. Glastechnische Berichte 56(Int. Glaskongr., 13th, Band 1): 608–613 (1983)
F.G.K. Baucke, J.A. Duffy, Ion migration study in a sodium borate glass: proposal of a new oxide transport. J. Electrochem. Soc. 127(10), 2230–2233 (1980)
B. Schmidt et al., In situ investigation of ion drift processes in glass during anodic bonding. Sens. Actuators A 67(1–3), 191–198 (1998)
A.T.J. van Helvoort et al., Anodic oxidation during electrostatic bonding. Philos. Mag. 84(6), 505–519 (2004)
A.T.J. van Helvoort, K.M. Knowles, J.A. Fernie, Characterization of cation depletion in pyrex during electrostatic bonding. J. Electrochem. Soc. 150(10), G624–G629 (2003)
K.B. Albaugh, D.H. Rasmussen, Rate processes during anodic bonding. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 75(10), 2644–2648 (1992)
N.J. Smith, M.T. Lanagan, C.G. Pantano, Thermal poling of alkaline earth boroaluminosilicate glasses with intrinsically high dielectric breakdown strength. J. Appl. Phys. 111(8), 083519-9 (2012)
A. Ellison, I.A. Cornejo, Glass substrates for liquid crystal displays. Int. J. Appl. Glass Sci. 1(1), 87–103 (2010)
N.J. Smith et al., Alkali-free glass as a high energy density dielectric material. Mater. Lett. 63(15), 1245–1248 (2009)
H. Lee et al., Dielectric breakdown of thinned BaO–Al2O3–B2O3–SiO2 glass. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 93(8), 2346–2351 (2010)
P. Dash et al., Activation energy for alkaline-earth ion transport in low alkali aluminoborosilicate glasses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 102(8), 082904–082905 (2013)
T. Murata et al., Electrode-limited dielectric breakdown of alkali free glass. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 95(6), 1915–1919 (2012)
E. Furman, High temperature performance of coiled glass capacitors. Presented at HiTEC 2012, International Microelectronics Assembly and Packaging Society (2012)
A.E. Owen, Properties of glasses in the system CaO-B2O3-Al2O3. Part. 1. The d. c conductivity and structure of calcium boroaluminate glasses. Phys. Chem. Glasses 2(3), 87–98 (1961)
S. G. Bishop, P. J. Bray, NMR studies of Ca boroaluminate glasses. Phys. Chem. Glasses 7(3) (1966)
M. T. Strzelecki, The corrosion behavior of barium aluminoborosilicate glass and its relation to glass structure. thesis in MatSE p. 132 (1999)
J.G. Wood et al., The effects of antimony oxide on the structure of alkaline-earth alumino borosilicate glasses. J. Non Cryst. Solids 349, 276–284 (2004)
Q. Zheng et al., Composition–structure–property relationships in boroaluminosilicate glasses. J. Non Cryst. Solids 358(6–7), 993–1002 (2012)
I.D. Tykachinskii et al., The coordination of boron and aluminum in some barium aluminosilicate glasses. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 13(6), 1660–1661 (1970)
L.-S. Du, J.F. Stebbins, Network connectivity in aluminoborosilicate glasses: a high-resolution 11B, 27Al and 17O NMR study. J. Non Cryst. Solids 351(43–45), 3508–3520 (2005)
W.J. Dell, P.J. Bray, S.Z. Xiao, 11B NMR studies and structural modeling of Na2O—B2O3—SiO2 glasses of high soda content. J. Non Cryst. Solids 58(1), 1–16 (1983)
H. Yamashita et al., Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of 0.139MO (or M’2O) and #xB7; 0.673SiO2 and #xB7; (0.188-x)Al2O3 and #xB7; xB2O3 (M = Mg, Ca, Sr and Ba, M’ = Na and K) glasses. J. Non Cryst. Solids 331(1–3), 128–136 (2003)
Y.D. Yiannopoulos, E.I. G. D. K. Chryssikos, Structure and properties of alkaline earth borate glasses. Phys. Chem. Glasses 42, 164–172 (2001)
S. Sen et al., Atomic-scale understanding of structural relaxation in simple and complex borosilicate glasses. Phys. Rev. B 75(9), 094203 (2007)
N. Smith, C. Pantano, T. Regier, Manuscript in preparation
N.J. Smith, Novel approaches to the surface modification of glass by thermal poling. Ph.D. thesis in Mater. Sci. Engr. p. 190 (2011)
G.C. Smith, Evaluation of a simple correction for the hydrocarbon contamination layer in quantitative surface analysis by XPS. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 148(1), 21–28 (2005)
C.W. Magee, E.M. Botnick, Hydrogen depth profiling using SIMS—problems and their solutions. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 19(1), 47–52 (1981)
M.M. Smedskjaer et al., Modifying glass surfaces via internal diffusion. J. Non Cryst. Solids 356(6–8), 290–298 (2010)
G.W. Graham et al., Raman investigation of simple and complex oxides of platinum. J. Raman Spectrosc. 22(1), 1–9 (1991)
S. Illievski et al., Practical IR extinction coefficients for water in commercial glasses determined by nuclear reaction analysis. Glass Sci. Technol. 73(2), 39–45 (2000)
P. McMillan, B. Piriou, The structures and vibrational spectra of crystals and glasses in the silica-alumina system. J. Non Cryst. Solids 53(3), 279–298 (1982)
B.O. Mysen, P. Richet, Silicate glasses and melts: properties and structure, 1st edn., Developments in geochemistry (Elsevier, Boston, 2005), p. 544
F. Geotti-Bianchini et al., New interpretation of the IR reflectance spectra of silica-rich films on soda-lime glass. Glastechnische Berichte 64(8), 205–217 (1991)
S.A. MacDonald et al., Dispersion analysis of FTIR reflection measurements in silicate glasses. J. Non Cryst. Solids 275(1–2), 72–82 (2000)
E.I. Kamitsos, G.D. Chryssikos, M.A. Karakassides, New insights into the structure of alkali borate glasses. J. Non Cryst. Solids 123(1–3), 283–285 (1990)
K. El-Egili, Infrared studies of Na2O-B2O3-SiO2 and Al2O3-Na2O-B2O3-SiO2 glasses. Phys. B 325, 340–348 (2003)
I. Polyakova et al., Application of the constant stoichiometry grouping concept to the Raman spectra of BaOAl2O3B2O3 glasses. Phys. Chem. Glasses Eur. J. Glass Sci. Technol. Part B 51, 52–58 (2010)
U.K. Krieger, W.A. Lanford, Field assisted transport of Na+ ions, Ca2+ ions and electrons in commercial soda-lime glass I: experimental. J. Non Cryst. Solids 102(1–3), 50–61 (1988)
R.A Schaut, The effect of boron oxide on the composition, structure, and adsorptivity of glass surfaces. Ph.D. thesis in MatSE (2008)
M.E. Fleet, S. Muthupari, Boron K-edge XANES of borate and borosilicate minerals. Am. Mineral. 85(7–8), 1009–1021 (2000)
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge The Office of Naval Research under Grant N00014-05-1-0541 and the Penn State Materials Research Institute for partial funding of this work. The authors also thank Vince Bojan and Josh Stapleton (Penn State University) for their help and guidance regarding materials analysis throughout this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, N.J., Pantano, C.G. Structural and compositional modification of a barium boroaluminosilicate glass surface by thermal poling. Appl. Phys. A 116, 529–543 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-014-8467-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-014-8467-3